
Combine datasets using Pandas merge(), join(), concat() and append()
Last Updated on October 29, 2020 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Vivek Chaudhary

In the world of Data Bases, Joins and Unions are the most critical and frequently performed operations. Almost every other query is an amalgamation of either a join or a union. Using Pandas we perform similar kinds of stuff while working on a Data Science algorithm or any ETL (Extract Transform and Load) project, joins and unions are critical here as well.
Just a little difference between join and unions before jumping onto the use cases of both. Both join and union are used to combine data sets, however, the result set of a join is a horizontal combination of the dataset where a result set of a union is a vertical combination of data set.
In Pandas for a horizontal combination we have merge() and join(), whereas for vertical combination we can use concat() and append(). Merge and join perform similar tasks but internally they have some differences, similar to concat and append. And in this blog, I had tried to list out the differences in the nature of these methods.
- merge() is used for combining data on common columns or indices.
create two data frames and build an understanding of how merge works.
import pandas as pd
d1 = {‘Id’: [‘A1’, ‘A2’, ‘A3’, ‘A4’,’A5'],
‘Name’:[‘Vivek’, ‘Rahul’, ‘Gaurav’, ‘Ankit’,’Vishakha’],
‘Age’:[27, 24, 22, 32, 28],}
d2 = {‘Id’: [‘A1’, ‘A2’, ‘A3’, ‘A4’],
‘Address’:[‘Delhi’, ‘Gurgaon’, ‘Noida’, ‘Pune’],
‘Qualification’:[‘Btech’, ‘B.A’, ‘Bcom’, ‘B.hons’]}
df1=pd.DataFrame(d1) df2=pd.DataFrame(d2)
Case 1. merging data on common columns ‘Id’
#Inner Join pd.merge(df1,df2) #simple merge with no additional arguments performs an inner/equi join equivalent to data base join operation
pd.merge(df1,df2, how='inner) #produces output similar as above, as pandas merge by default is an equi join
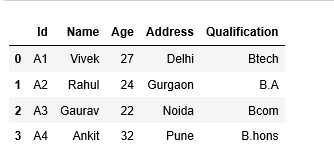
#Left Join pd.merge(df1,df2,how=’left’)
#matching and non matching records from left DF which is df1 is present in result data frame
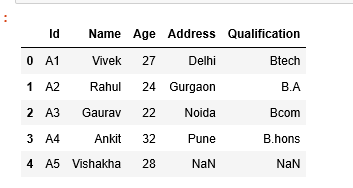
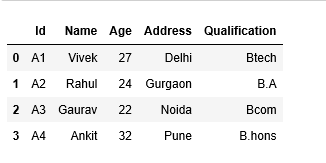
#Right Join pd.merge(df1,df2,how=’right’)
#matching and non matching records from right DF, df2 will come in result df #as of now we dont have any non matching record in right df
#outer join pd.merge(df1,df2,how=’outer’)
#all the matching and non matching records are available in resultant dataset from both data frames
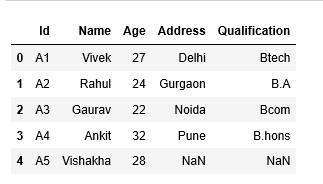
Case 2: merge data frames with no common columns
#changed the merging key in data frame d2
import pandas as pd
d1 = {‘Id’: [‘A1’, ‘A2’, ‘A3’, ‘A4’,’A5'],
‘Name’:[‘Vivek’, ‘Rahul’, ‘Gaurav’, ‘Ankit’,’Vishakha’],
‘Age’:[27, 24, 22, 32, 28],}
d2 = {‘ID’: [‘A1’, ‘A2’, ‘A3’, ‘A4’],
‘Address’:[‘Delhi’, ‘Gurgaon’, ‘Noida’, ‘Pune’],
‘Qualification’:[‘Btech’, ‘B.A’, ‘Bcom’, ‘B.hons’]}
df1=pd.DataFrame(d1) df2=pd.DataFrame(d2)
#lets check when merging keys are different ('Id' and 'ID')
pd.merge(df1,df2)
merging result in below error:
MergeError: No common columns to perform merge on.
to overcome the merge error, we can use pandas argument ‘left_on’ and ‘right_on’ to explicitly indicate pandas on what key columns we want to merge data frames, rest everything remains similar.
#df1 key column 'Id' #df2 key column 'ID'
pd.merge(df1,df2,left_on=’Id’,right_on=’Id’,how=’left’)
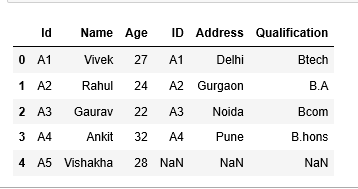
2. join() is used for combining data on a key column or an index.
create two data frames and build an understanding of how join works.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({‘key’: [‘K0’, ‘K1’, ‘K5’, ‘K3’, ‘K4’, ‘K2’],
‘A’: [‘A0’, ‘A1’, ‘A5’, ‘A3’, ‘A4’, ‘A2’]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({‘key’: [‘K0’, ‘K1’, ‘K2’],
‘B’: [‘B0’, ‘B1’, ‘B2’]})
Case 1. join on indexes
By default, pandas join operation is performed on indexes both data frames have default indexes values, so no need to specify any join key, join will implicitly be performed on indexes.
#default nature of pandas join is left outer join df1.join(df2, lsuffix=’_l’, rsuffix=’_r’)
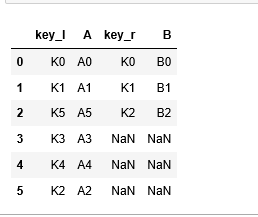
If there are overlapping columns in pandas join, it throws an error :
ValueError: columns overlap but no suffix specified: Index([‘key’], dtype=’object’)
With the help of the below use case try to understand the default nature of pandas join which is left outer join.
Create two data frames with different index values
df1 = pd.DataFrame({‘key’: [‘K0’, ‘K1’, ‘K5’, ‘K3’, ‘K4’, ‘K2’],
‘A’: [‘A0’, ‘A1’, ‘A5’, ‘A3’, ‘A4’, ‘A2’]},
index=[0,1,2,3,4,5])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({‘key’: [‘K0’, ‘K1’, ‘K2’],
‘B’: [‘B0’, ‘B1’, ‘B2’]},
index=[6,7,8])
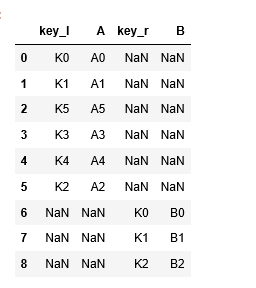
df1.join(df2,lsuffix=’_l’,rsuffix=’_r’)
#df1 is left DF and df2 is right DF
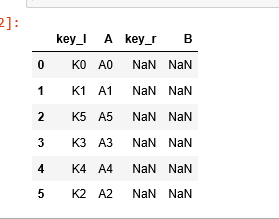
Index values in both data frames are different, in the case of inner/equi join resultant data set will be empty but data is present from left DF (df1).
#inner join df1.join(df2,lsuffix=’_l’,rsuffix=’_r’,how=’inner’)
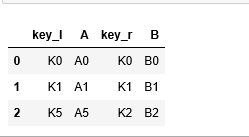
#outer join df1.join(df2,lsuffix=’_l’,rsuffix=’_r’,how=’outer’)
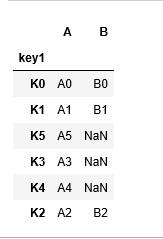
Case 2. join on columns
Data frames can be joined on columns as well, but as joins work on indexes, we need to convert the join key into the index and then perform join, rest every thin is similar.
#join on data frame column df1.set_index(‘key1’).join(df2.set_index(‘key2’))
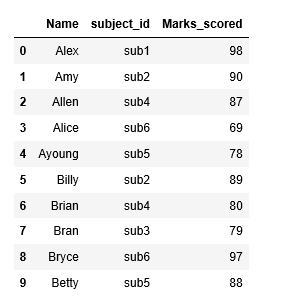
3. concat() is used for combining Data Frames across rows or columns.
create two data frames to understand how concat works. concat is a vertical operation.
Case 1. concat data frames on axis=0, default operation
import pandas as pd
m1 = pd.DataFrame({
‘Name’: [‘Alex’, ‘Amy’, ‘Allen’, ‘Alice’, ‘Ayoung’],
‘subject_id’:[‘sub1’,’sub2',’sub4',’sub6',’sub5'],
‘Marks_scored’:[98,90,87,69,78]},
index=[1,2,3,4,5])
m2 = pd.DataFrame({
‘Name’: [‘Billy’, ‘Brian’, ‘Bran’, ‘Bryce’, ‘Betty’],
‘subject_id’:[‘sub2’,’sub4',’sub3',’sub6',’sub5'],
‘Marks_scored’:[89,80,79,97,88]},
index=[4,5,6,7,8])
pd.concat([m1,m2])
Indexes of both the Data Frames are preserved in concat operation.
#ignore indexes from original data frames pd.concat([m1,m2],ignore_index=True)
sequential numbers are given to index values unlike previous output
Case 2. concat operation on axis=1, horizontal operation
#axis=1 works as join operation pd.concat([m1,m2],axis=1)
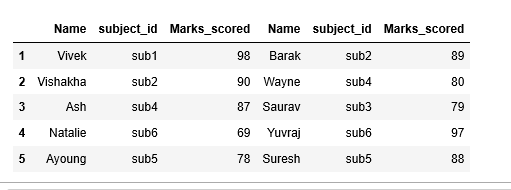
Case 3. concat unequal shape data frames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({‘A’:[1,2,3], ‘B’:[1,2,3]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({‘A’:[4,5]})
If we try to perform concat operation on df1 and df2 with unequal columns or data frames of different shapes. while performing concatenation operation on unequal shape data frames, pandas updates value as NaN for missing values.
Pandas NaN are float type in nature so values of series B changed to float.
df = pd.concat([df1,df2],ignore_index=True)
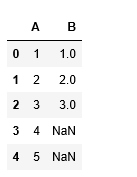
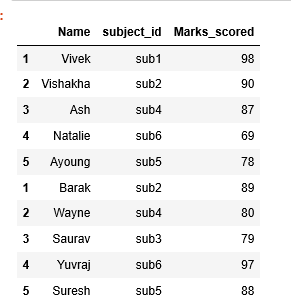
4. append() combine data frames vertically fashion
create two data frames to understand how append works.
Case 1. appending data frames, duplicate index issue
m1 = pd.DataFrame({
‘Name’: [‘Alex’, ‘Amy’, ‘Allen’, ‘Alice’, ‘Ayoung’],
‘subject_id’:[‘sub1’,’sub2',’sub4',’sub6',’sub5'],
‘Marks_scored’:[98,90,87,69,78]},
index=[1,2,3,4,5])
m2 = pd.DataFrame({
‘Name’: [‘Billy’, ‘Brian’, ‘Bran’, ‘Bryce’, ‘Betty’],
‘subject_id’:[‘sub2’,’sub4',’sub3',’sub6',’sub5'],
‘Marks_scored’:[89,80,79,97,88]},
index=[1,2,3,4,5])
with overlapping indexes append function throws error:
ValueError: Indexes have overlapping values:
m1.append(m2,verify_integrity=False) #verify_integrity=False is default argument m1.append(m2)
#output will be similar for both above lines of code
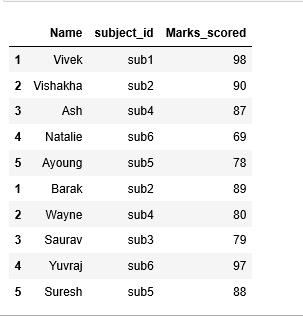
Case 2. append data frames with unequal shapes
create two new data frames with different shapes
m1 = pd.DataFrame({
‘Name’: [‘Vivek’, ‘Vishakha’, ‘Ash’, ‘Natalie’, ‘Ayoung’],
‘subject_id’:[‘sub1’,’sub2',’sub4',’sub6',’sub5'],
‘Marks_scored’:[98,90,87,69,78],
‘Rank’:[1,3,6,20,13]},
index=[1,2,3,4,5])
m2 = pd.DataFrame({
‘Name’: [‘Barak’, ‘Wayne’, ‘Saurav’, ‘Yuvraj’, ‘Suresh’],
‘subject_id’:[‘sub2’,’sub4',’sub3',’sub6',’sub5'],
‘Marks_scored’:[89,80,79,97,88],},
index=[1,2,3,4,5])
m1.append(m2)
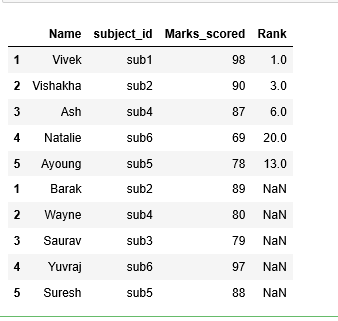
Summary:
· Pandas Data set combination operations to use cases
· Nature of every combination operation
· Pandas merge() , join() way of working and differences
· Pandas concat() , append() way of working and differences
Thanks to all for reading my blog and If you like my content and explanation please follow me on medium and your feedback will always help us to grow.
Thanks
Vivek Chaudhary
Combine datasets using Pandas merge(), join(), concat(), and append() was originally published in Towards AI — Multidisciplinary Science Journal on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.















