
Sports Analytics 101, Intro
Last Updated on June 10, 2022 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Nitin Chauhan
Originally published on Towards AI the World’s Leading AI and Technology News and Media Company. If you are building an AI-related product or service, we invite you to consider becoming an AI sponsor. At Towards AI, we help scale AI and technology startups. Let us help you unleash your technology to the masses.
I am writing a series of articles about how data analytics and machine learning can impact and be helpful in sports analytics. Throughout my life as an aspiring data scientist, I have always sought out guides to help me gain a deeper understanding of sports analytics. After years of research and courses, I have come up with the idea of creating a guide called Sports Analytics 101. I hope that this guide will help people like me gain a better understanding of and appreciation for data analytics.

Why is Sports analytics essential?
Sports analysis is primarily for the teams directly involved in the games or sports betting companies.
Sports analytics aims to help management make informed decisions by using data related to any sport or game — for example, players’ statistics, weather conditions, recent wins, and losses. Sports analysis aims to improve team performance and enhance winning chances. A success speaks volumes and trickles down to the fans in the stadium, to television contracts, fan store merchandise, parking, concessions, sponsorships, enrollment and retention, and local pride.
Some great examples ⚽️
- One of the world’s greatest football clubs — Real Madrid — is using Microsoft technology to transform its operations, performance, fitness, and relationships with its 500 million global fans.
- Fenway Sports Group, the owners of Liverpool FC, has a history of data adoption. It is famous that John Henry offered Billy Beane, the man behind Moneyball, a $12.5 million deal to become general manager of the Boston Red Sox in 2002 before exploring the football world.
Top global sports brands use advanced sports analytics to stay on top of their game regarding performance, fitness, and relationships with fans.
Introduction
It has been two decades since coaches began using data science to improve the performance of their players. Big data has been in use to help them make split-second decisions on the field, and sports analytics have helped them sign the “next big thing.” Referees are now using Video Assistant Technology (VAR) in football to help them make more precise decisions regarding penalties, free kicks, and red cards.
Since AI, specifically Deep Learning, has entered the picture, sports will change even more.
In this article, we will explore some of the most exciting applications of artificial intelligence in sports and the technology behind them, including:
- AI Ref or VAR
- Player Recommendation Engine
- Player Performance Analysis
- Talent Identification & Scouting
- Betting
1. AI Ref or VAR
Recap ⏳
Argentina drew 0–0 with England during the 1986 World Cup in the sweltering Mexican heat when Diego Maradona climbed with the England goalkeeper to meet a cross.
Despite being able to use his arms, the keeper was the favorite to reach the ball. Despite this, Maradona sprung into the air faster and met the ball with his head into the net. It’s no secret that wasn’t what happened. England’s defenders were enraged when Maradona touched the ball, gesturing to the referee that he had scored an illegal goal.
Present 🚀
Using AI Referees today, such a goal could be achieved in just minutes. All major decisions that affect the outcome of games would be judged more accurately, the margin for error would be slimmer — and, arguably, controversies would be hugely reduced if AI in sports was used to help the referees.
A perfect example is the Euro 2020 game between England and Denmark with the questionable penalty called by AI when Raheem Sterling went down near the goal. What would AI determine?
Using the AI Referee model trained, the AI referee ruled that Sterling made contact with the ball 150ms before Denmark would have reached the ball. The AI referee would still have awarded the penalty to England.
Yet — There might have been a different outcome if more camera angles had been available.
A. Offside Detection
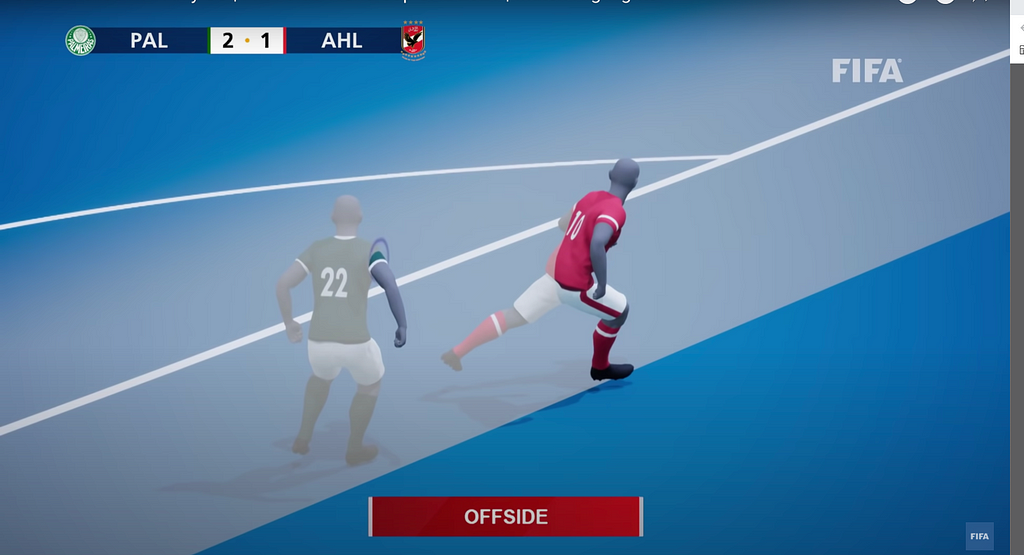
For example, detecting offside from overhead cameras can assist VAR in football to ensure goals are not given or denied incorrectly. At the same time, on-field tracking systems (such as Hawkeye) can judge line calls more accurately.
In clay tennis, technology still hasn’t been able to give a 100% accurate reading of a line call due to the slower movement of the ball.
Additionally, computer vision can help identify potential sports penalties to reduce mistakes and controversies and prevent games from swaying one way or the other due to poor refereeing decisions.
B. Goal-line Technology
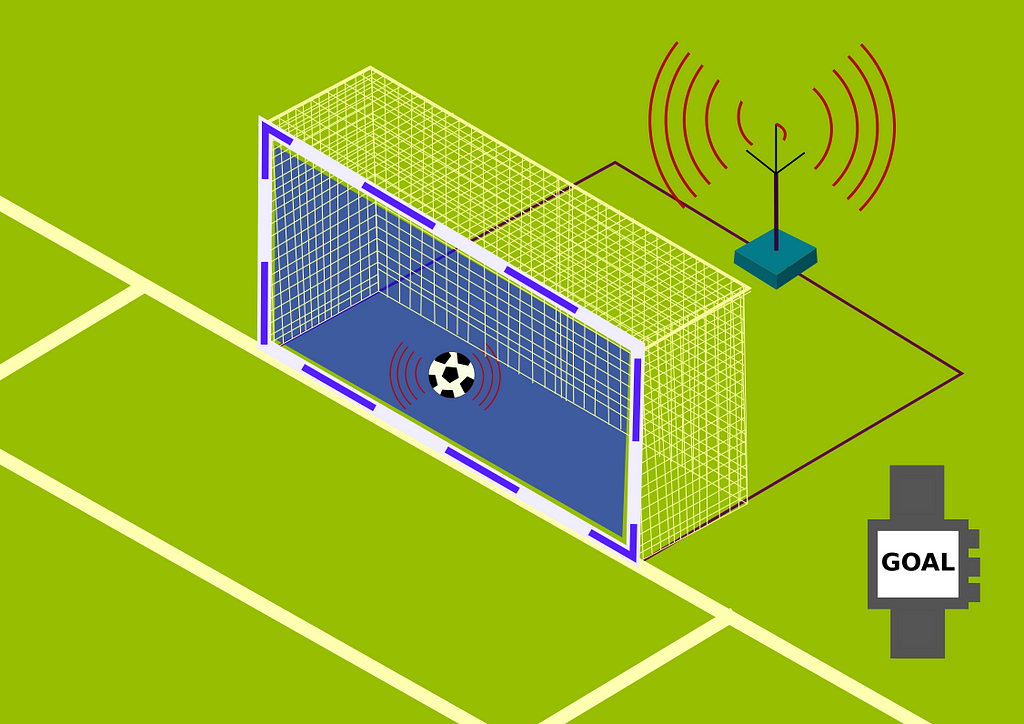
Similarly, goal-line technology was introduced into football after England failed to score an apparent equalizer against Germany at the 2010 World Cup. According to FIFA, it is a method for determining whether the ball has crossed the line in its entirety.
It uses magnetic fields and cameras to significant effect. Interestingly, it must meet various criteria to gain FIFA’s approval, including being able to work “ under adverse conditions accurately.”
A typical Goal-line technology relies on 14 strategically positioned cameras that are streamed to a cluster of computers, which use advanced image processing algorithms to
- Determine the object (ball),
- Distinguish it from interferences, such as a player’s shoulders, hand, and boots.
- Confirm whether the entire ball has crossed the line.
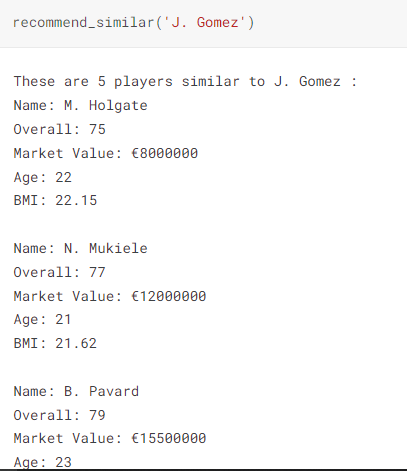
2. Player Recommendation Engine
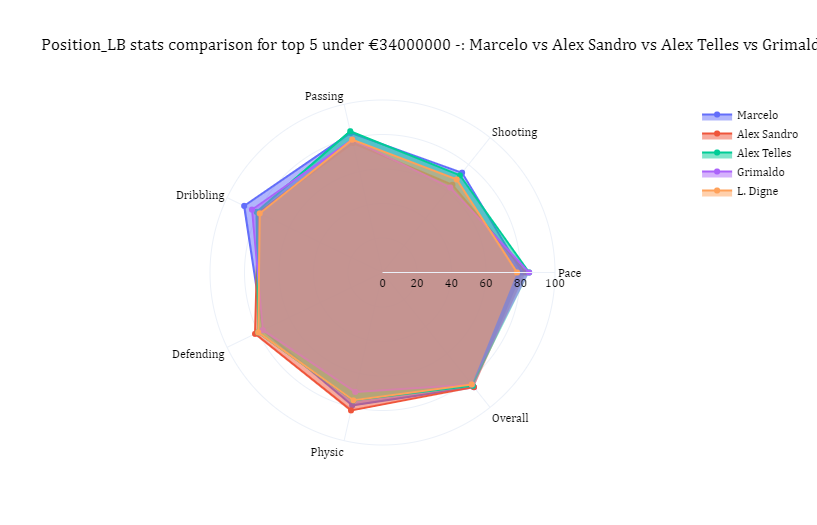
This application will allow you to search for players similar to a specifically selected football player. The latency requirement is that the results are fetched and displayed as quickly and efficiently as possible in real-time.
Current solutions: StatsBomb is the industry leader in football analytics. StatsBomb IQ’s similar player search tool can be regarded as state-of-the-art, but we have no idea how it’s implemented.
I have a similar project on estimating some key metrics used by professional scouts and analysts to compare player performance and recommend similar players in case of current players either leaving the club or injured.
Link to notebook here
3. Player Performance Analysis
A wearable that gathers information about the strain and tear levels can help athletes prevent serious injuries. AI is being used in sports to boost performance and health. But that’s only the beginning. With AI, teams can create strategies and tactics and maximize their strengths.
Using AI, player performance can now be analyzed in a more sophisticated way than ever. Using data and visuals, coaches can gain insight into their teams’ strengths and weaknesses on any given day, enabling them to change tactics and strategy, thus exploiting opponent weaknesses.
It applies to all sports, from football to tennis, handball, and swimming.
The development of a computer system that tracks players in handball has drawn attention, with a study describing the process: Computer vision, for example, is used to track and analyze human motion.
The cameras collect the data, and the output results are the Spatio-temporal trajectories of the players. These trajectories provide sports experts with valuable information about the players’ capabilities and performance.
They conducted three experiments using video sequences to identify the best method for automatic player tracking of:
- Tracking based solely on movement
- Color-based tracking
- Color tracking in combination with template tracking
Based on the results, color and template tracking was the most effective method, thanks to its speed and minimal human operator intervention.
4. Talent Identification & Scouting

These days, teams are involving more technology-based solutions in recruiting and scouting players. Baseball swings, football runs, basketball blocks — everything that happens on the field of play is tracked, with teams amassing terabytes of data.
The use of computer vision in sports involves tracking players’ movements and the orientation of their bodies during play (object tracking in videos).
This is how it looks on an example of soccer players. Labeling the data with the key point skeleton tool and training the model will allow it to track and predict the players’ movement.
Machine Learning algorithms are integrated into either aggregated or event-based data to “evaluate players’ skills and potential and rank them in various categories.
Machine Learning algorithms are integrated into either aggregated or event-based data to “evaluate players’ skills and potential and rank them in various categories.
Furthermore, teams can use computer vision to identify specific attributes (such as corner-taking ability in soccer) that determine future performance.
With this data’s insights, teams can make better recruitment choices, ensuring teams are built on successful strategies by buying uncapped players for cheap before developing them and selling them for a profit.
5. Betting (Sports Gambling)

Additionally, sports analytics has contributed to the growing sports gambling industry, which accounts for approximately 13% of the global gambling market. It has an enormous impact on and off the field within sports. You would be hard-pressed to find a professional sporting event with nothing riding on the outcome when sports gambling is valued somewhere between $700 and $1 billion. It is extremely popular with groups of all kinds, from avid sports fans to recreational gamblers. Many gamblers are drawn to sports gambling because there is much information and analytics at their disposal when making decisions.
Key takeaways 📝
In sports, machine learning is booming, with new applications emerging every year. Everything except the games themselves is set to be improved by data and technology.
The key is balance. AI can be good in theory, but it cannot be at the expense of the fan experience in sports. For example, using facial recognition to smoothen the process of fans or spectators entering the stadium without any hassle also removes the turnstiles, which — for many European football fans, at least — are synonymous with a romantic vision of match day.
AI is undoubtedly the future of sports technology, but we’re not yet there. We’re probably just at the beginning. And that’s exciting.
If you like this article, follow me for more relevant content. Also, feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn, and let’s be part of an engaging network.
Sports Analytics 101, Intro was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. It’s free, we don’t spam, and we never share your email address. Keep up to date with the latest work in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














