
Introduction to Machine Learning: Exploring Its Many Forms
Last Updated on November 5, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): RaviTeja G
Originally published on Towards AI.

These days, Machine Learning is everywhere, right? If you are here, You might have gotten curious as to what exactly machine learning is! So, Let me explain it in simple terms for you, At a high level, machine learning is all about teaching computers to make smart choices by showing them lots of examples and letting them learn from the data. Let’s Discuss more about it, and here’s what lies ahead!
Table Of Contents
- How Machine Learning Works
∘ Applications of Machine Learning - Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Machine Learning
∘ Types of Supervised Learning
∘ Regression
∘ Classification - Unsupervised Machine Learning
∘ Types of Unsupervised Learning
∘ Clustering Algorithms
∘ Dimensionality Reduction
∘ Anomaly Detection
∘ Association Rule Learning
∘ Autoencoders - Semi-Supervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
∘ Conclusion
∘ Announcement #100daysMLDL
How Machine Learning Works
what happens in machine learning is basically that we have a piece of code ( which is referred to as an algorithm ) to find patterns in the data by analyzing a lot of previous data available ( this process is called Training). Say, an adult person’s height and his/her father’s height have a pattern of, Father Height=m*(person height)+c.
Based on the patterns observed, the algorithm will create a mathematical equation by adjusting the parameters( here m, c) and finding the best parameters that can give an accurate match of the data (here it finds the best values for the parameters m and c, that can represent the data), which is referred to as a Model ( say, Father Height=1*Person Height+0.5). well, it’s not always an equation, but to simplify our understanding, we can consider it this way.
Now with the model we have, If someone says their height, we can predict their father's height with the model we have ( the equation ), right? Don’t fight with me if this doesn’t give the correct prediction for your height and your father's height! The values are dummies!!
But there is a sea of algorithms out there, So In Machine learning, we study these algorithms to find the best algorithm that could make accurate predictions with your new data.
Applications of Machine Learning
Let’s accept it, Machine Learning is all around us, making our lives easier and more convenient. Here are a few examples.
1. Recommender Systems: Imagine you’re on a streaming platform: You’ve watched a few science fiction movies, and suddenly it suggests more sci-fi films. That’s machine learning at work! It analyzes your past choices and those of other viewers to recommend content you’ll enjoy.
2. Virtual Personal Assistants: Think about Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant: They understand your voice commands and provide helpful responses. Machine learning algorithms enable them to recognize speech patterns and improve their understanding of your voice over time.
3. Self-Driving Cars: Picture a car that drives itself: Self-driving cars use machine learning to interpret data from sensors and cameras, helping them make decisions like when to stop, go, or change lanes. They learn to navigate safely by observing real-world traffic.
4. Fraud Detection: When your bank detects unusual activity on your account: And again, Machine learning algorithms are at work. They analyze your spending patterns and flag transactions that deviate from the norm, protecting you from fraudulent activities.
5. Medical Diagnostics: When doctors use AI to detect diseases: Machine learning assists in analyzing medical images, like X-rays and MRI scans, to identify abnormalities early. It can also help predict patient outcomes based on historical data.
These applications are just the tip of the iceberg and the possibilities of Machine Learning are endless in various fields, and it also feels magical when you predict new data, right?
Types of Machine Learning
we know that it’s mostly about finding the best algorithm for our data, now It’s time to explore various categories of algorithms, their purpose, and a few applications. Broadly they are classified into 4 categories: Supervised, Unsupervised, Semi-Supervised, and Reinforcement Learning. Let’s understand them in detail.
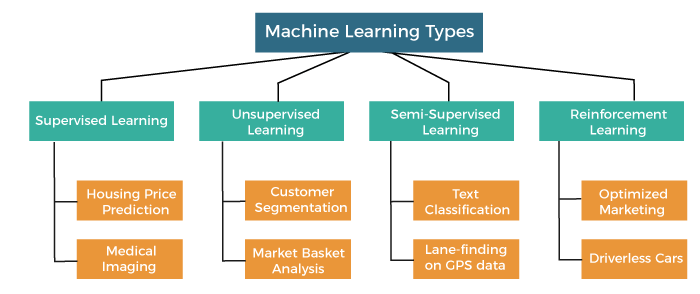
1. Supervised Machine Learning
This is the most popular for performing machine learning operations. It is used for the data where there is a precise mapping between the input and output data. Say, this shapeU+1F34E, we have a precise label for this as “Apple”. We show a few of these to the algorithm ( through code ), and the next time you show that shape, it will be predicted as an apple.

Given data in the form of examples with labels, we can send these to the algorithm, and over time the algorithm will find the approximate pattern between the examples and their labels. Once it’s fully trained, we can send the new data to the generated model and it will make a prediction.
These supervised algorithms are called ‘Task-Oriented’. As we provide it with more data, it will be able to learn more properly to make better predictions.
Few applications:
1. Face Recognition
2. Voice Recognition
3. Spam Classification
And many more…
Types of Supervised Learning
Broadly we can classify supervised learning into 2 categories
1. Regression
2. Classification
Regression
To put it simply, Regression algorithms predict the continuous variable( integer/float) based on the input variables. The example used at the start of this article can be taken as a supervised regression algorithm, which predicts the father's height based on an adult person's height. Because the height we are predicting will be a continuous variable (float).
Algorithms under Regression
- Linear Regression
- Polynomial Regression
- Lasso Regression
- Ridge Regression
- Exponential Regression
- Logarithmic Regression
Few Applications
- Student Score prediction based on the previous test scores.
- House price prediction based on the room size, locality, etc.
Classification
We use classification algorithms to predict the categories, but not the continuous variable. Say, You want to specify whether the email is spam or not, here, the prediction variable is not a number, it’s just a yes or no — category.
Algorithms under Classification
- Logistic Regression
- K-Nearest Neighbours
- Decision Trees
- Random Forest
- Support Vector Machine
- Naive Bayes
- Ada-Boost
- XG Boost
- Gradient Boosting
Few Applications
- Email Spam Detection based on the previous email data.
- Image Classification of identifying between cat and dog.
2. Unsupervised Machine Learning
As the name suggests, we can see it as the opposite of supervised machine learning. In supervised, we have an input and output label, whereas in unsupervised, there is input data, but the data is not explicitly labeled!! These algorithms are able to learn from the data by finding implicit patterns.
Take an example of showing different fruits from a basket to the algorithm, and based on the shape, size, and colors, it will separate these into different groups, and when you show a new fruit, then it will make the prediction of group.
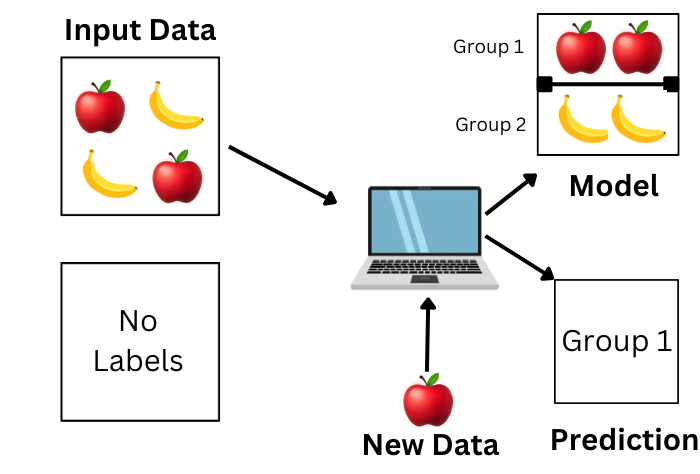
Unsupervised algorithms identify the data based on various factors such as their density, structures, similar segments, and other similar features.
Few Applications
1. Recommendation Systems
2. Customer Behaviour Analysis
3. Grouping News Articles
And many more…
Types of Unsupervised Learning
Broadly we can classify them into 5 categories such as
- Clustering Algorithms
- Dimensionality Reduction
- Anomaly Detection
- Association Rule Learning
- Autoencoders
Let’s understand these categories' purpose and explore the algorithms that come under these categories.
Clustering Algorithms
Clustering is a technique of grouping similar sets of objects in the same group that are different from the objects in the other group based on the similarities. Like the above basket of fruits segmentation.
Algorithms under Clustering
- K-Means
- DBSCAN
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Mean Shift
Dimensionality Reduction
Dimensionality reduction is like simplifying a complex problem by focusing on its most important aspects. It’s a technique that reduces the number of features (dimensions) in a dataset while retaining its essential information. This simplification makes data analysis more efficient and easier to visualize.
Algorithms under DR
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding(t-SNE)
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is like finding the odd one out in a group. It’s a technique used in data analysis to identify unusual or rare data points that don’t conform to the expected patterns, basically the outliers. This is valuable for detecting anomalies in various fields, from fraud detection in financial transactions to identifying equipment malfunctions in industrial systems. Train a model on only one class if anything lies outside of this class, it may be an anomaly.
Algorithms under Anomaly Detection
- One class K-Means
- One class SVM
- Isolation Forest
Association Rule Learning
Association rule learning is like finding interesting connections between things people buy at a store. It’s a machine learning technique that uncovers relationships in data, helping to identify patterns, trends, and associations between items or events. Association rule learning is a valuable tool in understanding consumer behavior, optimizing inventory, and enhancing personalized recommendations.
Algorithms under AR
- Apriori
- FP-Growth ( Frequent Pattern Growth)
- Eclat Algorithm
Autoencoders
They’re a type of neural network that takes complex data, compresses the data into a code, and then tries to recreate the input data from a summarized code. This compression-decompression process can be used to remove noise from visual data like images, video, and medical scans to improve the quality.
3. Semi-Supervised Learning
Semi-supervised learning is, for the most part, just what it sounds like, a training dataset with both labeled and unlabeled datasets. This method is particularly useful when extracting relevant features from the data is difficult, and labeling all the examples is time-intensive!
A Popular training method that starts with a fairly small set of labeled data is using General Adversarial Networks(GANs), like two deep learning networks in the competition, each trying to outsmart the other!
One of the networks, called a generator, tries to create new data points that mimic the training data. The other network, the discriminator, pulls in the newly generated data and evaluates whether they are part of the training data or fake.
The networks improve in a positive feedback loop as the discriminator gets better at separating the fakes from the originals, and the generator improves its ability to create convincing fakes.
Eg: Medical Images like CT scans or MRIs.
4. Reinforcement Learning
It’s an approach where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment. The agent takes actions, receives feedback in the form of rewards or punishments, and adjusts its behavior to maximize long-term rewards. It’s often used in robotics, game-playing, and autonomous systems, just like the trial and error method.
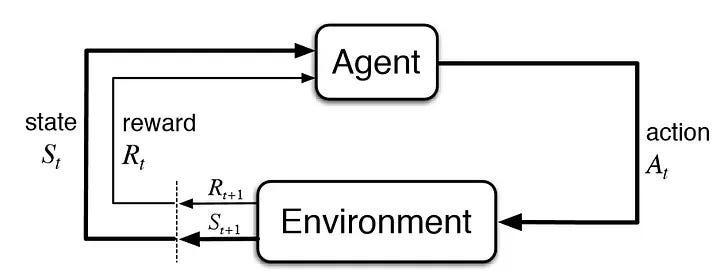
The overall aim is to predict the best next step to earn the biggest final reward. If we take the game of chess, each action can be each move, and the state will be the current situation of the game, the rewards in the middle of the steps can be the opponent pieces it captures. The biggest final reward is to win the game. so, it learns everything through experience.
Conclusion
I hope you got the clarity of what is machine learning, and understood that supervised learning is where the data with labels is given, and unsupervised is where the data without any particular labels is given to the algorithm, While semi-supervised is about half labeled and other without labels, and Reinforcement learning is totally magic, where it learns everything on trail and error, beautiful I must say!!
This is the basic knowledge you need to know about machine learning before you dive deep into learning these algorithms. Learning the algorithms in detail is crucial in data science, I myself have been on this incredible journey, and in the upcoming days, I will be posting in detail intuition for these algorithms. Follow me for more and Subscribe to not miss any exciting data science articles!
If you are interested in Pandas, Numpy, Matplolib, Seaborn, and Plotly, then look no further, I also have detailed articles on these essential libraries for Data Science, Here’s a curated List.

Detailed Guides for all the Essential Data Science Libraries
View list8 stories


Announcement #100daysMLDL
Day 18/100 — Introduction to Machine Learning.
Simply head over to my GitHub repository for direct access to all the code and resources. Here’s a Repo Link to the challenge. I invite you all to join me on this exhilarating journey! Whether you’re a fellow data enthusiast or just curious about the world of machine learning, there’s something here for everyone. Let’s learn, grow, and inspire each other. Thank you for reading, Happy learning, and Have a good day 🙂
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI














