
Data Engineering Using Julia Lang
Last Updated on July 26, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Vivek Chaudhary
Originally published on Towards AI.
The objective of this blog is to understand how to build a Data Engineering pipeline using Julia Lang. There are a lot of blogs on the internet that talk about the theory of DE, and here I am going to talk CODE, less theory more code.

Import necessary libraries and dataset
using CSV
using DataFrames
using Dates#load the datasets into memory
emp_df = CSV.read("D:\\Julia\\emp.csv", DataFrame)print(typeof(emp_df))
#first()to access top 5 records
first(emp_df,5)
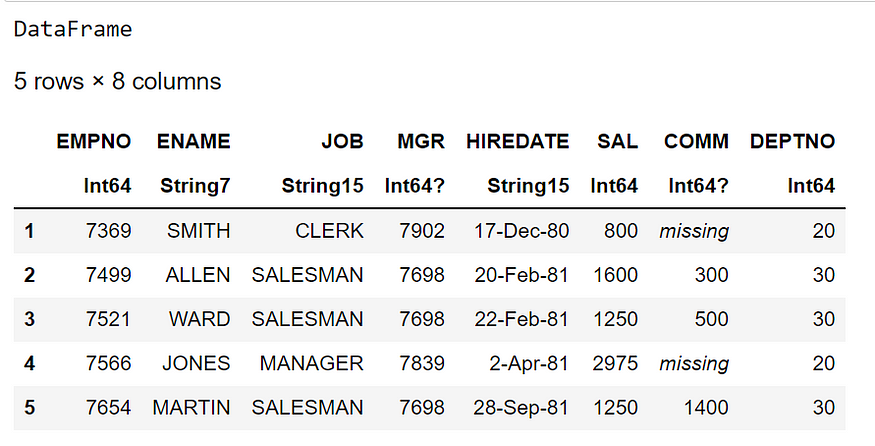
dept_df = CSV.read("D:\\Julia\\dept.csv", DataFrame)
print(typeof(dept_df))
first(dept_df,5)

Data operations
- Filter records
#filter out records for deptno=30
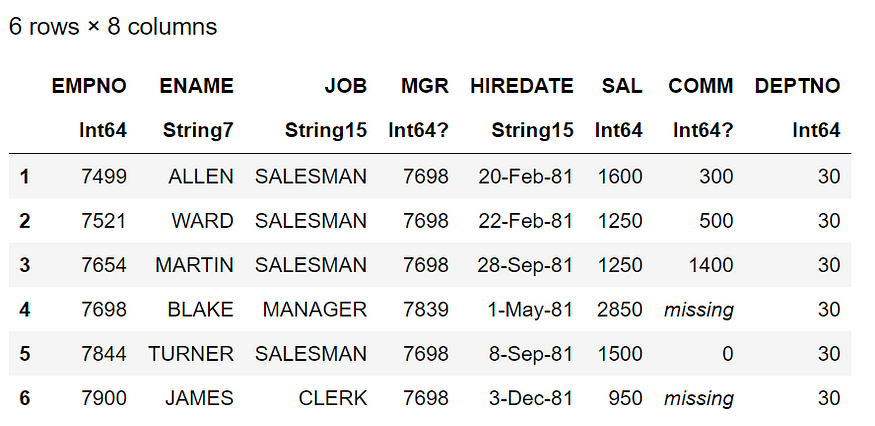
dept30=filter(row ->row[“DEPTNO”] == 30,emp_df)
dept30
#row is a keyword in julia via we can access the column names
#filter multiple conditions
filter(row ->row.SAL> 500 && row.SAL <=1800,emp_df)

2. Sort records
srt_df= sort(emp_df, order(:DEPTNO, rev=false))
first(srt_df,7)

3. Group & Aggregations
#create a seperate small subset for groupby ops
group_df= select(emp_df,”DEPTNO”,”SAL”)
first(group_df,7)

#groupby creates a grouped dataframe other than normal dataframe, somewhat similar to pandas groupby
typeof(gd)#access group information using array indexes
println(gd[1])
println(gd[2])
println(gd[3])

Aggregations
using Statisticsprintln(“sum of sal deptwise “,combine(gd, :SAL => sum))
println(“ — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — “)
println(“avg of sal deptwise “,combine(gd, :SAL => mean))

println(“max of sal deptwise “,combine(gd, :SAL => maximum))
println(“ — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — “)
println(“sum of sal deptwise “,combine(gd, :SAL => minimum))

4. Julia UDFs
#WAF to calculate tax of employees and add Tax as derived column in existing dataframe.
#function is the keyword to write a udffunction taxes(sal)
tax=0
if sal>500 && sal<=1250
tax=sal*.125
elseif sal>1250 && sal<=1750
tax=sal*.175
elseif sal>1750 && sal<=2500
tax=sal*.225
elseif sal>2500
tax=sal*.25
else
tax=0
end
end#create a derived column to add calculated taxesemp_df[!, “Taxes”] = taxes.(emp_df.SAL)
first(emp_df,8)

5. Joins
#merge the emp_df with grouped df
agg_df= innerjoin(emp_df,grp_df, on= :DEPTNO)
first(agg_df,10)

Perform SQL like select on the data frame and write dataset to a CSV file:
CSV.write("D:\\Julia\\empagg_out.csv",
select(agg_df, "EMPNO", "ENAME", "SAL", "COMM", "DEPTNO","Taxes","SAL_sum" => "SalSum"))
Join emp and dept datasets
inner_df= innerjoin(emp_df,dept_df, on= :DEPTNO)
first(inner_df,8)

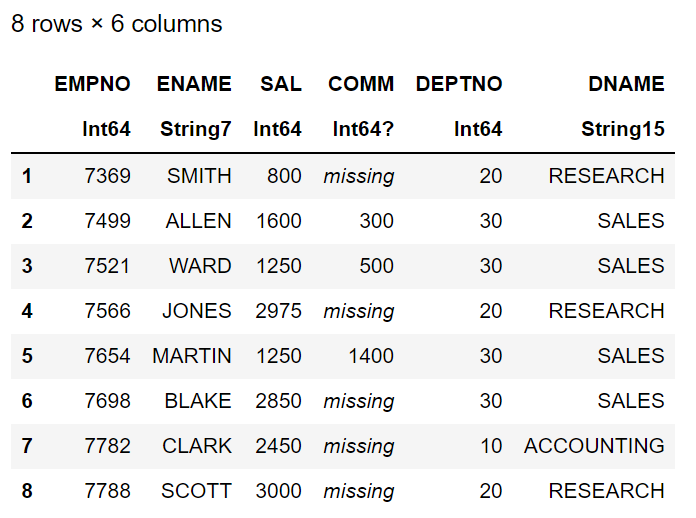
out_df=select(inner_df,”EMPNO”,”ENAME”,”SAL”,”COMM”,”DEPTNO”,”DNAME”)
first(out_df,8)
CSV.write(“D:\\Julia\\empd_out.csv”, out_df)
Summary:
· Read CSV datasets
· Data operations: filter, sort, groupby, aggregations, joins.
· UDFs and derived column.
· Write Julia data frames to CSV files
Thanks to all for reading my blog If you like my content and explanation please follow me on medium and share your feedback, that will always help all of us to enhance our knowledge.
Thanks
Vivek Chaudhary
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














