
Why was Ethical AI Avatar born?
Last Updated on November 9, 2021 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Supriya Ghosh
Artificial Intelligence

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is seen as a wave of transformation by many in the technological world.
But this certainly gives birth to its own set of challenges and issues.
And in fact, this leads us to ask questions like –
Will AI drive us around in the future?
Or
Will AI fight wars for us?
Or
Will AI take charge of human healthcare?
Or
Will AI do agriculture for us?
And many more.
The questions are almost infinite and never-ending and persuade people to shift their thoughts from the functional capabilities of AI systems to the safety and ethics behind such powerful systems. The major challenge here is to build a system with the common good of humanity and with ethical considerations.
The most fundamental thing to understand here is — what we want these systems to ultimately achieve and design it accordingly.
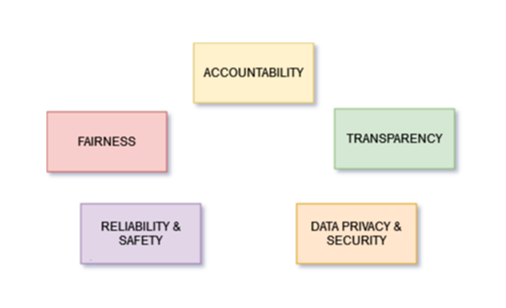
3 Major areas of concern with advancement in AI lies in:
1. Privacy and Surveillance,
2. Bias and Discrimination,
3. Correct judgment and Accountability
To address all these concerns, the Ethical AI Avatar was born.
What is Ethical AI?
“ Ethical AI ” implies adopting AI in a manner that is transparent, responsible, and accountable which means it should remain consistent with laws, regulations, norms, customer expectations, and societal values. Ethical AI should be able to safeguard against any bias and discrimination, incorrect judgment, and respect privacy at scale.
Let me depict a few Use cases in AI which will make you understand the underlying serious ethical concerns.
Ethical AI Example: Healthcare
Healthcare is an area where practitioners have been the early adopters of AI but its patient engagement, care delivery, and population health are prone to issues such as bias, and violations of data privacy.
Bias in society is reflected in historical health data and, if not corrected, can cause AI systems to make biased decisions. For e.g., who gets access to healthcare management services on priority, based on the reported racial makeup of study populations and gender split introduces malpractices and is the cause of discrimination.
How Ethical AI considerations are shaping up to solve the above Healthcare issue?
FDA is developing additional regulatory compliance to reduce bias and is stringent on enforcing firms to monitor and periodically report on the real-world performance of their algorithms. Firms are being constantly directed towards ensuring the choices they make in terms of customers and partners they work with, the composition of their data teams, and the data they collect to contribute towards minimizing bias.
One of the cases of Google Health, which is working towards screening and detection of breast cancer beforehand, not only is religiously improving performance along with a 10-fold reduction in cost and validating the algorithm’s performance in different clinical settings but it is also making large investments to ensure that algorithm performs with fairness across different racial groups.
Ethical AI Example: Autonomous Vehicle
Imagine an autonomous car with failed brakes going at full speed towards an elderly person almost in mid-80’s and a child who is 10 years old. By deviating a little, one can be saved. This time, the car’s algorithm has to take the decision not the human driver.
Who would get chosen, the old person or the child?
There is no right answer for this and purely it's an ethical dilemma, that shows the importance of Ethical AI.
How Ethical AI should solve the above Autonomous Vehicle issue?
The algorithm should be highly efficient to take a controlled decision to both avoid hitting the streetwalker/pedestrian as well as cut the risk for the people inside the car. Hence, liability and control become primarily important. Existing bodies like the National Highway Transportation Safety Association, which oversees vehicle safety have a wide role to play in such Ethical AI business.
Ethical AI Example: Court of Law
AI in judicial systems is believed to evaluate cases and apply justice in a better, faster, and more efficient way than a judge. It can help as machines can evaluate and weigh relevant factors better than humans, taking advantage of its speed and large data ingestion capacity. But whether decisions made are devoid of any bias and subjectivity is a big ethical question.
There are many ethical challenges:
1. Lack of transparency of AI tools and algorithms.
2. AI is not neutral, and decisions are susceptible to inaccuracies, discrimination, and bias based on the human-fed data at the initial level.
How Ethical AI should solve the above Court of Law issue?
There needs to be a “ sense of urgency” to make lawmakers act.
U.S. lawmakers recently introduced the Algorithmic Accountability Act which, if enforced completely can solve known problems such as algorithmic bias as well as privacy and security concerns.
While ethical AI has a major role to play, but context also matters at all levels including tactical. For e.g., In an industrial manufacturing application, Ethical AI focuses on safety and reliability while in consumer-facing industries or public services, in-discrimination and fairness take priority.
One more concern of current artificial intelligence technologies is the threat of adversarial examples. Adversarial examples manipulate the behavior of AI systems by making small changes to their input data that are mostly invisible to humans. This happens mainly because AI algorithms work in ways that are fundamentally different from the human brain.
Adversarial examples can happen by accident, or they can also be deliberately injected into harmful adversarial attacks against critical AI systems which can cause a safety threat.
The European Commission has laid out several essential requirements for developing ethical and trustworthy artificial intelligence.
It recommends that AI systems should be able to fall back from machine learning to rule-based systems or ask for a human to intervene.
Human intervention requires Human-in-the-loop systems.
You can go through one of my earlier write-up mentioned below to understand Human-in-the-loop systems thoroughly.
Integrating Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) in machine learning application is a necessity not a choice.
Also, the end-user should know about the confidence level and the general reliability of the AI system they’re using.
To prevent unfair bias against certain groups, guidelines also recommend that AI developers make sure their AI systems’ data sets are all-inclusive.
If we don’t act upon this now and build ethical AI, then implications down the road can be far grimmer than people realize. We should keep working towards building ethical AI to the maximum extent.
Final Thoughts
The adoption of ethical AI principles is essential for the healthy development of all AI-driven technologies and self-regulation by the industry will be much more effective than any other effort.
These AI-based decisions need to be made explainable and continuously monitored. Data is the fuel of all AI systems, and the collection and usage of consumer data need to be carefully tracked, especially in large-scale commercial systems.
As more consumers and businesses become aware of the importance of ethical AI, these types of safeguards will become more prevalent in the coming years.
Thanks for reading !!!
You can follow me on medium as well as
LinkedIn: Supriya Ghosh
Twitter: @isupriyaghosh
Why was Ethical AI Avatar born? was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














