What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Last Updated on May 6, 2022 by Editorial Team

Learn what is machine learning (ML), how it works, and its importance in five minutes
Last updated on May 6, 2022
Authors(s): Roberto Iriondo, Pratik Shukla
Who should read this article?
Anyone curious who wants a straightforward and accurate overview of what is machine learning, how it works, and its importance. We go through each of the pertinent questions raised above by slicing technical definitions from machine learning pioneers and industry leaders to present you with a fundamental and simplistic introduction to the fantastic, scientific field of machine learning.
A glossary of terms can be found at the bottom of the article, along with a small set of resources for further learning, references, and disclosures.
What is machine learning?

The scientific field of machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence, as defined by Computer Scientist and machine learning pioneer [1] Tom M. Mitchell: “Machine learning is the study of computer algorithms that allow computer programs to automatically improve through experience [2].”
An algorithm can be thought of as a set of rules/instructions that a computer programmer specifies, which a computer can process. Simply put, machine learning algorithms learn by experience, similar to how humans do. For example, after having seen multiple examples of an object, a compute-employing machine learning algorithm can become able to recognize that object in new, previously unseen scenarios.
Machine learning behaves similarly to the growth of a child. As a child grows, her experience E in performing task T increases, which results in higher performance measure (P).
For instance, we give a “shape sorting block” toy to a child. (Now we all know that in this toy, we have different shapes and shape holes). In this case, our task T is to find an appropriate shape hole for a shape. Afterward, the child observes the shape and tries to fit it in a shaped hole. Let us say that this toy has three shapes: a circle, a triangle, and a square. In her first attempt at finding a shaped hole, her performance measure(P) is 1/3, which means that the child found 1 out of 3 correct shape holes.
Second, the child tries it another time and notices that she is a little experienced in this task. Considering the experience gained (E), the child tries this task another time, and when measuring the performance(P), it turns out to be 2/3. After repeating this task (T) 100 times, the baby now figured out which shape goes into which shape hole.
So her experience (E) increased, her performance(P) also increased, and then we noticed that as the number of attempts at this toy increased. The performance also increases, which results in higher accuracy.
Such execution is similar to machine learning. What a machine does is, it takes a task (T), executes it, and measures its performance (P). Now a machine has a large number of data, so as it processes that data, its experience (E) increases over time, resulting in a higher performance measure (P). So after going through all the data, our machine learning model’s accuracy increases, which means that the predictions made by our model will be very accurate.
Why do we need machine learning?
For instance, we have a set of images of cats and dogs. What we want to do is classify them into a group of cats and dogs. To do that, we need to find out different animal features, such as:
- How many eyes does each animal have?
- What is the eye color of each animal?
- What is the height of each animal?
- What is the weight of each animal?
- What does each animal generally eat?
We form a vector on each of these questions’ answers. Next, we apply a set of rules such as:
If height > 1 feet and weight > 15 lbs, then it could be a cat.
Now, we have to make such a set of rules for every data point. Furthermore, we place a decision tree of if, else if, else statements and check whether it falls into one of the categories.
Let us assume that the result of this experiment was not fruitful as it misclassified many of the animals, which gives us an excellent opportunity to use machine learning.
What machine learning does is process the data with different kinds of algorithms and tells us which feature is more important to determine whether it is a cat or a dog. So instead of applying many sets of rules, we can simplify it based on two or three features, and as a result, it gives us a higher accuracy. The previous method was not generalized enough to make predictions.
Machine learning models help us in many tasks, such as:
- Object Recognition
- Summarization
- Prediction
- Classification
- Clustering
- Recommender systems
- And others
Major Machine Learning Algorithms:
These are the major machine learning algorithms currently being used today.
1. Regression (Prediction)
We use regression algorithms for predicting continuous values.
Regression algorithms:
- Linear Regression
- Polynomial Regression
- Exponential Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Logarithmic Regression
2. Classification
We use classification algorithms for predicting a set of items’ classes or categories.
Classification algorithms:
- K-Nearest Neighbors
- Decision Trees
- Random Forest
- Support Vector Machine
- Naive Bayes
3. Clustering
We use clustering algorithms for summarization or to structure data.
Clustering algorithms:
- K-means
- DBSCAN
- Mean Shift
- Hierarchical
4. Association
We use association algorithms for associating co-occurring items or events.
Association algorithms:
- Apriori
5. Anomaly Detection
We use anomaly detection for discovering abnormal activities and unusual cases like fraud detection.
6. Sequence Pattern Mining
We use sequential pattern mining for predicting the next data events between data examples in a sequence.
7. Dimensionality Reduction
We use dimensionality reduction to reduce the size of data to extract only useful features from a dataset.
8. Recommendation Systems
We use recommenders algorithms to build recommendation engines.
Examples:
- Netflix recommendation system.
- A book recommendation system.
- A product recommendation system on Amazon.
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms:
Machine Learning algorithms are generally categorized according to their purpose.
- Supervise Machine Learning Algorithms
- Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms
- Semi-supervised Machine Learning Algorithms
- Reinforcement Learning
Now, let us have a brief look at each of the categories of the Machine Learning Algorithms.
1. Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms:
Here, human specialists play the role of teacher, feeding the computer with training data comprising the input/predictors and showing it the correct answers (output), with the expectation that the machine will be able to learn patterns from the data. In simple terms, we can say that here we provide supervision to the algorithm while it is in the training phase. A supervised machine learning algorithm uses the training data to find patterns and then uses the learned behavior to predict the value of the target variable on new data points.
Examples of Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms:
- Nearest Neighbor
- Naive Bayes
- Decision Trees
- Linear Regression
- Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Neural Networks
2. Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms:
In unsupervised machine learning algorithms, there is no concept of the teacher. The dataset we have is unlabelled with no true value of the target variable. Instead, the unsupervised machine learning algorithms find patterns in data to perform their job. Unsupervised machine learning algorithms are useful especially in the case where subject matter experts are not sure about what to look for in the dataset, i.e., which features are essential. Unsupervised machine learning algorithms are specially used for pattern detection and descriptive modeling. These algorithms attempt to mine for rules, recognize patterns, summarize and aggregate data points in order to derive useful insights and better represent the data to consumers using techniques applied to the input data.
Examples of Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms:
- K-means clustering
- Principle Component Analysis
- Hierarchical Clustering
3. Semi-supervised Machine Learning Algorithms:
In supervised machine learning algorithms, all the data is labeled — while in unsupervised machine learning algorithms, we don’t have any labeled data. Semi-supervised learning is somewhere in the middle. In many practical instances, the cost of labeling is relatively significant because it necessitates the use of qualified human experts. As a result, semi-supervised algorithms are the best options for model development when labels are absent in the majority of observations but present in a few. These methods take advantage of the fact that unlabeled data contains crucial information about group parameters, even if the group memberships are unknown.
4. Reinforcement Learning:
The reinforcement learning algorithm (called the agent) continuously learns from the environment in an iterative fashion. The agent learns from its environment’s experiences until it has explored the whole spectrum of conceivable states.
Reinforcement Learning is a discipline of Artificial Intelligence that is a form of Machine Learning. It enables machines and software agents to automatically select the best behavior in a given situation in order to improve their efficiency. For the agent to learn its behavior, it needs only simple reward feedback, which is known as the reinforcement signal.
How does machine learning work?
How does machine learning work? ~ Yann LeCun, Head of Facebook AI Research | Source: Youtube [3]
In the video above [3], Head of Facebook AI Research, Yann LeCun, simply explains how machine learning works with easy-to-follow examples. Machine learning utilizes various techniques to intelligently handle large and complex amounts of information to make decisions and/or predictions.
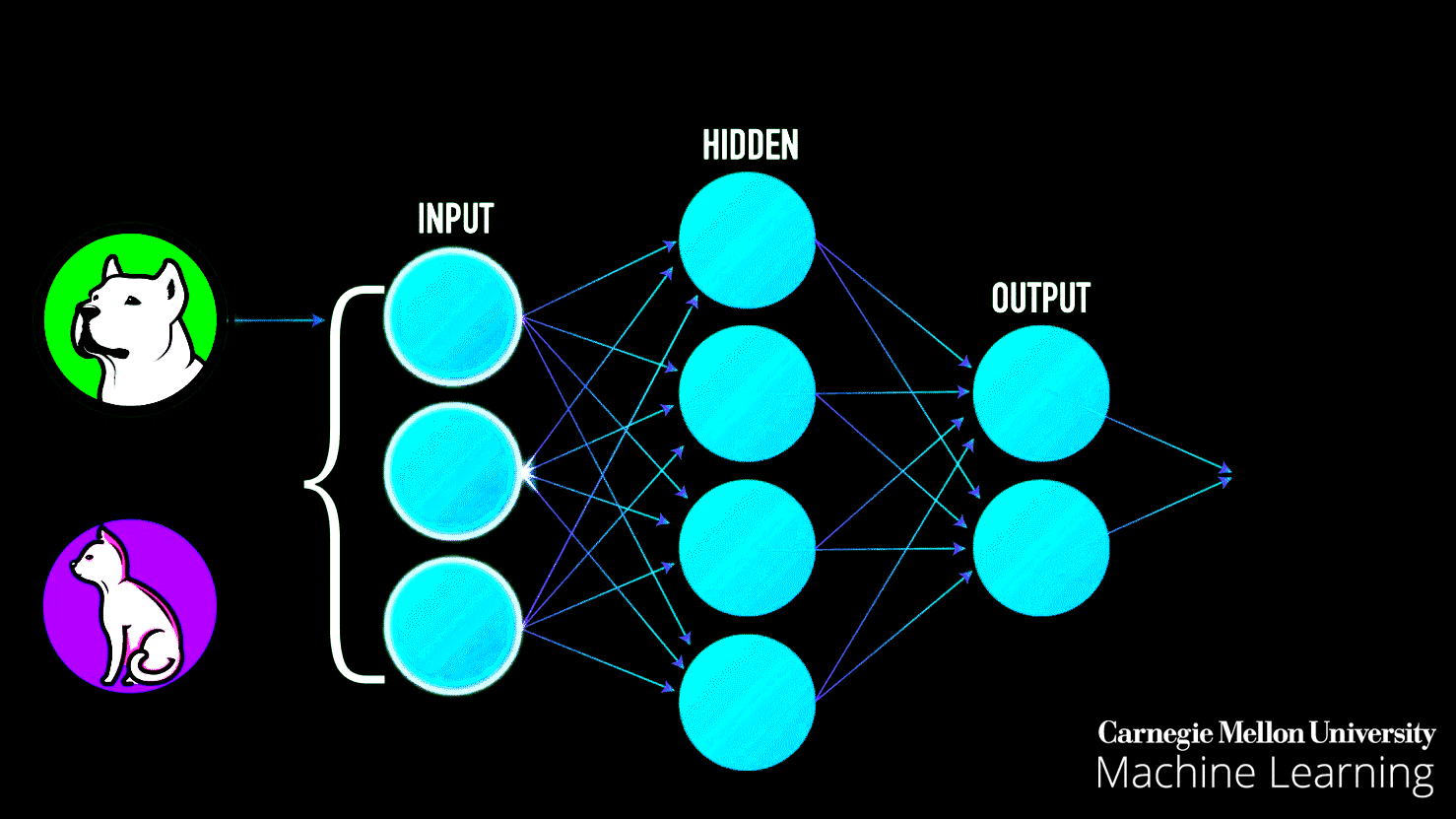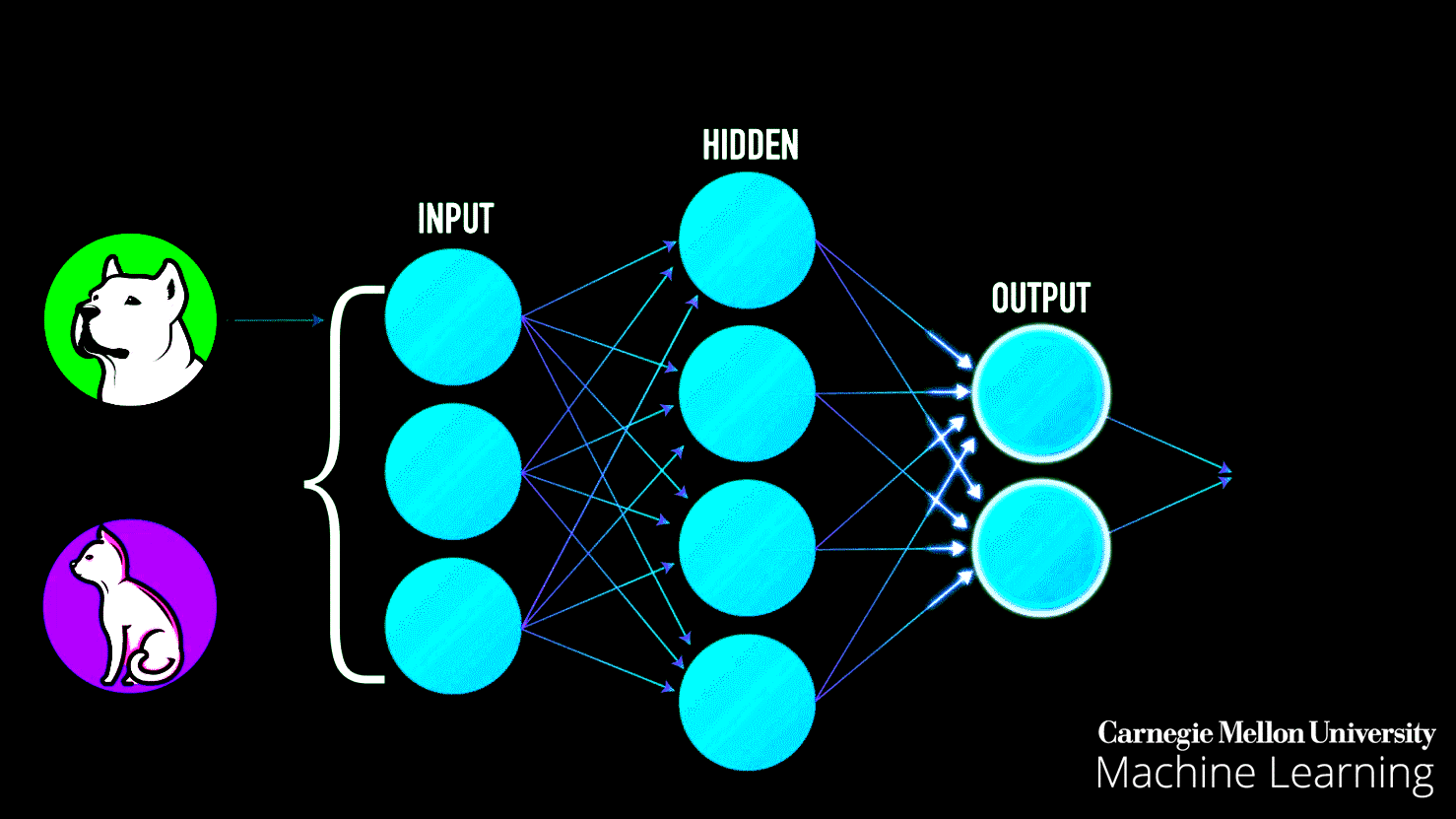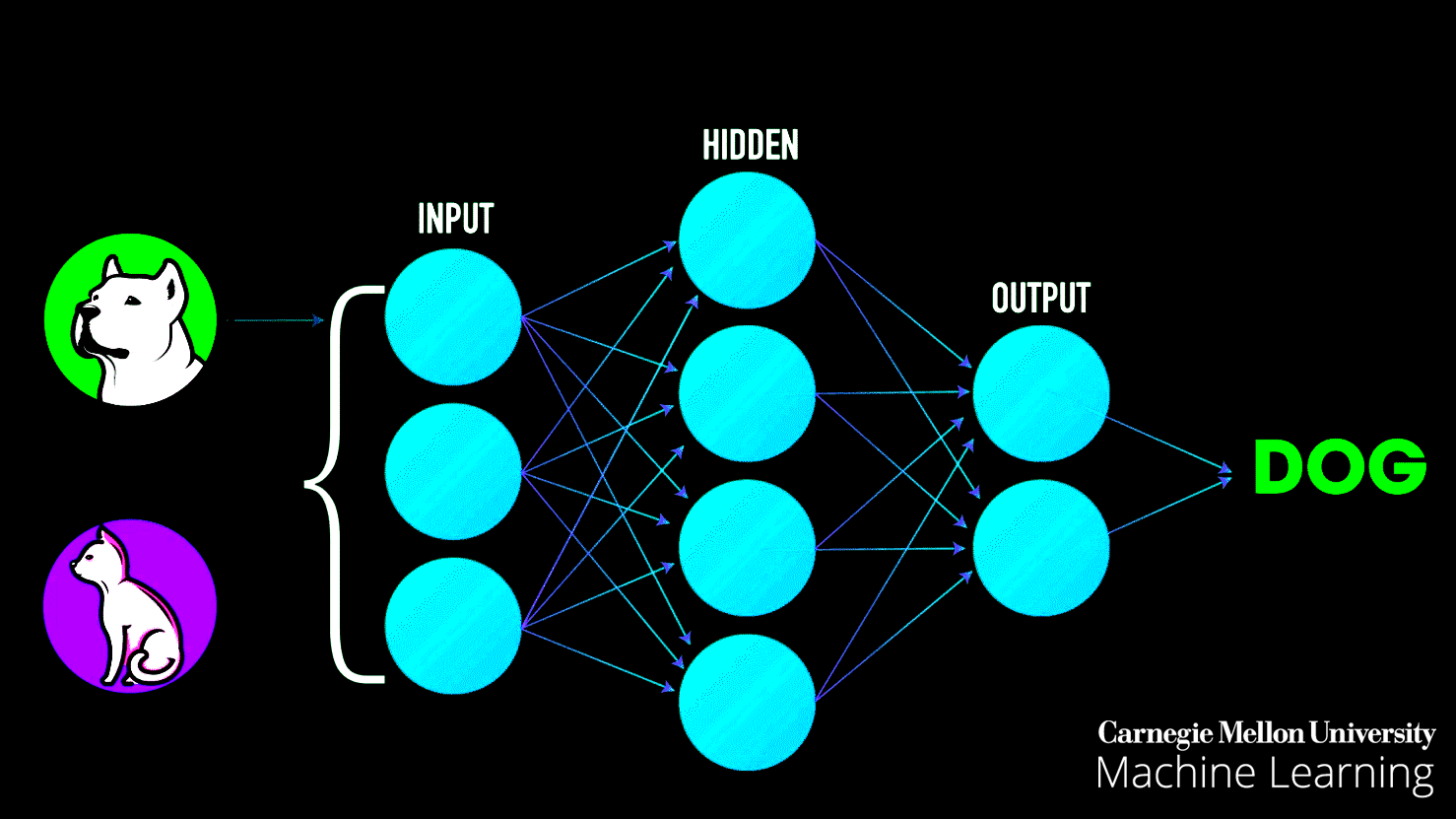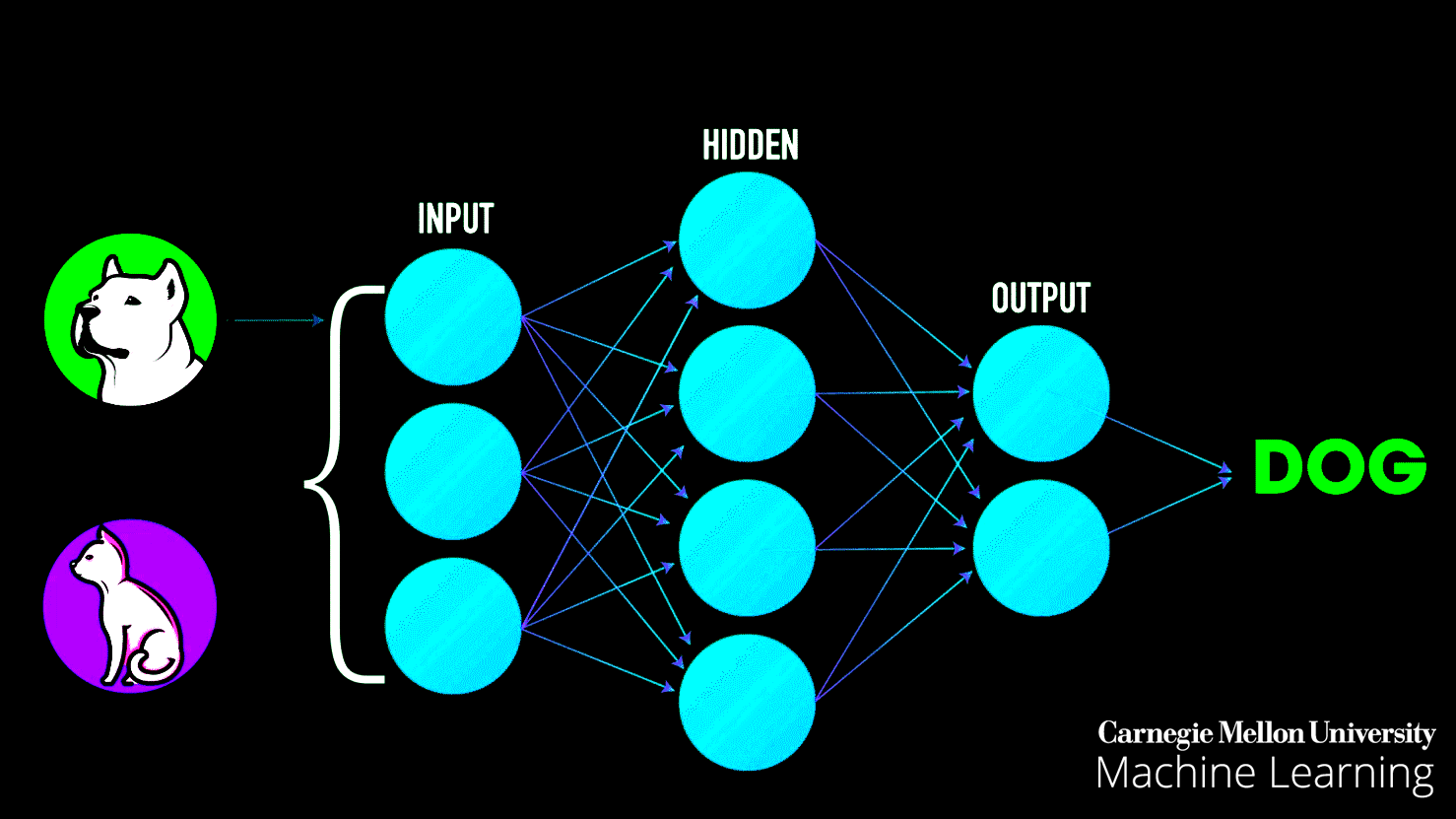
In practice, the patterns that a computer (machine learning system) learns can be very complicated and difficult to explain. Consider searching for dog images on Google search — as seen in the image below, Google is incredibly good at bringing relevant results, yet how does Google search achieve this task? In simple terms, Google search first gets a large number of examples (image dataset) of photos labeled “dog” — then the computer (machine learning system) looks for patterns of pixels and patterns of colors that help it guess (predict) if the image queried it is indeed a dog.
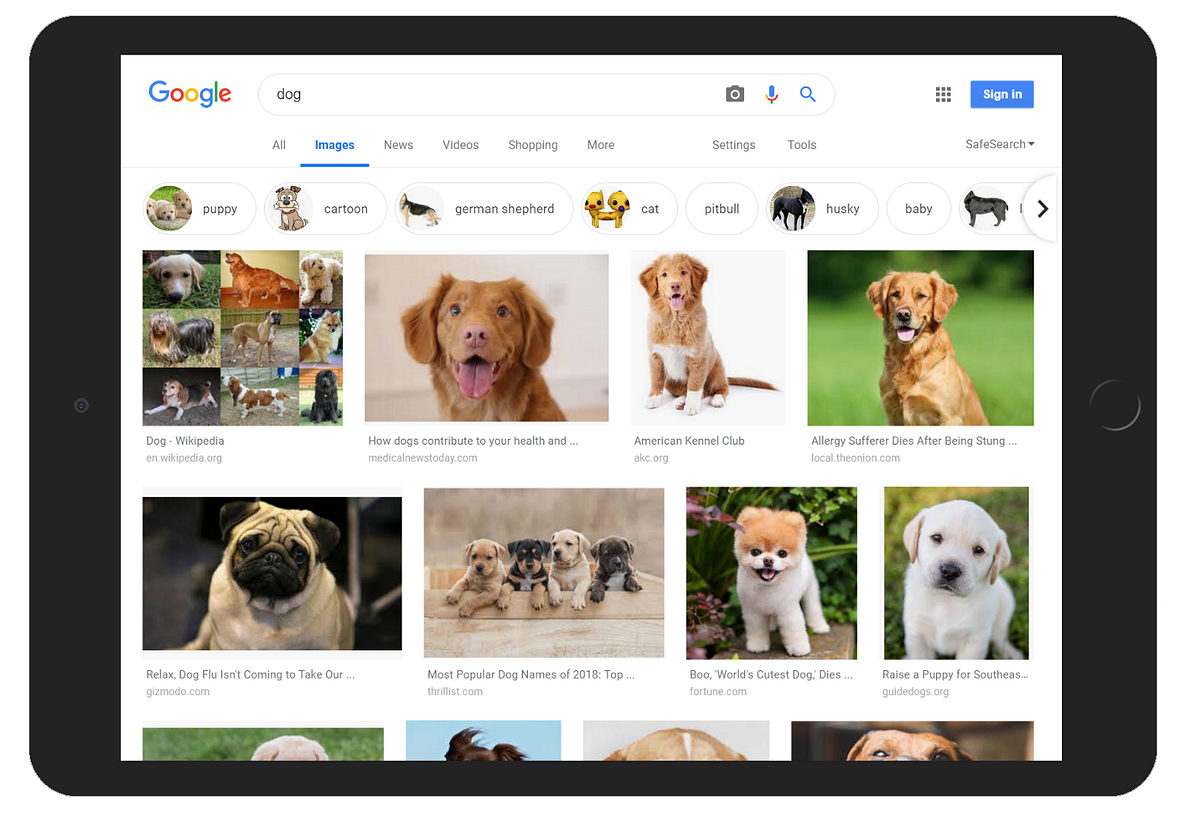
At first, Google’s computer makes a random guess of what patterns are reasonable to identify a dog’s image. If it makes a mistake, then a set of adjustments are made for the computer to get it right. In the end, such a collection of patterns learned by a large computer system modeled after the human brain (deep neural network), that once is trained, can correctly identify and bring accurate results of dog images on Google search, along with anything else that you could think of — such process is called the training phase of a machine learning system.
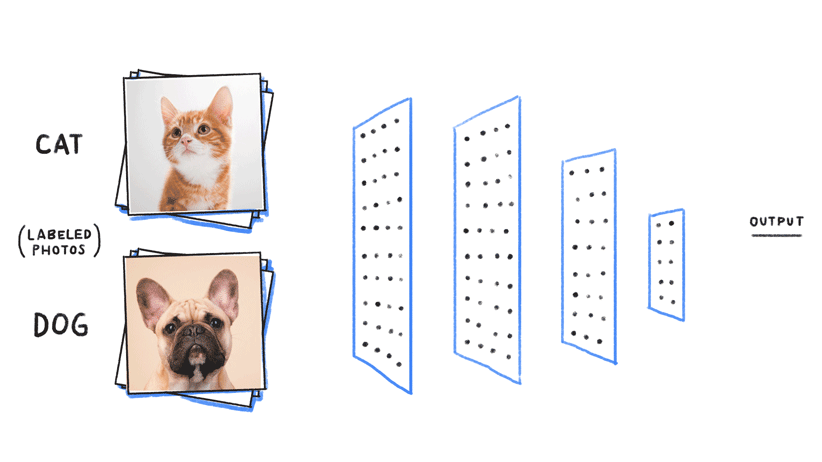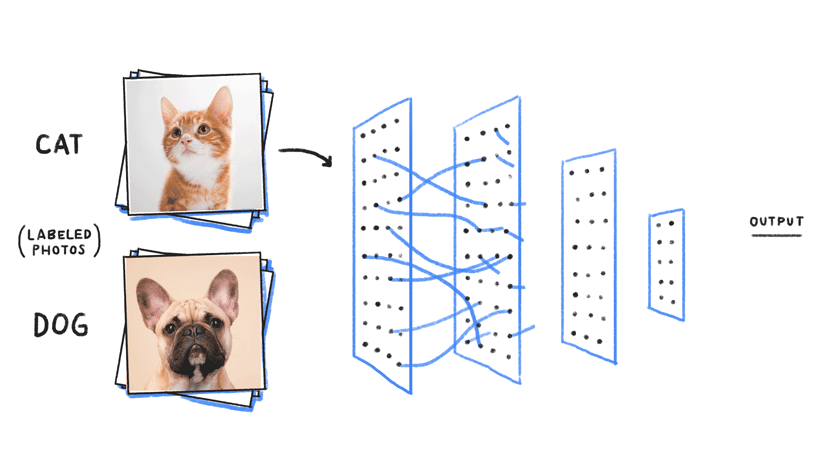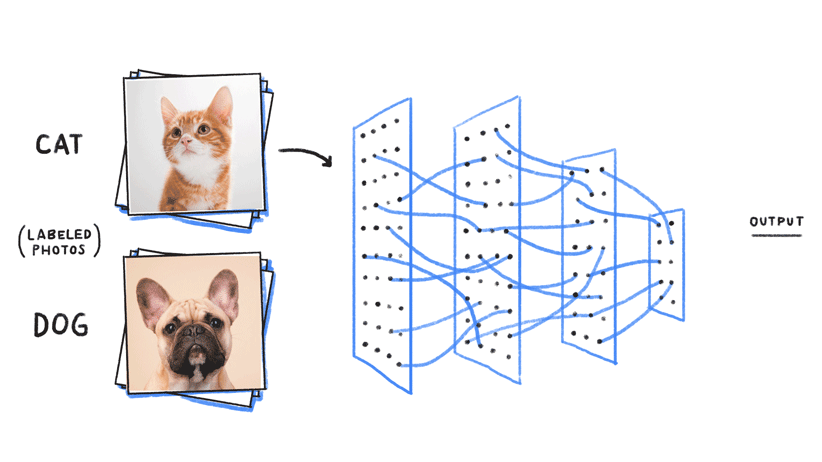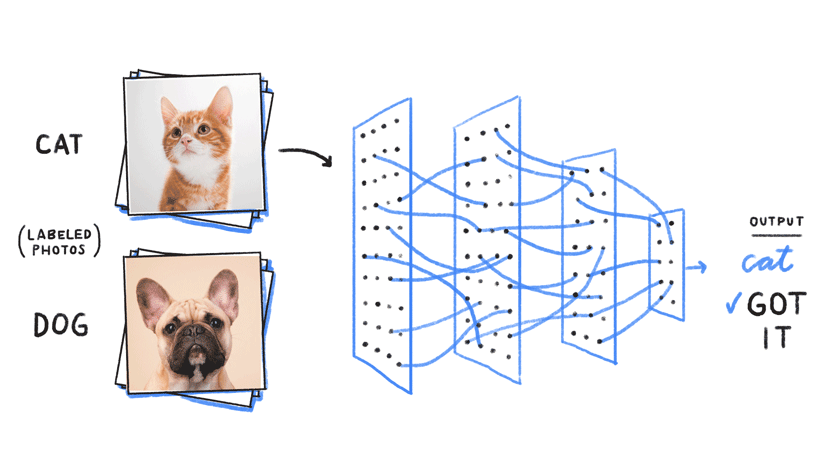
Imagine that you were in charge of building a machine learning prediction system to try and identify images between dogs and cats. As we explained above, the first step would be to gather a large number of labeled images with “dog” for dogs and “cat” for cats. Second, we would train the computer to look for patterns on the images to identify dogs and cats, respectively.

Once the machine learning model has been trained [7], we can throw at it (input) different images to see if it can correctly identify dogs and cats. As seen in the image above, a trained machine learning model can (most of the time) correctly identify such queries.
Why is machine learning important?

Machine learning is incredibly important nowadays. First, because it can solve complicated real-world problems in a scalable way, and second, because it has disrupted a variety of industries within the past decade [9] and continues to do so in the future, as more and more industry leaders and researchers are specializing in machine learning, along taking what they have learned to continue with their research and/or develop machine learning tools to impact their own fields positively. Third, artificial intelligence has the potential to incrementally add 16% or around $ 13 trillion to the US economy by 2030 [18]. The rate at which machine learning is causing a positive impact is already surprisingly impressive [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16], which has been successful thanks to the dramatic change in data storage and computing processing power [17] — as more people are increasingly becoming involved, we can only expect it to continue with this route and continue to cause amazing progress in different fields [6].
Who uses machine learning and why?
The value of machine learning technology has been acknowledged by most businesses that deal with significant amounts of data. Organizations can work more effectively or gain an advantage over competitors by gleaning insights from this data — frequently in real-time.
- Financial Services
- Health Care
- Government
- Retail
- Oil and Gas
- Transportation
Advantages and Disadvantages of Machine Learning:
- Advantages:
- Trends and patterns are easily discernible
- No human intervention
- Continuous improvement with low cost
- Handling multidimensional data
- Handling a variety of data
- Wide applications
2. Disadvantages:
- Requires a large number of data
- Utilization of time and resources
- Result interpretation
- Susceptibility to errors in critical domains
What does the future look like for Machine Learning?
The future of machine learning is fascinating. Machine learning applications are currently used in practically every mainstream domain. Healthcare, search engine optimization, digital marketing, and education are just a few of the industries that have benefited. Working on a topic without this new technology looks to be nearly unachievable in terms of achieving objective results. Machine Learning may be a debatable benefit to a business or organization, whether it is a multinational corporation or a start-up because repetitive tasks that are currently completed manually will be completed automatically in the future. Below are a few examples by which we can verify the future of machine learning
- Accurate search engine results
- Accurate customizations based on preferences
- Quantum computing is on the rise
- The exponential growth of data
- Automated self-learning machines
- Automotive and self-driving vehicles
- Manufacturing
Acknowledgments:
The author would like to thank Anthony Platanios, Doctoral Researcher with the Machine Learning Department at Carnegie Mellon University, for constructive criticism and editorial comments in preparation for this article.
DISCLAIMER: The views expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not represent the views of Carnegie Mellon University, nor other companies (directly or indirectly) associated with the author(s). These writings do not intend to be final products yet rather a reflection of current thinking, along with being a catalyst for discussion and improvement.
Glossary of Terms:
Key Machine Learning Definitions
Glossary of the most used definitions in machine learning
References:
[1] For pioneering contributions and leadership in the methods and applications of machine learning. | “Prof. Tom M. Mitchell.” National Academy of Engineering. Retrieved October 2, 2011.
[2] Machine Learning Definition | Tom M. Mitchell| McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math; (March 1, 1997), Page 1 | http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs.cmu.edu/user/mitchell/ftp/mlbook.html
[3] How does Machine Learning work? | Yann LeCun | Youtube | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmXB636p_E8
[4] Andrew Ng: Why AI is the New Electricity | Shana Lynch | Stanford Business | https://www.gsb.stanford.edu/insights/andrew-ng-why-ai-new-electricity
[5] Breaking it down: A Q&A on machine learning | Google | https://www.google.com/about/main/machine-learning-qa/
[6] In Ten Years: The Future of AI and ML | Foursquare | https://medium.com/foursquare-direct/in-ten-years-the-future-of-ai-and-ml-fa68a527f378
[7] Training ML Models | Amazon Web Services | https://docs.aws.amazon.com/machine-learning/latest/dg/training-ml-models.html
[8] Machine learning models training process | Amazon Web Services | https://docs.aws.amazon.com/machine-learning/latest/dg/training-process.html
[9] 5 Industries Machine Learning is Disrupting Right Now | Disruption, Inc.| https://disruptionhub.com/5-industries-machine-learning-disrupting/
[10] Facebook Has Released a Machine Learning Tool to Help Engineers Code | DesignNews | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmXB636p_E8
[11] Lithium-ion Battery Book Written by Machine Learning Algorithm | ChemistryWorld | https://www.chemistryworld.com/news/lithiumion-battery-book-written-by-machine-learning-algorithm/3010380.article
[12] Machine Learning Algorithm Predicts Who Will Survive Game of Thrones | VW | https://www.chemistryworld.com/news/lithiumion-battery-book-written-by-machine-learning-algorithm/3010380.article
[13] Machine Learning is Making Pesto Even More Delicious | MIT Technology Review | https://www.technologyreview.com/s/613262/machine-learning-is-making-pesto-even-more-delicious/
[14] Machine learning generated artwork auctions off for $ 432,500 | Data-Driven Investor | https://medium.com/datadriveninvestor/machine-learning-generated-artwork-auctions-off-for-432-500-c377be74146f
[15] How machine learning will fundamentally change the lives of healthcare providers | Radiology Business | https://www.radiologybusiness.com/topics/artificial-intelligence/machine-learning-ai-healthcare-workflow-clinicians
[16] Google’s AI is better at spotting advanced breast cancer than pathologists | MIT Technology Review | https://www.technologyreview.com/the-download/612292/googles-ai-is-better-at-spotting-advanced-breast-cancer-than-pathologists/
[17] Visualizing the Trillion-Fold Increase in Computing Power | Visual Capitalist | https://www.visualcapitalist.com/visualizing-trillion-fold-increase-computing-power/
[18] The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on The World Economy | The Wall Street Journal | Intelligence in the economy | PWC | https://www.pwc.co.uk/economic-services/assets/macroeconomic-impact-of-ai-technical-report-feb-18.pdf
[19]Machine Learning Algorithms For Beginners with Code Examples in Python| Towards AI Editorial Team|https://pub.towardsai.net/machine-learning-algorithms-for-beginners-with-python-code-examples-ml-19c6afd60daa
Published via Towards AI














