Trends in AI – February 2023
Last Updated on February 15, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Sergi Castella i Sapé
Originally published on Towards AI.
Trends in AI — February 2023
Bing + ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, Claude, and LAION… ChatGPT keeps setting the course of Language Model’s applications. Generative audio sees massive progress (MusicLM, AudioLDM, SingSong…), a comeback of GANs for image synthesis, text to 3D video generation, watermarking the output of LMs, and more.
 Image by Zeta Alpha
Image by Zeta Alpha
Just over a month into 2023, we’re already running out of qualifiers to report on how hectic things have gotten here in AI-world. ChatGPT has continued to dominate and disrupt the tech space well beyond the AI niche: Microsoft and Google are openly and fiercely competing for the next big transition in web search and conversational tech. An explosion of features powered by language models is being shipped at an unprecedented pace. Audio + ML has had its busiest month in years, with several works making substantial progress on the problem. Video generation with diffusion model keeps getting better. Prompting keeps finding new uses. The amount of low-hanging fruit awaiting is staggering, and the FOMO creeps are at an all-time high. So let’s just dive in!
🗞️ News
Microsoft is busy milking the ChatGPT momentum, doubling down onits partnership with OpenAI: including LMs as part of their Azure services, Teams products, and now finally, as part of its web search in Bing.
Google had been comfortably sitting unchallenged dominating web search ads, and accumulating piles of gold IP for years, recently announced Bard, their conversational agent based on Lambda. Moreover, Google also invested heavily in Anthropic ($400M), a rising startup set to compete with OpenAI in Language Model services with Claude, an unreleased conversational language model that has generated some buzz.
Open-source initiatives are also evolving fast. Most prominently, the LAION open assistant is under development, and they’re now crowdsourcing data to instruct-tune (with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, RLHF).
Finally, Runway — The company behind the Stable Diffusion model series — recently announced GEN-1, their new video diffusion model to edit videos with text prompts.
🔬 Research
Every month we analyze the most recent research literature and select a varied set of 10 papers you should know of. This month we’re covering topics such as Language Models, Diffusion Models, Music Generation, Multimodality, and more.
1. MusicLM: Generating Music From Text | Project Page
By Andrea Agostinelli, Timeo I. Denk, et al.
❓ Why → Generative music/audio has completely boomed in the past few weeks. Interestingly, both diffusion models and autoregressive discrete ones show impressive performance. Here’s the growing list of audio AI works in the past month by archinet.
💡 Key insights → Unlike other recent generative audio work using continuous diffusion models, MusicLM is a fully autoregressive and fully discrete music generation model. It cleverly leverages existing work (SoundStream [1] and w2v-BERT [2]) to bootstrap representation learning at different timescales and achieve music generation with previously unseen coherence over long time spans, up to several minutes. The authors call this technique hierarchical representation because autoregressive modeling happens at different granularity levels, which is key to achieving long-term coherence.
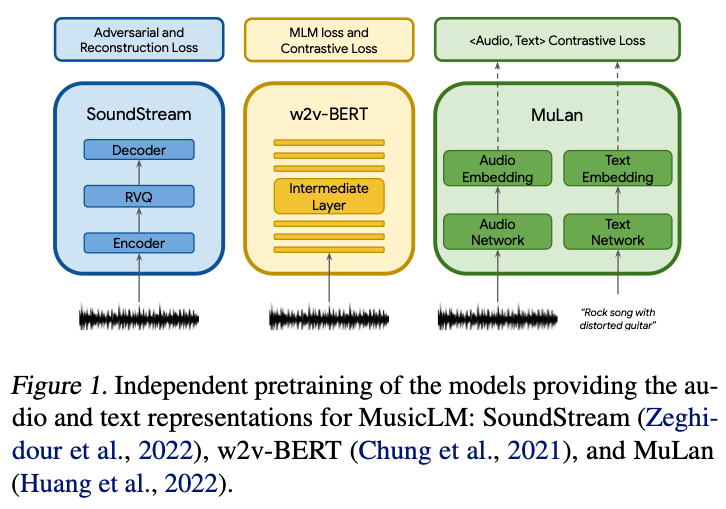 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.11325.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.11325.pdf
One of the key components of this project is the data, in a very interesting way. For MuLan [3], they take the frozen model, and for SoundStream and w2v-BERT they use the free music archive. But then, to train the tokenizers and the autoregressive model (i.e., the model that actually spits out a generation of music representations), they use their own proprietary dataset with 5M audio clips amounting to 280k hours of music at 24kHz. This means that between low-level and high-level representations, the model was trained on around 1 billion (high-level) and 50 billion (low-level) tokens. This means that in terms of training data, MusicLM is comparable to GPT-2, which was trained on roughly 30 billion tokens.
You can go check out their project page to listen to some samples of their music. If you’re interested in the topic of audio generation, here’s the growing list of audio AI works in the past month by archinet (Table below).
 Source: https://github.com/archinetai/audio-ai-timeline
Source: https://github.com/archinetai/audio-ai-timeline
2. A Watermark for Large Language Models
By John Kirchenbauer, Jonas Geiping, Yuxin Wen, Jonathan Katz, Ian Miers, Tom Goldstein.
❓ Why → With the rising popularity of chatGPT among the mainstream, concerns about cheating and attribution have also grown. Where should the usage of these models be allowed? Can the output of a model be detected?
💡 Key insights → This work proposes a method to watermark outputs from proprietary language models, such as those from OpenAI. One of the guiding principles for this watermark is that it should never ever result in false positives (i.e., “false accusations” to a person). That said, the method works as follows:
- Given a token, a deterministic pseudorandom algorithm splits the language model vocabulary into white/black-listed tokens that can appear right after.
- The model generates output only from the whitelisted vocabulary at each inference step.
- To avoid generation degradation, this process is only applied to high entropy tokens (e.g. they only mess with white/black-listing when several continuations can be used, but leave it alone when a token needs to come after another). The method is a bit more complex, and the authors provide theoretical guarantees from an information theoretic perspective, but you get the gist of it.
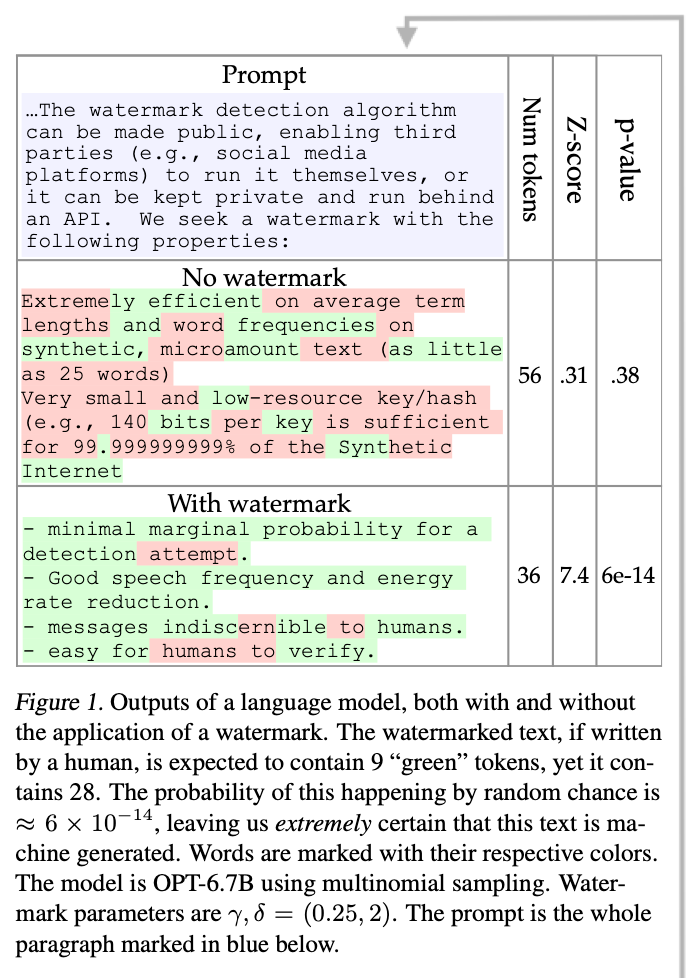 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.10226.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.10226.pdf
Now, this technique is robust to some attacks such as just swapping some words here and there, as the authors show, but it is not bulletproof and can be fooled with enough effort (e.g. having a third-party language model paraphrase the output of the first language model). Still, OpenAI is rumored to plan a release with a similar watermarking technique, hoping to reduce fraudulent use of the technology.
Other zero-shot techniques to detect the output of LMs have been developed, such as DetectGPT [4], they have a higher false positive rate.
3. Demonstrate-Search-Predict: Composing retrieval and language models for knowledge-intensive NLP | Code
By Omar Khattab, Keshav Santhanam, Xiang Lisa Li, David Hall, Percy Liang, Christopher Potts, Matei Zaharia.
❓ Why → We’ve talked about retrieval-augmented LMs a lot, augmenting a LM with an external, explicit memory has the potential to revolutionize how we find information. This work represents a step beyond augmenting LMs with retrieval.
💡 Key insights → Most retrieval-augmented LMs work in a retrieve-then-read fashion: given a prompt, a query is made to the retrieval model (RM) which is then used as context for the generation of LM. But sometimes complex information needs require more complex interaction between the LM and the RM, which is what this paper proposes to model.
The Demonstrate-Search-Predict (DSP) is a framework for in-context learning, where an LM and a frozen RM interact exchanging natural language and scores. This shows improved performance in knowledge intensive multi-hop question-answering scenarios (i.e. when the answer can’t be found right away). The authors provide a python implementation for defining LM and RM interaction through the 3 steps: demonstration (few-shot examples automatically mined from training samples), search (RM and LM interactions), and prediction (generating a final answer).
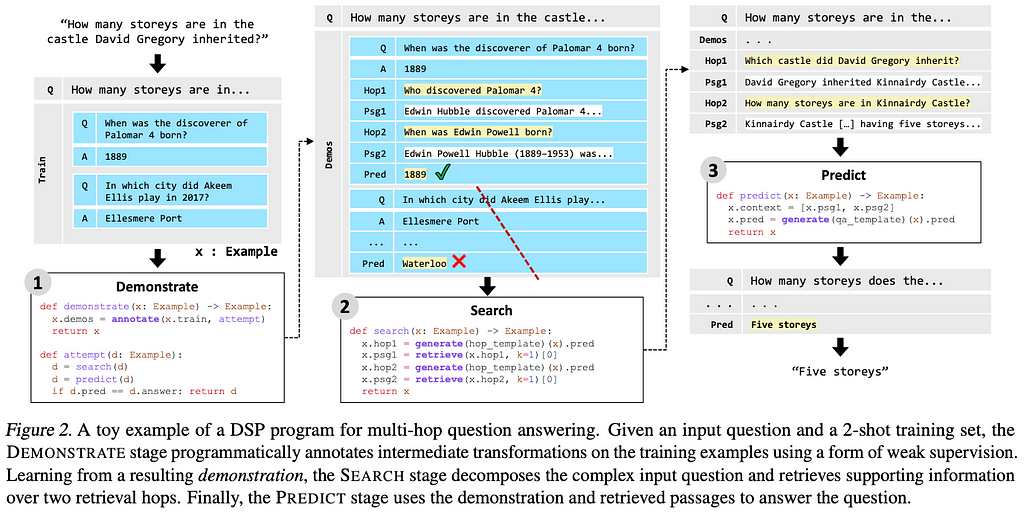 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.14024.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.14024.pdf
Other works you might find interesting in the space of LMs are REPLUG: Retrieval-Augmented Black-Box Language Models, Faithful Chain-of-Thought Reasoning, and Large Language Models Can Be Easily Distracted by Irrelevant Context (the latest prompting trick is to add “ignore unnecessary information”).
4. The Flan Collection: Designing Data and Methods for Effective Instruction Tuning
By Shayne Longpre, Le Hou, Tu Vu, Albert Webson, Hyung Won Chung, Yi Tay, Denny Zhou, Quoc V. Le, Barret Zoph, Jason Wei, Adam Roberts.
❓ Why → What’s the best all-around public, fully open-source language model that you can deploy and run yourself? It looks like FLAN-T5.
💡 Key insights → Originally proposed in FLAN [5], instruction tuning (not to be confused with InstructGPT) is the process of including labeled data in the form of natural language instructions in the training of LMs.
This study compares existing open-source pretrained instruction-tuned models in various settings: held-in or held-out tasks (did the model see the tasks during training?) and zero or few-shot learning. All models compared belong to the T5 family, and have 3 billion parameters, except for the OPT-IML-Max [8] with 175 billion parameters.
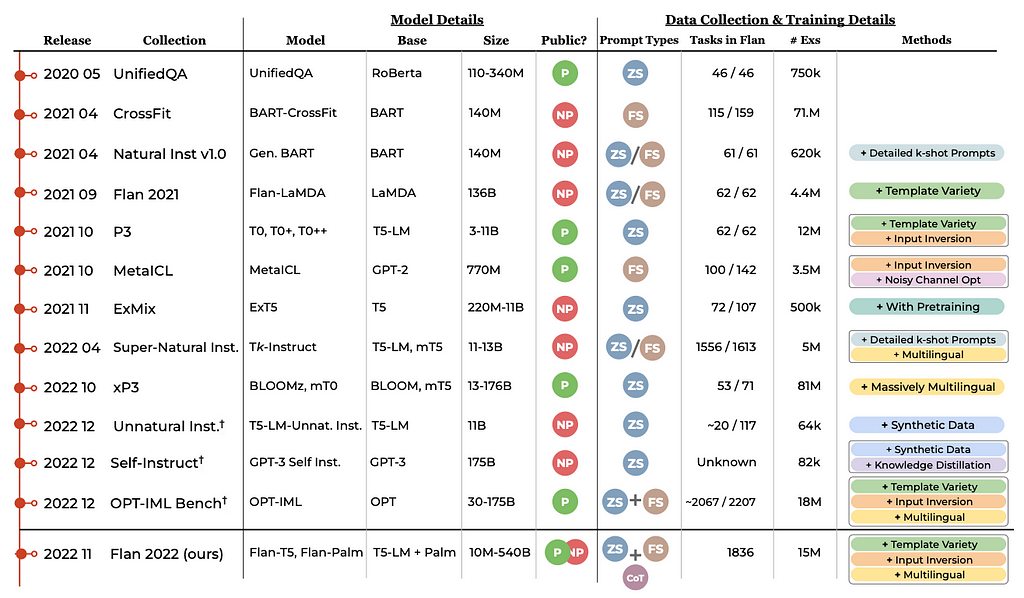 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.13688.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.13688.pdf
The top takeaways are (1) mixing up zero and few-shot examples during training help performance in all settings, (2) instruction tuning proves again to enable smaller small models to achieve the performance of models that are an order of magnitude larger.
These results confirm the existing popular wisdom that Flan T5 is currently the most usable middle-scale (3–10B) model for zero and few-shot learning.
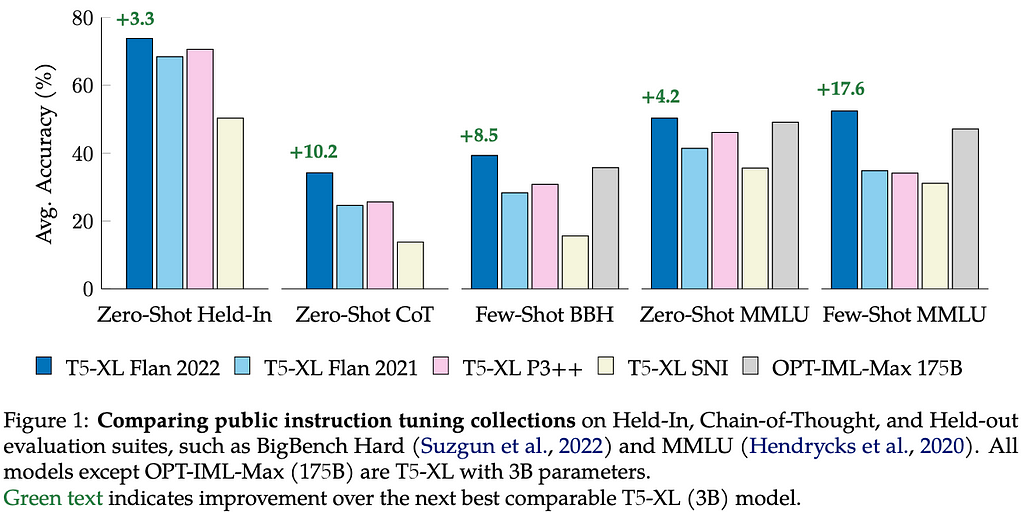 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.13688.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.13688.pdf
5. Tracr: Compiled Transformers as a Laboratory for Interpretability | Code
By David Lindner, János Kramár, Matthew Rahtz, Thomas McGrath, Vladimir Mikulik.
❓ Why → Viewing Transformers as computers could uncover a new understanding of what computation these models can perform.
💡 Key insights → The Restricted Access Sequence Processing Language (RASP [6] is a domain-specific language to express the computations that a transformer can perform. Think about a Transformer as a computing platform whose input is a sequence of categorical variables, and operators that can (1) select, (2) do element-wise computation, or (3) do a select-aggregate computation.
Tracr is a method that compiles RASP directly into Transformer weight values. For instance, below, there’s a program to sort a sequence.
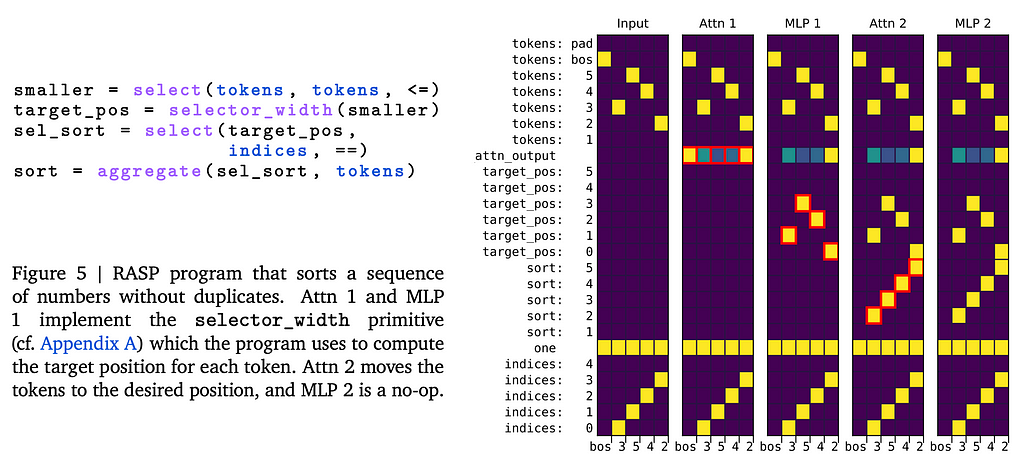 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05062.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05062.pdf
For now, this has very limited practical applications, but it can serve as a tool to better understand the kind of computations that Transformers perform. Moreover, it could serve as a bridge to implement symbolic operations within neural networks, or to replace neural network components with more efficient algorithms when certain weight patterns that implement certain algorithms are detected.
The paper also compares how compiled weights compare to weights learned by gradient descent, confirming empirically how these two methods converge to the same results.
6. Extracting Training Data from Diffusion Models
By Nicholas Carlini, Jamie Hayes, Milad Nasr, Matthew Jagielski, Vikash Sehwag, Florian Tramèr, Borja Balle, Daphne Ippolito, Eric Wallace.
❓ Why → In the meteoric rise of generative AI, ownership, attribution, and privacy of training data have become an area of heated debate. This work highlights the shortcomings and risks of diffusion models when it comes to reproducing the exact images it was trained on, which is concerning because training data is often not fully filtered and ends up including private information.
💡 Key insights → The gist of what they do in this paper is remarkably simple, generate images with stable diffusion with prompts that match those found in the training set, and see how often the model spits out the exact same image it was trained on.
The main takeaways are:
- The more powerful the model, the more likely it is to retrieve training images.
- GAN-based image generation models can also generate images from the training dataset but are less susceptible to direct memorization. Interestingly, GANs and DMs have a strong tendency to memorize the same images, which suggests there’s some commonality among those image/prompt pairs that makes them “memorable”.
 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.13188.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.13188.pdf
This work doesn’t investigate autoregressive image generation models, but it would certainly be interesting to see how they compare to diffusion models given that they’re also trained to exactly replicate training data, unlike GANs.
7. Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Language Models
By Zhuosheng Zhang, Aston Zhang, Mu Li, Hai Zhao, George Karypis, Alex Smola.
❓ Why → Chain-of-thought[9] proved a year ago that a lot of reasoning could be squeezed from existing language models. Now the technique is applied in a multimodal setting (vision + language).
💡 Key insights → This work investigates question answering, including images, in models of size up to 1 billion parameters. Interestingly, previous research found that chain-of-thought can hurt reasoning performance in small models, and joint vision + language models generate a lot of hallucinations in reasoning. The authors propose to solve this by decoupling the rationale generation and answering in two stages. This results in increased performance which, for instance, surpasses the previous state of the art in the ScienceQA benchmark (which was interestingly a text-to-text only language model, GPT-3.5 via OpenAI’s APIs).
While this is an interesting work for reasoning that includes images, we’d be very interested to see how bigger models perform with this approach, given that we’ve seen previously that much better CoT reasoning emerges at larger scales.
 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.00923.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.00923.pdf
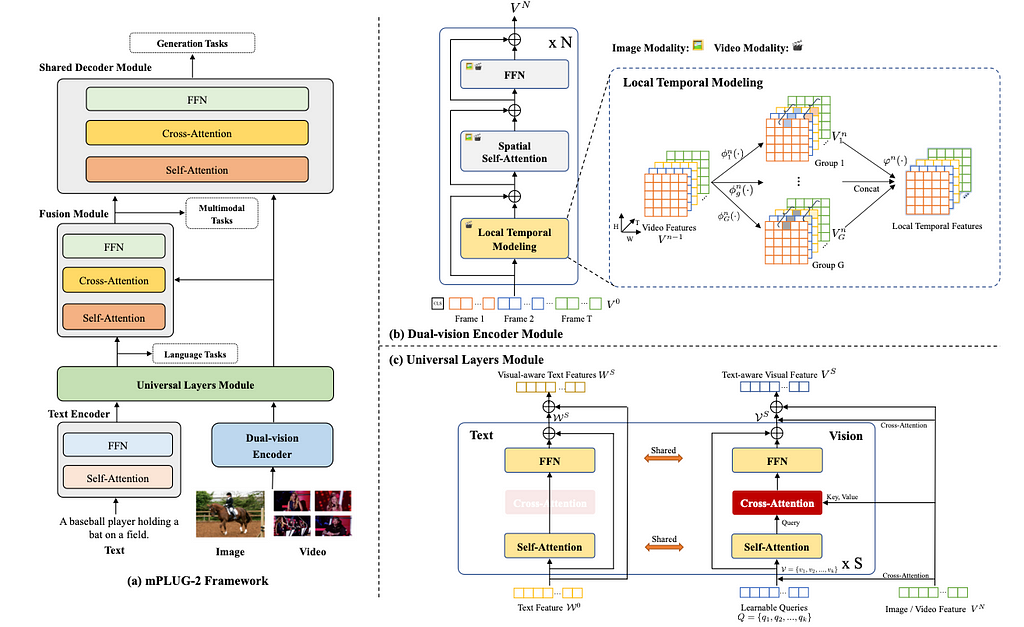
8. StyleGAN-T: Unlocking the Power of GANs for Fast Large-Scale Text-to-Image Synthesis | Code
By Axel Sauer, Tero Karras, Samuli Laine, Andreas Geiger, Timo Aila.
❓ Why → GANs refuse to die in the dawn of Diffusion Models.
💡 Key insights → Although Diffusion Models have become the bread and butter of image generation thanks to their impressive versatility and robustness, GANs still present some advantages over them. Most prominently, they’re much more efficient: a single forward pass suffices to generate an image, whereas diffusion models require multiple steps to do so.
This work proposes the latest GAN iteration: StyleGAN-T, to address the modern requirements of large-scale text-to-image synthesis. For instance, strong text alignment, controllable output variation, training stability on diverse data, etc. Overall, it’s a very solid work of engineering applying modern neural networks and optimization practices to GAN-based image generation.
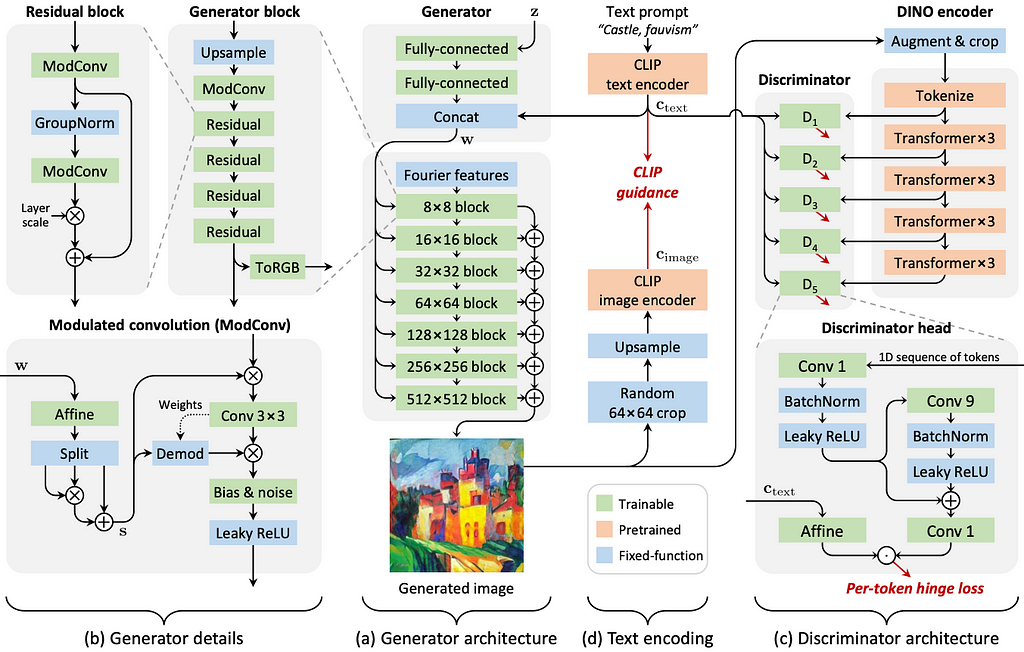

Still, StyleGan-T shares some similitude with famous existing diffusion models like DALL·E 2, such as the conditional generation guidance using CLIP embeddings. The authors highlight that this GAN model results in a better alignment-variation tradeoff with the text prompt (i.e., you want the resulting image to reflect the prompt but also have reasonable variability when generated multiple times).
All-in-all, GANs are still competitive when considering constraints such as efficiency, but we don’t expect them to make diffusion models obsolete anytime soon, as these keep improving and finding new uses.
9. Text-To-4D Dynamic Scene Generation (MAV3D) | Project Page
By Uriel Singer, Shelly Sheynin, Adam Polyak, Oron Ashual, Iurii Makarov, Filippos Kokkinos, Naman Goyal, Andrea Vedaldi, Devi Parikh, Justin Johnson, Yaniv Taigman.
❓ Why → Adding one more dimension to generating images: generating 3D video.
💡 Key insights → One of the most impressive feats of this work is that there are not a lot of 3D video and text data pairs out there, unlike for images, so that needs to be worked around. To do so, the authors rely on an existing pretrained text-to-video model (Make-A-Video[7], also from Meta) as a “scene prior” for a NeRF model, which is optimized to create a 3D representation of the scene. In hand-wavy terms, during the optimization process, the NeRF model creates a sequence of views of a scene from contiguous spacetime coordinates, and then the diffusion model is used to score the image realism and the alignment with the text prompt using a technique called Score Distillation Sampling.
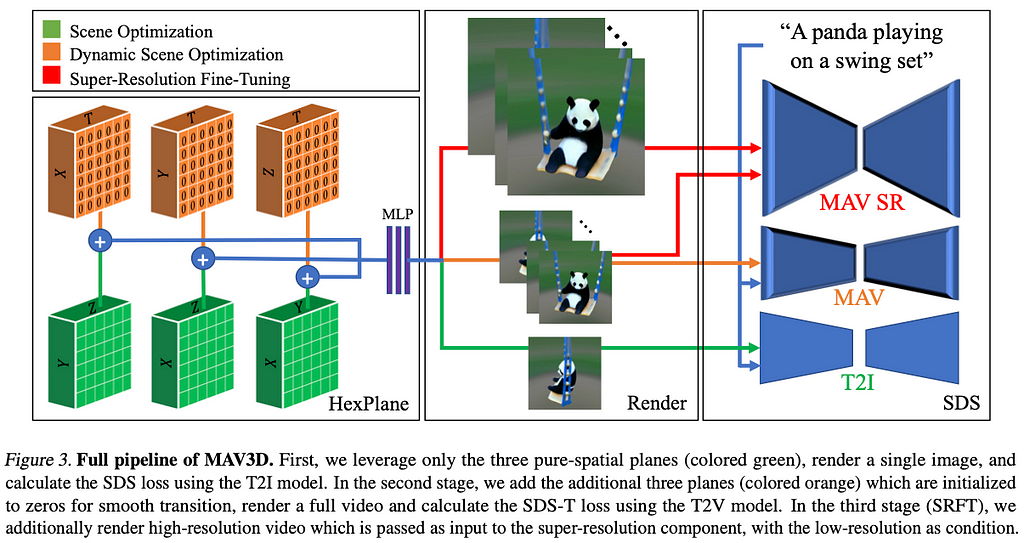 Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.11280.pdf
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.11280.pdf
The work can be seen as an extension of DreamFusion [8], a text-to-3D image model, where a time dimension is added. The videos resulting from this model are short and don’t contain any narrative, which is still a challenging aspect of longer-form video generation.
10. PADL: Language-Directed Physics-Based Character Control | Project Page | Code
By Jordan Juravsky, Yunrong Guo, Sanja Fidler, Xue Bin Peng.
❓ Why → A fun one to wrap up the selection! LMs applications beyond text.
💡 Key insights → This work uses LMs to map natural language instructions into character control. Think of moving a character in a video game with arbitrary complex high-level language instructions. This has a lot of potential in the context of accessibility (e.g., designing animations much faster with reduced explicit input), new videogame experiences, or even novel general human-computer interactions with increasingly complex instructions.
The method involves learning a skill embedding that aligns language instructions with character motions, training a policy, and finally, an aggregation policy is learned to combine skills and tasks (e.g., involving objects and complex interactions).
References:
[1] “SoundStream: An End-to-End Neural Audio Codec” by Neil Zeghidour, Alejandro Luebs, Ahmed Omran, Jan Skoglund, Marco Tagliasacchi, 2021.
[2] “W2v-BERT: Combining Contrastive Learning and Masked Language Modeling for Self-Supervised Speech Pre-Training” by Yu-An Chung, Yu Zhang, Wei Han, Chung-Cheng Chiu, James Qin, Ruoming Pang, Yonghui Wu, 2021.
[3] “MuLan: A Joint Embedding of Music Audio and Natural Language” by Qingqing Huang, Aren Jansen, Joonseok Lee, Ravi Ganti, Judith Yue Li, Daniel P. W. Ellis, 2022.
[4] “DetectGPT: Zero-Shot Machine-Generated Text Detection using Probability Curvature” by Eric Mitchell, Yoonho Lee, Alexander Khazatsky, Christopher D. Manning, Chelsea Finn, 2023.
[5] “Finetuned Language Models Are Zero-Shot Learners” by Jason Wei, Maarten Bosma, Vincent Y. Zhao, Kelvin Guu, Adams Wei Yu, Brian Lester, Nan Du, Andrew M. Dai, Quoc V. Le, 2021.
[6] “Thinking Like Transformers” by Gail Weiss, Yoav Goldberg, Eran Yahav, 2021.
[7] “Make-A-Video: Text-to-Video Generation without Text-Video Data” by Uriel Singer, Adam Polyak, Thomas Hayes, Xi Yin, Jie An, Songyang Zhang, Qiyuan Hu, Harry Yang, Oron Ashual, Oran Gafni, Devi Parikh, Sonal Gupta, Yaniv Taigman, 2022.
[8] “OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models” by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen, Christopher Dewan, Mona Diab, Xian Li, Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Myle Ott, Sam Shleifer, Kurt Shuster, Daniel Simig, Punit Singh Koura, Anjali Sridhar, Tianlu Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, 2022.
[9] “Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models” by Jason Wei, Xuezhi Wang, Dale Schuurmans, Maarten Bosma, Brian Ichter, Fei Xia, Ed Chi, Quoc Le, Denny Zhou, 2022.
Trends in AI — February 2023 was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














