
Hosting FastAPI with Saturn Cloud Deployments
Last Updated on November 18, 2021 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Sayar Banerjee
Originally published on Towards AI the World’s Leading AI and Technology News and Media Company. If you are building an AI-related product or service, we invite you to consider becoming an AI sponsor. At Towards AI, we help scale AI and technology startups. Let us help you unleash your technology to the masses.
Hosting FastAPI with Saturn Cloud Deployments

Hi all, this article will explore the process of deploying a FastAPI application on Saturn Cloud. FastAPI is a robust web framework for building APIs with the Python language. Saturn Cloud is a platform dedicated to scaling Machine Learning and Big Data pipelines and more.
The model will predict median house prices in California. Let's jump right into it.
Resources
👉 FastAPI
👉 Joblib
Data Exploration
The dataset I will use for training our machine learning model is called "California Housing Prices." It can be found here.
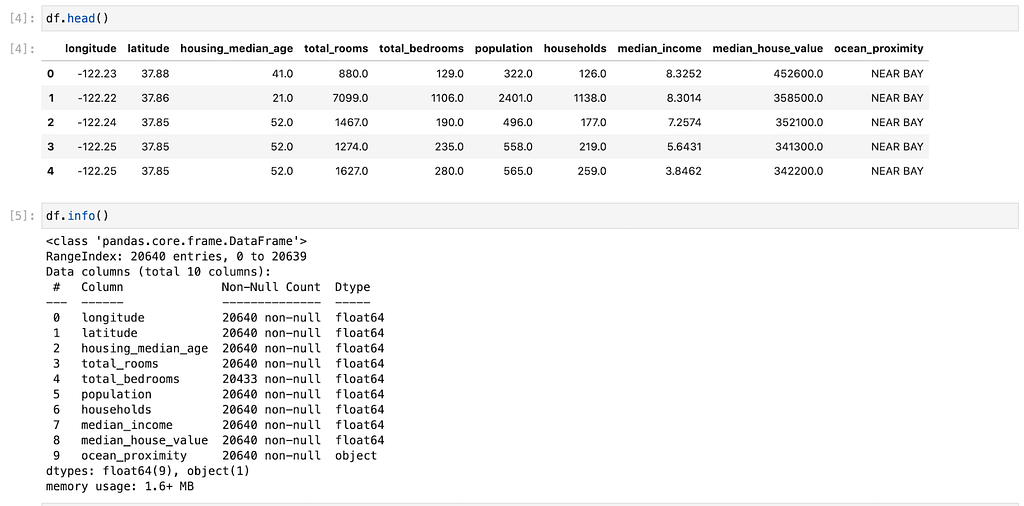
The contents of our data are as follows:
The data pertains to the houses found in a given California district and some summary stats about them based on the 1990 census data. Be warned, the data isn't clean, so there are some preprocessing steps required! The columns are as follows, and their names are pretty self-explanatory:
- longitude
- latitude
- housing_median_age
- total_rooms
- total_bedrooms
- population
- households
- median_income
- median_house_ value
- ocean_proximity
On doing a rudimentary exploration of the dataset, I found the following:
A correlation plot between all the numerical features shows us the following:
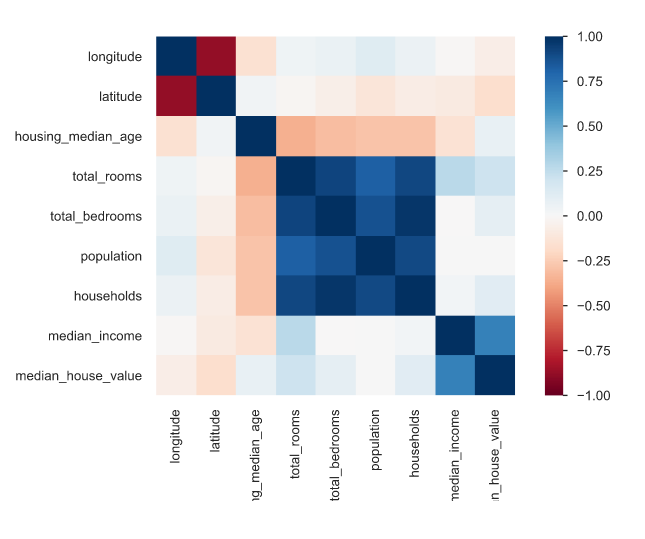
According to the graph, most numerical features have very little correlation with median_house_value except median_income, which seems to have a strong positive correlation of around 0.68.
Data Cleaning/Feature Engineering
Since the total_bedrooms feature had missing values, I had to impute it. For simplicity, I chose the median as the metric to impute the feature.
Additionally, two new features were engineered, namely, "rooms_per_households" and "population_per_household."
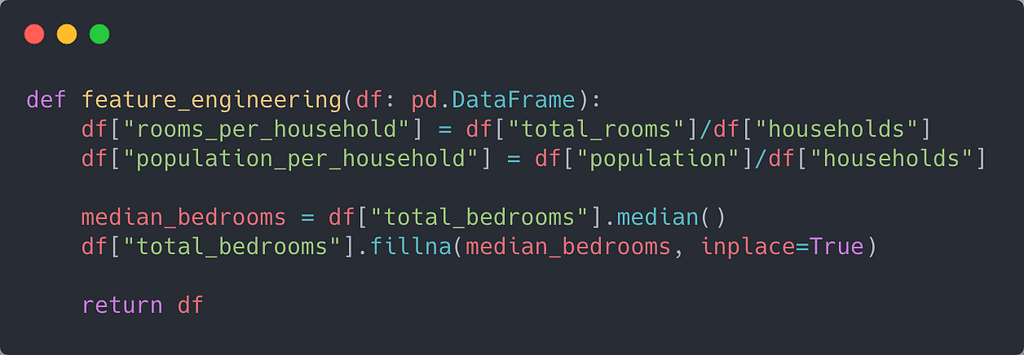
Training the Model
Our repository looks like this:
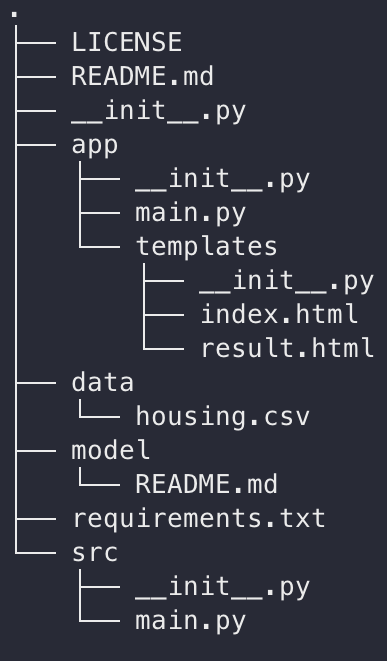
The requirements.txt file contains our dependencies. It is crucial to have all the dependencies added to this file as it will be used during our deployment.
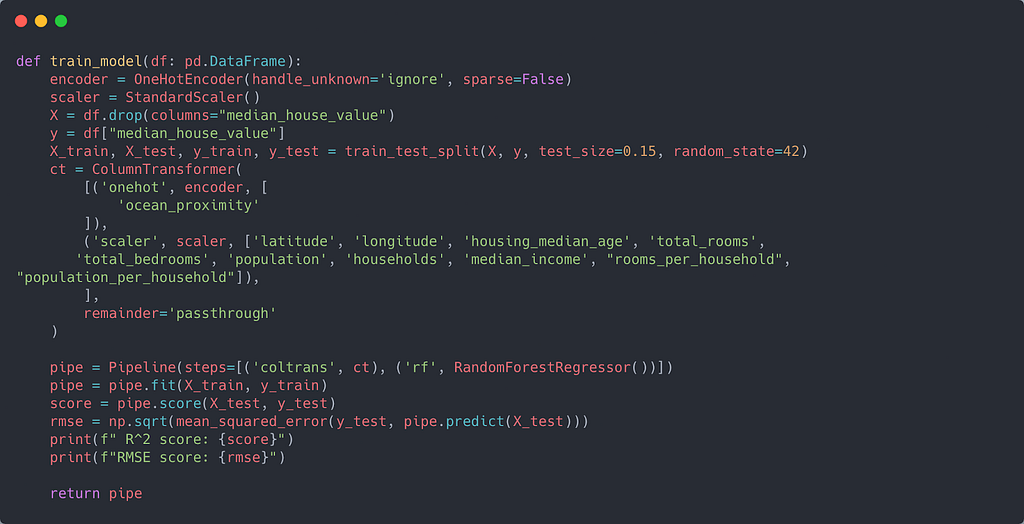
The file src/main.py contains our training script. Let us take a look at some of the essential functions in the script.
Our training model pipeline is relatively standard. There is just one categorical column (ocean_proximity). For the other numerical columns, I applied a standard scaler. The ColumnTransformer estimator helps to facilitate feature transformations on heterogeneous data.
As for the model, I chose the Random Forest algorithm. I created the pipeline using scikit-learn's Pipeline class.
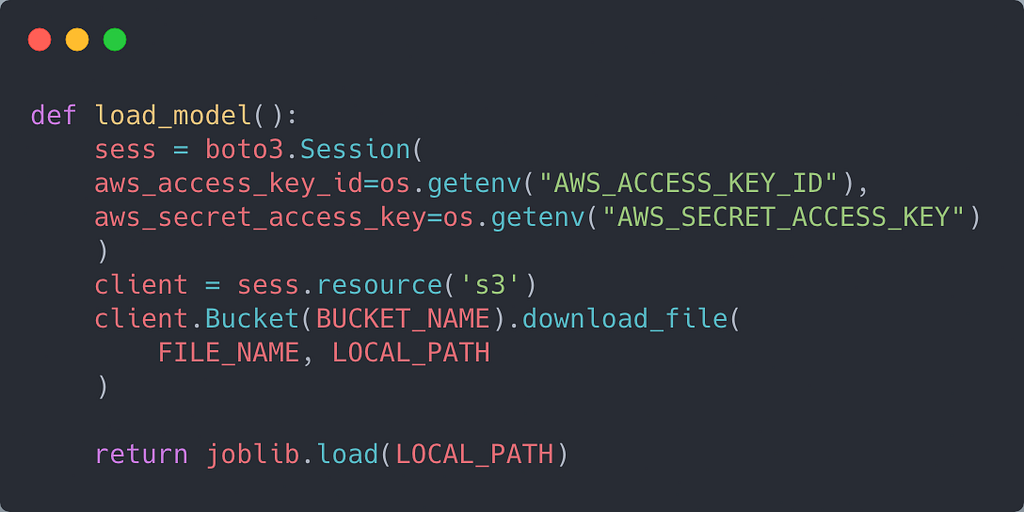
I used joblib to save our model. Since the model file was quite large (>100Mb), I decided to store it in AWS S3. The model's R² score was around 0.81, and the RMSE was around 49k.
Setting up FastAPI Server and Frontend
As you may have guessed, app/main.py contains our code for the server. Since the model is stored in AWS, I used boto3 to download a local copy to the server.
If your bucket and file are private, you may need to set up authentication to access it on Saturn Cloud. You can do it by following this guide.
I wrote a simple function to load our model from AWS:
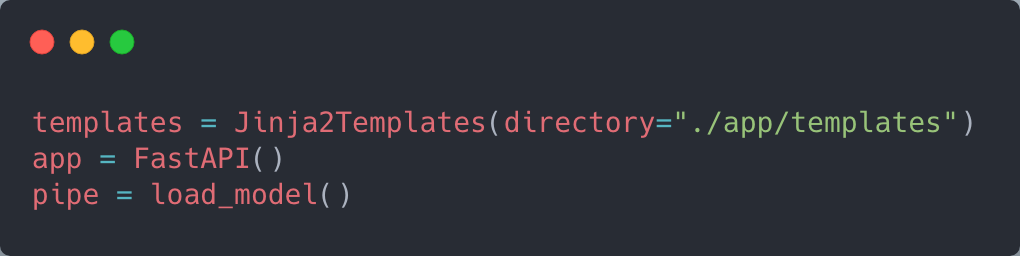
The variables BUCKET_NAME and FILE_NAME are self-explanatory. LOCAL_PATH is the path to where the model will be copied locally.
I also defined global variables for the app, model, and templates.
Homepage
Since I'm creating an application, it's essential to have a homepage to serve as an interface for the model server.
I created a homepage for the app so that users can enter values for each of the features. To render the page, I used Jinja2Templates, which is provided out of the box by FastAPI templates.TemplateResponse renders our landing page titled "index.html."

index.html contains a form that will serve as the frontend for our application. The body of the page looks like this:
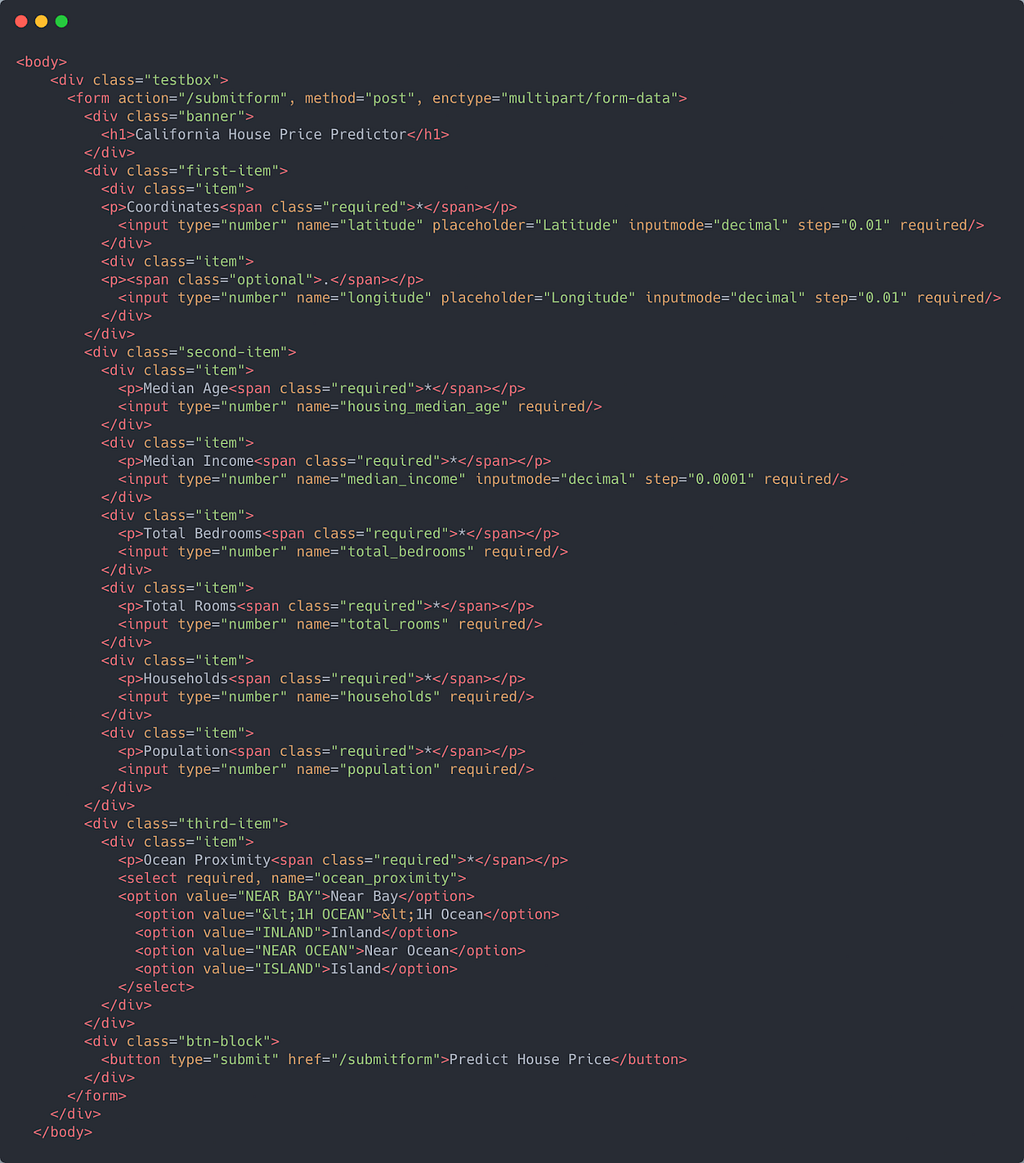
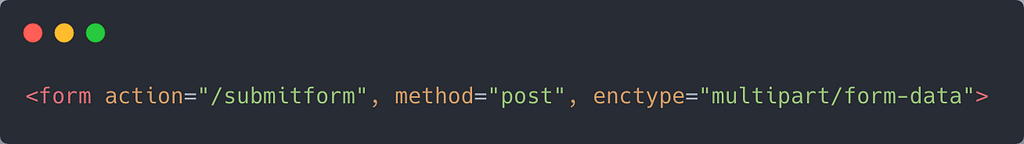
If you look closely at the form tag, you will see that the action attribute is set to "/submitform" and the request method is a POST request.
Our FastAPI server needs to have a method that handles the form data. This method needs to be decorated by app.post("/submitform") to handle the request appropriately.
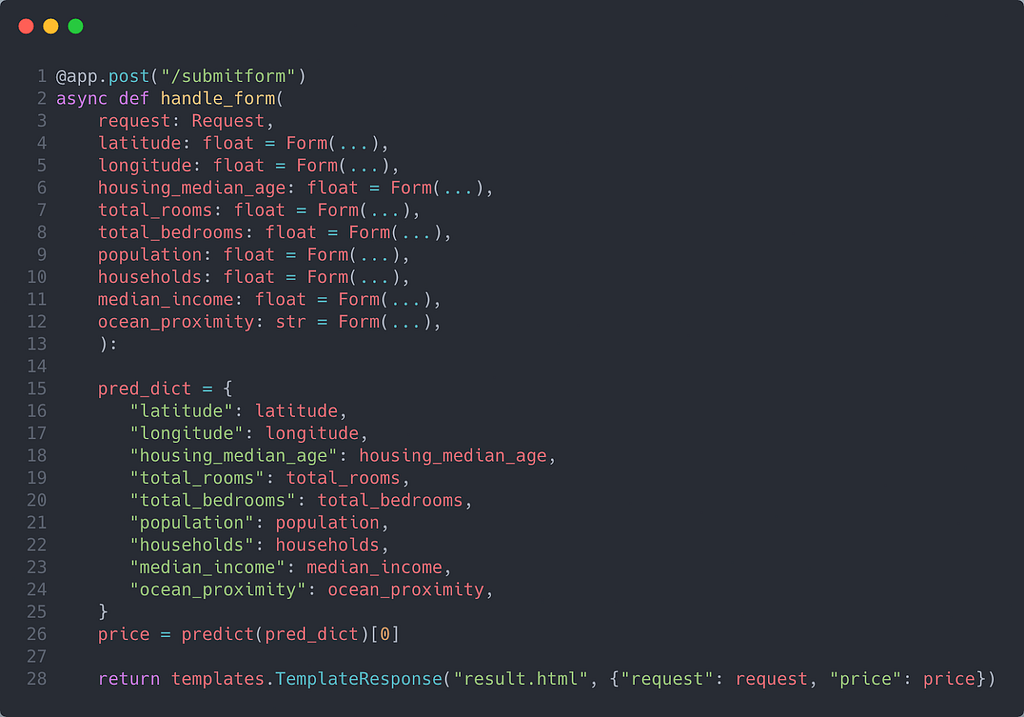
You will notice that each of the variables is set as form parameters using Form. This class tells FastAPI that each variable's input is being received from a form.
You will also notice that line 26 has a method called predict. This method is actually where the model pipeline is fed the input from the form using the appropriate format. Since the pipeline can only receive input from a data frame, I first convert the data into a data frame. I then created the features as part of the feature engineering process. Finally, I return the model's predictions.

Once I had the price prediction, I used templates.TemplateResponse again to return a page called result.html. Along with "request", I also passed "price" through the TemplateResponse method. Finally, I rendered the price on the body of result.html.

Deploying to Saturn Cloud
Before setting up the deployment, I pushed all of the code to Github. To deploy it, you must have your repository connected to Saturn Cloud. To do so, you can follow this guide.
Once your repo is connected, head over to resources and select "New Deployment".
After this, you will be greeted with a form:
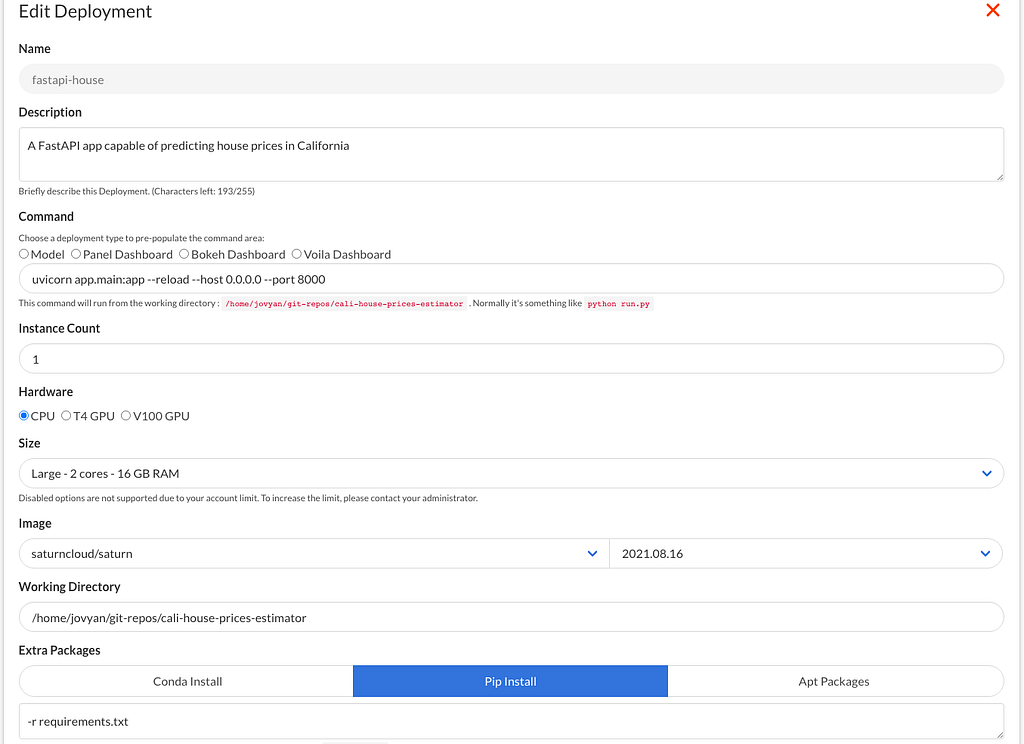
There are a few things to note when filling out the form. For instance, the "Command" is what the deployment will run to start your application.
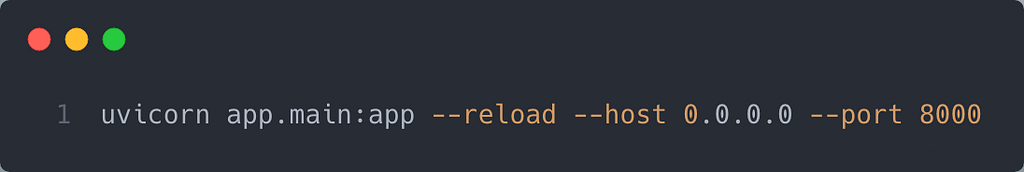
Note that Saturn Cloud requires your applications to listen using port 8000.
Also, note the Extra Packages header. This is the script that will be used to install additional packages before the command is run. Since Saturn Cloud's default image does not have certain libraries like FastAPI and Uvicorn, pass "-r requirements.txt" to the text box.
This ensures that the script "`pip install -r requirements.txt` "is run before startup, containing dependencies for the additional packages.
Note that you can also write the individual names of each package in this section to install them.
Once you hit the Create button, your deployment will be created. Click on it and add your Github repo to the deployment. Ensure that you add the path to the Github resource to your working directory. Once that is done, click the green arrow to start the deployment.
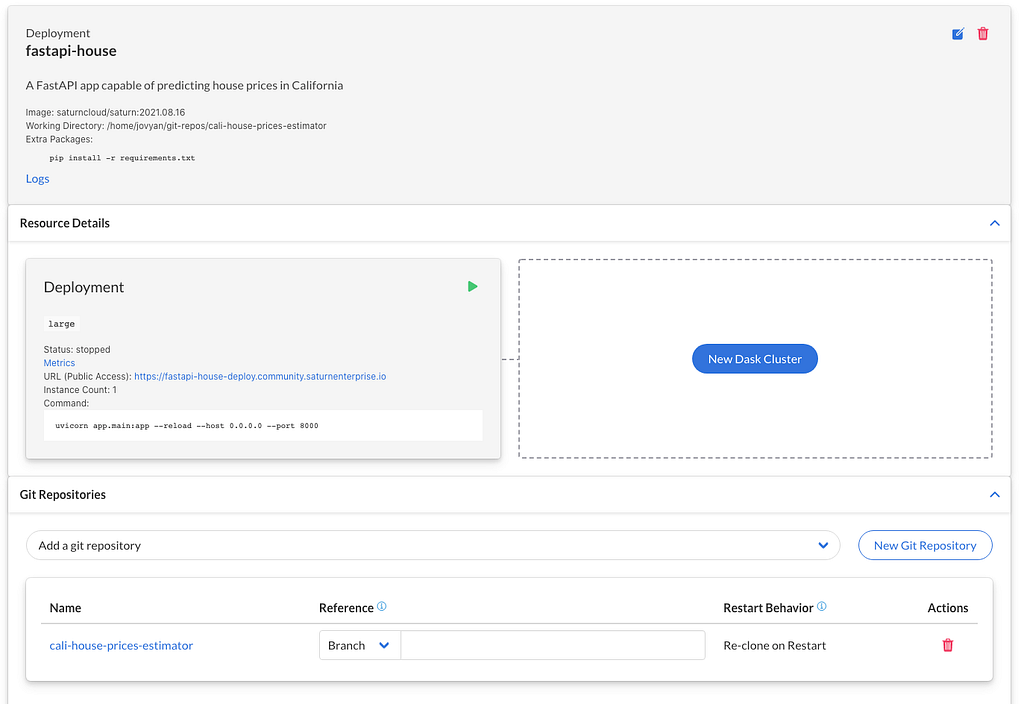
Once your deployment is ready, click on the public URL. You should see a page like this:
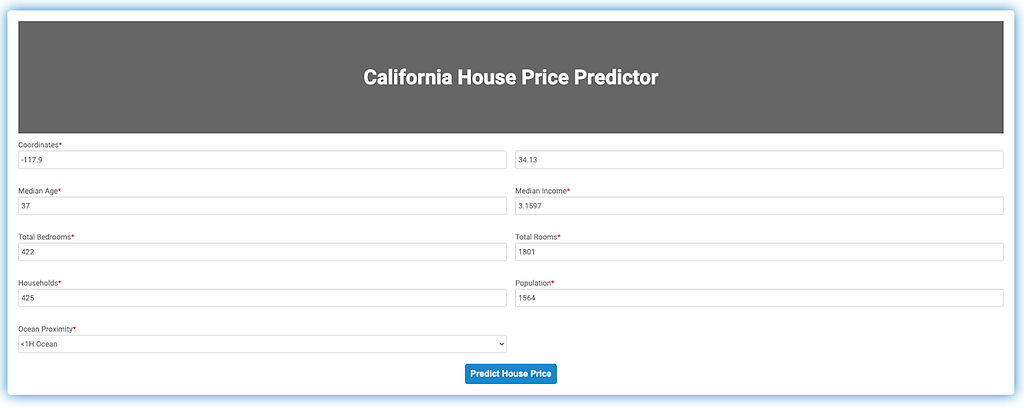
Once you fill out the form, you will see a page with the predicted price:

Note that I used the last example of my test set as input. The actual median house price was $133000, so the model did a reasonably good job! 😀
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully learned how to deploy a FastAPI model on Saturn Cloud! If you're curious about using their environment, they offer 30 free hours a month for data scientists and teams. I hope you enjoyed reading this article. Until next time! ✋
Data Science was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. It’s free, we don’t spam, and we never share your email address. Keep up to date with the latest work in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














