Causal Inference with Machine Learning: Why It Matters in Business Decision-Making
Last Updated on September 27, 2024 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Hajime Takeda
Originally published on Towards AI.
Understanding Traditional Approaches and the Rise of Causal Machine Learning
TL; DR: Causal inference has traditionally been used in fields such as economics, health studies, and social sciences. In recent years, algorithms combining causal inference and machine learning have been a hot topic. This article explains why causal inference is necessary, with a focus on practical business use cases, and discusses both traditional causal inference and causal inference with machine learning.
1. Business Context — Typical Scenario
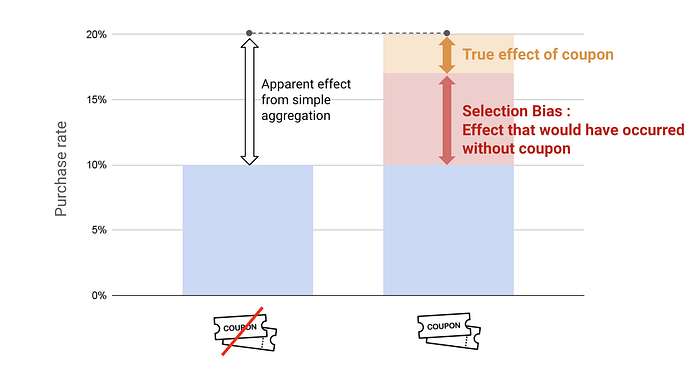
Let’s consider a typical situation that many data scientists face in business. Imagine you’re assisting a colleague from the marketing team, and they say:
“The marketing team sent coupons to some users, and their purchase rate was twice as high as those who didn’t receive them. So, the coupons must have doubled the purchase rate!”

Would you agree with this conclusion? At first glance, you might be inclined to agree. But wait, what if you knew this information:
But wait, what if you knew this information:
Now, this new information raises a red flag. So, what’s the potential issue here?
2. Pitfall : Selection Bias
The key question is: What is the true impact of the coupons? If we distribute coupons based on certain intentional criteria, we can’t make a fair comparison between purchase rates. Why? Because the customers who received the coupons might have made a purchase regardless — they’re already more engaged. They could be influenced by other factors like newsletters or social media, and these factors introduce what’s known as selection bias.
💡 Selection Bias: The distortion of a causal effect due to non-random assignment of participants, which leads to comparing groups that are not truly comparable.
3. What is Causal Inference?
Causal inference is about figuring out if there’s a cause-and-effect relationship between a specific action (the “treatment”) and its result (the “outcome”). Traditionally, it has been a cornerstone in fields like healthcare. For example, one common use case is assessing whether a new medication effectively treats a disease. In this context, administering the medication is the “treatment,” and the patient’s recovery is the “outcome.”
But causal inference isn’t just for healthcare. In e-commerce or marketing, “treatments” might include actions like sending coupons, running advertisements, or sending direct mail campaigns.

4. What is the challenge?
The main challenge in causal inference is that we can only observe one outcome for each individual. If we had a time machine, we could give a customer a coupon, then rewind time and see what happens if we didn’t give them the coupon. Unfortunately, in the real world, we can’t do this — we can only observe one scenario for the same person.
This is where causal inference steps in: it allows us to estimate the outcome that didn’t happen, known as the “counterfactual.”
💡Counterfactual: The hypothetical outcome that we cannot observe for the same individual.

5. Why Not Just Do an A/B Testing?
You might wonder, “Why not just run an A/B test?”
Great question! In the world of causal inference, A/B testing is known as a Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT), often considered the “gold standard” for answering causal questions. Here’s how it works:
First, you randomly divide your customers into two groups: the “treatment group” and the “control group.” The treatment group receives the coupon, and let’s say their purchase rate ends up at 40%. The control group doesn’t receive the coupon, and their purchase rate is 20%. The difference between these two rates — 20 percentage points — represents the effect of the coupon.
The critical point in an RCT is randomization. By randomly assigning customers to the two groups, we ensure that any other factors (like customer preferences or behavior) are balanced across both groups, which helps eliminate bias.
💡 Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT): An experimental method where participants are randomly assigned to groups to test the effect of an intervention.

6. Limitations of RCT
So, if we understand RCTs, does that mean they’re always the perfect solution? Unfortunately, no. While RCTs are praised for their simplicity and robustness, there are many situations where RCTs just aren’t feasible.
1. Opportunity Loss
Imagine running an RCT where half of your customers don’t receive the new product or offer you’re testing. This could mean missing out on potential sales and growth — an “opportunity loss” that businesses can’t always afford.
2. Time Constraints
RCTs can be time-consuming. They often require weeks or even months to gather enough data to draw reliable conclusions. That delay can mean missing the market window or losing a competitive edge. Time is money, after all!
3. Difficulties with External Stakeholders
RCTs become even more complex when multiple stakeholders are involved. Not every client or partner has the resources or ability to execute an RCT effectively.
But it’s not just in business where RCTs face limitations. In healthcare, it’s simply unethical to assign patients with life-threatening conditions to a control group and provide them with a placebo instead of potentially life-saving treatment.
That’s where causal inference comes in — providing a way to measure reliable causal effects when RCTs aren’t an option.
But even causal inference has its challenges…
7. Simpson’s Paradox — Challenges of Observed Data
When RCTs aren’t an option, we often turn to observed data. But interpreting this data isn’t always straightforward. Let’s look at an example from Judea Pearl’s famous book, “The Book of Why.”
Imagine a graph with exercise amount on the x-axis and cholesterol levels on the y-axis. At first glance, the data seems to show that people who exercise more actually have higher cholesterol levels. But hold on — that doesn’t make sense!
What’s missing? Age.
When we break down the data by age groups, a different story emerges: within each age group, those who exercise more tend to have lower cholesterol levels. This discrepancy is known as Simpson’s Paradox — where an overall trend seems to contradict the patterns seen within individual subgroups.
💡 Simpson’s Paradox: A phenomenon where a trend appears in different groups of data but reverses or disappears when these groups are combined.

8. Confounding variable
In this example, age is a confounding variable — one that influences both exercise levels and cholesterol. Failing to account for such confounders can lead to misleading conclusions. That’s why, in causal inference, identifying and controlling for these variables is crucial.
So, how can we navigate these complexities? Enter Causal Machine Learning.
💡 Confounding Variable: A hidden factor that affects both the cause and effect, distorting the true relationship.
9. A Brief History of Causal Machine Learning
So, how can we navigate these complexities? Enter Causal Machine Learning.
The groundwork for causal inference was laid between the 1970s and 1990s by pioneers like Judea Pearl and Donald Rubin. Fast forward to around 2010, and we began to see the fusion of these concepts with machine learning. By 2019, user-friendly libraries like CausalML and EconML were introduced, making these methods more accessible to practitioners.

So, what sets causal machine learning apart? Unlike traditional causal inference, it can handle more complex, high-dimensional data at the individual level, making it highly valuable in today’s data-rich environments.

10. Causal Inference vs. Traditional Machine Learning
You might be asking, “Why use causal machine learning instead of standard machine learning?” Great question!
Traditional Machine Learning is all about prediction based on correlation. It answers questions like, “What will the customer buy next?” and “What’s the probability?” It’s focused on forecasting outcomes using patterns in the data.
Causal Machine Learning, on the other hand, digs deeper to uncover cause-and-effect relationships. It helps answer questions like, “Did the coupon actually have an impact?” and “How significant was that impact?” This is crucial for understanding the true effectiveness of interventions.

Accordingly, the way variables are treated is different. In traditional machine learning, something like “coupon availability” is just one of the features (X) in the dataset. But in causal machine learning, “coupon availability” is considered a treatment variable. This distinction is important because the main goal is to determine how this treatment variable affects the outcome.
💡 Treatment Variable: The factor or intervention being tested to determine its effect on an outcome.
11. Conclusion
- Causal Machine Learning combines causal inference with machine learning to identify true cause-and-effect relationships in complex, high-dimensional data, going beyond traditional correlation-based predictions.
- Limitations of RCTs: While RCTs are considered the gold standard for causal analysis, they often face practical and ethical challenges, making them unsuitable in many real-world scenarios.
- The Importance of Addressing Confounding Variables: Understanding phenomena like Simpson’s Paradox emphasizes the need to control for confounding variables to avoid misleading conclusions when using observed data.
12. Reference
- The Book of Why: https://www.amazon.com/Book-Why-Science-Cause-Effect/dp/046509760X
- Causal Inference and Discovery in Python: https://www.amazon.com/Causal-Inference-Discovery-Python-learning/dp/1804612987
- YouTube (PyData London 2024) : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GH7xOPCIfIQ
Thank you for reading! If you have any questions/suggestions, feel free to contact me on Linkedin! Also, I would be happy if you follow me on medium.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














