
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for Text Localization, Detection, and More!
Last Updated on November 10, 2021 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Towards AI Team
AI news, research and updates, an exciting natural language API, our first book on descriptive statistics, and our monthly editorial picks!
If you have trouble reading this email, see it on a web browser.
Happy Tuesday, Towards AI family! It has been a little while since we sent our last newsletter. In this edition, we are bringing you some exciting goodies we think you will love. To get started, this research paper on Liquid Time-constant Networks led by Ramin Hasani et al. from MIT showcases novel recurrent neural network models that can change their underlying equations to adapt to new data inputs to reduce complexity massively continuously.

Have you tried out expert.ai’s natural language API demo (no signup needed to try it!). Simply, select a language, choose a document or use a sample text up to 10,000 characters, click analyze, and you will see the different types of natural language analysis expert.ai performs.
We recently launched our book on descriptive statistics with Python, if you haven’t checked it out. This article or this PDF provides a sample of the first 36 pages of the book. Please don’t forget that you can access this work, many more books, and other goodies by becoming a member.
This work on reinforcement learning led by MineRL is fascinating. They are leading state-of-the-art work in the advancement and development of breakthrough RL methods for machine learning research. Check them out, especially if you are interested in Minecraft and reinforcement learning.
Next, if you are interested in computer vision, check out this research from Carnegie Mellon led by Mihir Prabhudesai, Hsiao-Yu Fish Tung, et al., their model can recognize new objects and provide answers to complex visual questions from tiny labeled datasets.
At the beginning of each year, Gradient Flow gathers some groundwork of the year’s technology developments in areas concerning big data, analytics, machine learning, and AI and share their predictions on a trends report. If you haven’t checked it out, their 2021 trends report is very comprehensive.
Next in NLP, powerful language models (LM) such as GPT-3 and T5 have an impressive ability to answer queries in complex scenarios by continuing textual prompts. However, how confident are they? Zhengbao Jiang et al. discuss this LM problem in detail in this paper.
Now into the monthly picks! We pick these articles based on readers, fans, and views a specific piece gets. We hope you enjoy reading them as much as we did. Also, we started doing something new! We will pick our top-performing articles, and our editors will choose a couple of essays that didn’t have outstanding performance, but due to their quality — they made the cut for the month.
If you can, please share our subscription link with your friends, colleagues, and acquaintances. One email per month; unsubscribe anytime! If you have any feedback on how we can improve, please feel free to send us an email.
📚 Editor’s choice featured articles of the month ↓ 📚

Tesseract OCR for Text Localization and Detection by Sharon Lim
Optical character recognition (“OCR”) systems have been widely used to provide automated text entry into computerized systems. However, conventional OCR systems’ inability to read more than a handful of type fonts and page formats still remains unresolved. As a result, conventional OCR has never achieved more than a marginal impact on the total number of documents requiring conversion into its digital form.
[ Read More ]

Descriptive Statistics for Data-driven Decision Making with Python by Pratik Shukla, Roberto Iriondo
Descriptive statistics is essential for decision making based on data. Using descriptive statistics will give you a way to make straightforward decisions on your decision making without complex methodology. Descriptive statistics form the fundamental platform for every quantitative data analysis. “Descriptive Statistics for Data-driven Decision Making with Python” is a book by Pratik Shukla and Roberto Iriondo. Between us, we have worked together for the past year to create this material and prepare you for straightforward, data-driven decision making.
[ Read More ]

How AI Will End the One-Size-Fits-All Approach in Human Assessment by Okan Bulut
Assume that you walk into a store to buy a nice suit (or a dress) for yourself. You walk around the store for a while and finally find a good one that you really like. When you ask the sales associate to help you find the right size, she/he says, “We only sell one-size-fits-all clothes. You can try on the suit in the fitting room and see if it actually fits you.” This story may sound like dystopian fiction to you because today, most clothing stores around the world offer different sizes of clothing and additional tailoring/alteration services. Therefore, you would probably never buy a one-size-fits-all suit.
[ Read More ]

Genetic Algorithm for Trading Strategy Optimization in Python by Louis Chan
If you have heard of systematic trading or algorithmic trading, you must know that optimization of strategy is among the most important factors that dictate whether the strategy would even break even. And the worst part is: optimization is very computationally heavy. Imagine a simple MACD crossover strategy, and there will be at least 3 parameters: fast, slow and signal moving average period, and hundreds of possible values for each, making it more than a million possible combinations.
[ Read More ]

Step-by-step implementation of GANs on custom image data in PyTorch: Part 2 by Varshita Sher
In Part 1 on GANs, we started to build intuition regarding what GANs are, why we need them, and how the entire point behind training GANs is to create a generator model that knows how to convert a random noise vector into a (beautiful) almost real image. Since we have already discussed the pseudocode in great depth in Part 1, be sure to check that out, as there will be many references to it!
[ Read More ]

Creating AI Web Apps using TensorFlow, Google Cloud Platform, and Firebase by Jonathan Quijas
Training Machine Learning models for a web app with ML functionalities are only part of the entire project’s development scope. One often overlooked aspect is going beyond the sandbox and into a production environment. This article will demonstrate how to easily serve a TensorFlow model via a prediction service using Google Cloud Platform (GCP) AI Platform and Cloud Functions. Afterward, I will show how to deploy and host the web client using Firebase to query the model using HTTP requests.
[ Read More ]
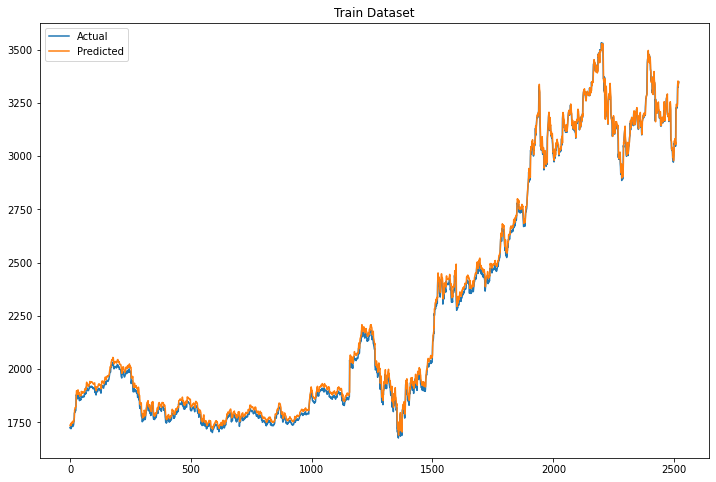
How to Predict Stock Prices with LSTM by George Pipis
Long short-term memory (LSTM) is an artificial recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture used in deep learning with feedback connections. Not only can process single data points such as images, but also entire sequences of data such as speech or video. For example, LSTM applies to tasks such as unsegmented, connected handwriting recognition, speech recognition, machine translation, anomaly detection, time series analysis, etc.
[ Read More ]
Basics of Time Series with Python by Amit Chauhan
Time series analysis is a part of daily activities happening around us concerning time. As the day, month, years are passing with observation around us left with some information. We took help from statistical analysis to make the data/information in some formats and do analysis to get this information. With more and more data generated everywhere, it is not easy to use simple low-level analysis tools. So, the new tools and algorithms are developed to make that data in a suitable format in large amount and solve our purpose to get information.
[ Read More ]

Thinking Fast and Slow and the Third Wave of AI by Louis (What’s AI) Bouchard
These are the reasons why Francesca Rossi and her team at IBM published this paper proposing a research direction to advance AI. Drawing inspiration from cognitive theories of human decision making. Where the premise is: if we gain insights into human capabilities that are still lacking in AI, such as adaptability, robustness, abstraction, generalizability, common sense, and causal reasoning, we may obtain similar capabilities as we have in an AI system.
[ Read More ]

You Will Never Succeed If You Keep Applying for Jobs Online by Arunn Thevapalan
People hire people. Companies don’t.
I realized I’d be graduating from college soon. I wasn’t sure what’s next. I’ll need a job, I decided. Data Science seemed to be cool. I started applying online. I figured the more companies I applied to, the better my chances of getting noticed.
Bulk applying is a numbers game. I need to put myself out there for every opportunity that gets listed. I didn’t have the time to tailor cover letters and CVs for every job, so I’d use the same generic one for all. After all, it’s got everything about me.
[ Read More ]

Deep Hashing for Similarity Search by Rutuja Shivraj Pawar
In recent years Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) [1] search has become a prominent topic of research to process the ever-increasing amount of data in real-world applications effectively. ANN has various applications, including Pattern recognition, Recommendation Systems, Similarity Search, Cluster Analysis, etc. However, in this article, we will focus primarily on the application of Similarity Search. Further, among the existing ANN techniques, Hashing has become effectively popular in managing, storing, and processing high-dimensional data due to its fast query speed and low memory costs [2–10].
[ Read More ]

Methods, Challenges, and Hazards of Collecting Tweets by Stephen DeFerrari
After finishing a sentiment analysis project on Covid vaccine-related tweets, I was left feeling like I only saw a small part of the picture. I had built the project using tweets somebody else graciously collected and posted on Kaggle. The criteria for collection was having the hashtag “#CovidVaccine” with retweets filtered out.
[ Read More ]

Image De-noising Using Deep Learning by Chintan Dave
Denoising an image is a classical problem that researchers are trying to solve for decades. In earlier times, researchers used filters to reduce the noise in the images. They used to work fairly well for images with a reasonable level of noise. However, applying those filters would add a blur to the image. And if the image is too noisy, then the resultant image would be so blurry that most of the image’s critical details are lost.
[ Read More ]

Setup Your Raspberry Pi Quickly by Nikolas Malamas
Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer with easy use developed for teaching the basics of computer science. It is a great tool to start experimenting with small projects like IoT, home automation, websites, games, and many more. You can find many projects shown by the Raspberry Pi Foundation here. The last released model is the Raspberry Pi 4 Model B, a quite cheap but powerful choice.
[ Read More ]

Tweet Topic Modeling Part 1: Using Twint to Scrape Tweets by John Bica
Topic modeling is an unsupervised machine learning approach to find the “hidden” topics (or clusters) inside a collection of textual documents (a corpus). Its real strength is that you don’t need labeled or annotated data, but instead, it accepts the raw text data as input only, hence why it is unsupervised. In other words, the model does not know what the topics are when it sees the data but rather produces them using statistical relationships between the words across all documents.
[ Read More ]
🙏 Thank you for being a subscriber with Towards AI! 🙏
Follow us ↓
[ Facebook ] |[ Twitter ]| [ Instagram ]| [ LinkedIn ] | [ Github ] | [ Google News ]
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for Text Localization, Detection, and More! was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.












