
The What, Why and How of Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Last Updated on March 24, 2022 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Amrutha Moorthy
Originally published on Towards AI the World’s Leading AI and Technology News and Media Company. If you are building an AI-related product or service, we invite you to consider becoming an AI sponsor. At Towards AI, we help scale AI and technology startups. Let us help you unleash your technology to the masses.

Humankind stands out in splendid isolation due to ability of speech and advanced communication. However, pace of communication has been a quest as old as humankind.
What is OCR?
Optical Character Recognition, or OCR, is the process of programmatically identifying characters visually and converting that to the best-guess equivalent computer code.
Why OCR?
Time is valuable and there have been automation in last century to speed the time-consuming tasks. Converting from one form of communication to another is cumbersome and ability to convert speech or words to other forms have been continuous evolution.
The amount of time that is wasted during the rewriting of a document for the sake of digitization is unbelievably high. Upon using a technology to make content interchangeable, the novelty was sought in the speed of conversion.
How would today’s OCR technology help?
Considered a significant boon for businesses worldwide today, OCR is the science and technology behind the conversion of printed text within images, non-editable electronic documents (PDF), and hard-copy records into various machine-searchable and editable data formats. The formats include data storage in Word, Excel, and PDF — besides others.
· For individuals, it means convenience and productivity in personal life.
· For business, it means real savings to your bottom line.
With SaaS solutions for business needs, there is massive data collected and stored. There’s just no humanly-sustainable way to handle the Big Content problem without automation.
Machines cant interpret any content. What they can do is draw extremely accurate comparisons between examples of text and the patterns present in an image. Over the years, there has been great innovation to use machine learning for OCR and it has yielded impressive results. Today, we have very evolved packages and wrappers that are easy to integrate as well as quicker.
History of OCR Tools
The quest for an effective tool began in the 1800s. The Nipkow Disk was an image scanning device all the way back in 1885. Later devices started by interpreting Morse Code to read text aloud. The first scanners capable of reading text required that the text be in a special font that was easy for the scanning software to recognize. In 1974, Kurzweil Computer Products developed the first omni-font software.

The first OCR (Optical Character Recognition) device was developed in late 1920s by the Austrian engineer Gustav Tauschek (1899–1945), who in 1929 obtained a patent on OCR (so called Reading Machine) in Germany, followed by Paul Handel who obtained a US patent on OCR (so called Statistical Machine) in USA in 1933 (U.S. Patent 1915993). In 1935 Tauschek was also granted a US patent on his machine (U.S. Patent 2026329).
OCR in 2021
Machine Learning helps us to scale the accuracy and flexibility of OCR, and automation through business-configured workflows makes sure that this massive data volume gets handled gracefully, consistently, and reliably by tools that work for us.
So, what are some answers for communication that we can seek through OCR? What is the Machine Learning approach we can follow? Lets find out.
In recent time, there is massive content captured through Images, Videos through CCTVs and other means. It is of great value to convert the content to machine editable content. Examples of applications of OCR include:
· Read name plates of vehicles from dashcam or CCTV
· Convert handwritten manuscripts to editable documents
· Convert scanned copies of books to editable content.
All programming languages have rich libraries and packages to facilitate OCR operations. Python being one of the popular choice for Machine learning also has Python has Python-tesseract as an optical character recognition (OCR) tool. That is, it will recognize and “read” the text embedded in images.
Python-tesseract is a wrapper for Google’s Tesseract-OCR Engine. It is also useful as a stand-alone invocation script to tesseract, as it can read all image types supported by the Pillow and Leptonica imaging libraries, including jpeg, png, gif, bmp, tiff, and others. Additionally, if used as a script, Python-tesseract will print the recognized text instead of writing it to a file.
Installation: Visit and Install Tesseract; scroll down to find the latest installers for 32-bit and 64-bit systems; download them as needed.
WARNING: Tesseract should be either installed in the directory which is suggested during the installation or in a new directory. The uninstaller removes the whole installation directory. If you installed Tesseract in an existing directory, that directory will be removed with all its subdirectories and files.
The workaround when all directory are removed and you are unable to recognize numpy or any other libraries in Jupyter then you may want to create a new environment using the steps illustrated here:
Ensure you select this new environment in Jupyter to be unblocked and successfully run notebook.
We will now use this to explore an image and convert the content to editable data. We can further choose to use this data for series of operations.
Let’s navigate through various steps involved….
Step 1. Import Modules:
import pytesseract
from PIL import Image
import os
Step 2. Verify the directory of Tesseract and copy the entire path
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r”C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe”
Step 3. First, open the image with the image function, then use pytesseract to get all the image’s data, and store all the text in a variable.
img = Image.open(“About-Book.png”)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(img)

Step 4. Print the text retrieved from the image:
print(text)
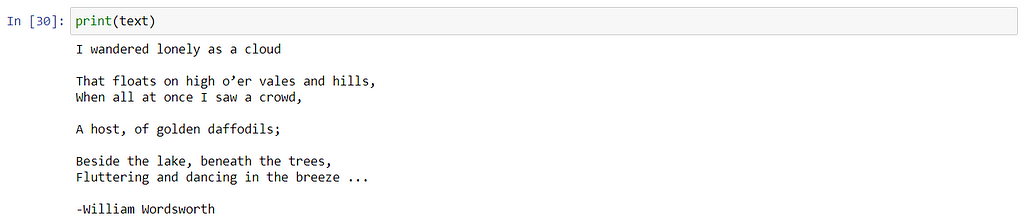
We can see that the words from the image are correctly identified. We can now use this for any useful application. For fun, we will now convert this data into handwriting!
Pywhatkit: It is a library that may be used for a variety of things, including sending WhatsApp messages, watching YouTube videos, searching Google, and writing handwritten text.
pip install pywhatkit
We will use the text _to_handwriting function from pywhatkit to convert text to the specified RGB color; in this case, the RGB for blue is 0, 0, 250.
kit.text_to_handwriting(text, rgb=[0, 0, 250], save_to=”handwriting-eng.jpg”)
The handwriting thus obtained is strikingly realistic!
We can display this in a new window programmatically:
img_out = cv2.imread(“handwriting-eng.jpg”)
cv2.imshow(“Text to Handwriting”, img_out)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

Up next, let us explore a few operations using a language other than English. I will be considering Kannada, one of the Dravidian languages of South India.
Let us check if pytesseract supports other languages. The executable has inbuilt language model for English, Spanish, French but none of Indian languages. In order to be used with other languages, we need to provide langdata and tessdata that provide training data and LSTM Trained Models on OCR Engine for most languages:
https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/langdata
https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tessdata
This GitHub folder contains source training data for Tesseract for lots of languages.
Copy the langdata and tessdata folders to C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR
The steps to read Kannada text in image and capturing the texts in string:
Step 1. Install the modules
import pytesseract
from PIL import Image
import os
import cv2
Step 2. Verify the directory of Tesseract and copy the entire path
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r”C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe”
Step 3. First, open the image with the image function, then use pytesseract to get all the image’s data, and store all the text in a variable.
img = Image.open(“Kannada.png”)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(img)

Step 4. Print the text retrieved from the image:
print(text)

We are now able to display all the text in Kannada!
Its time to make tasks with this content. I chose to do the following 2 operations:
· Transliteration of Kannada to English (Latin) ISO 15919 with om_transliterator in Python.
· Read the Kannada text aloud through Python using gTTS package.
Transliteration: Romanization is simply the conversion of writing from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script. In our case, from Kannada to Roman. Over the period, multiple systems and standards like Hunterian transliteration, ITRANS, IAST, ISO 15919 (2001), etc have evolved to Romanize Indic scripts.
For this transliteration exercise, I will use “om-transliterator” by this talented contributor.
https://pypi.org/project/om-transliterator/
Installation: pip install om-transliterator
Code to display the text:
from om_transliterator import Transliterator
transliterator = Transliterator()
transliterated_text = transliterator.knda_to_latn(text)
Watch the transliteration now!
print(transliterated_text)
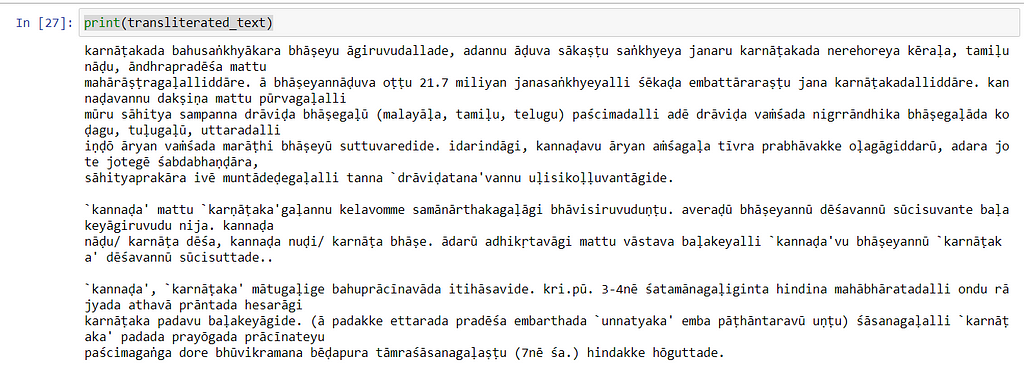
Up next, let us read the content out loud! Let’s make Python speak for us!
Python provides hundreds of thousands of packages that allow developers to write pretty much any types of program. Two cross-platform packages you can use to convert text into speech using Python are PyTTSx3 and gTTS.
We will use gTTS for our experiment: https://pypi.org/project/gTTS/
pip install pyttsx3
Code:
from gtts import gTTS
from playsound import playsound
language=’kn’
myobj=gTTS(text=text,lang=language,slow=True)
myobj.save(“About-kannada.mp3”)
The mp3 file is stored in your directory. This was fun exercise!

Now let us also learn about commercially available easy-to-use and handy OCR tools. The popular SaaS tools are:
1. IBM Datacap — Datacap streamlines the capture, recognition and classification of business documents to extract important information from them. Datacap has a strong OCR engine, multiple functions as well as customisable rules. It works across multiple channels, including scanners, mobile devices, multifunction peripherals and fax.
2. Google Document AI — One of the solutions in the Google Cloud AI suite, the Document AI (DocAI) is a document processing console that uses machine learning to automatically classify, extract, enrich data and unlock insights within documents.
3. AWS Textract — AWS Textract automatically extracts text and other data from scanned documents using machine learning and OCR. It is also used to identify, understand, and extract data from forms and tables. For more information check out this detailed breakdown of AWS Textract.
4. Adobe Acrobat DC — Adobe provides a comprehensive PDF editor with an in-built OCR functionality.
5. OCR Using Microsoft OneNote — Microsoft OneNote is predominantly a note keeper that can also double as an OCR. It offers a simple and easy method for Optical Character Recognition with a slight limitation that it does not support table and columns.
OCR With Google Docs — You can convert image files to text with Google Drive.
Conclusion:
With the demo using Python and pytesseract packages, we have seem major leap in Image to text conversion. Thus, the latest OCR Packages and SaaS tools help businesses save time and resources that would otherwise be spent on data entry & manual verification. With OCR, the entire process of data conversion from original paper document, image or PDF takes less than few minutes, and the final recognized document looks just like the original!
Additional Reading:
Learn about LSTM: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/12/fundamentals-of-deep-learning-introduction-to-lstm/
Learn about pytessaract: https://pypi.org/project/pytesseract/
The What, Why and How of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. It’s free, we don’t spam, and we never share your email address. Keep up to date with the latest work in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.












