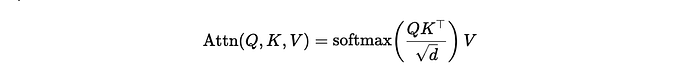TAI #121: Is This the Beginning of AI Starting To Sweep the Nobel Prizes?
Last Updated on October 19, 2024 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Towards AI Editorial Team
Originally published on Towards AI.
What happened this week in AI by Louie
This week, our attention was on the Nobel prizes, where two prizes were awarded explicitly for AI research for the first time. The Physics prize was awarded for foundational work in machine learning and neural network science, while the Chemistry award was for applied uses of AI in chemistry and biology-specific models. However, we are not quite there yet on LLMs competing for the literature prize! The Nobel committee’s decision to award the chemistry prize for AlphaFold was unusually quick for Nobel standards, coming just four years after the model release. Also, on a similar theme this week, discussion in the AI world surrounded Anthropic CEO’s in-depth opinion piece on the potential for radical benefits from AI, particularly in science and medicine.
In Physics, the prize went to Geoffrey Hinton, often called the “Godfather of AI,” and John Hopfield for their foundational work in machine learning using artificial neural networks. Hopfield’s creation of a neural network that stores and reconstructs patterns laid the groundwork for AI’s development in the 1980s, while Hinton’s work on neural networks, including the Boltzmann machine, has been key to modern AI systems such as deep learning. These neural networks, modeled after the human brain, are now integral to technologies ranging from facial recognition to language translation. Hinton, who has been both a pioneer and a critic of AI’s rapid expansion, emphasized the transformative potential of AI but also warned of its risks, including its potential to outsmart humans and disrupt job markets.
In Chemistry, the Nobel Prize was awarded to John Jumper and Demis Hassabis from DeepMind for their work on AlphaFold and to David Baker of the University of Washington for computational protein design. AlphaFold, a deep-learning AI model, has revolutionized biology by predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins with remarkable accuracy. Since its debut in 2020, AlphaFold has transformed the way researchers approach protein structures, providing a tool that accelerates and democratizes access to molecular insights once thought unattainable. By facilitating protein structure prediction from amino acid sequences, AlphaFold has catalyzed new discoveries across biology and medicine, including in drug development and vaccine research. Baker’s contributions to designing entirely new proteins using AI-driven approaches also played a critical role in the field’s evolution, with significant applications ranging from therapeutic enzymes to novel vaccines.
Anthropic’s CEO, Dario Amoedi, explored the transformative potential of AI, arguing that while its risks are significant, its upside is radically underestimated. At the point where “Powerful AI” is fully realized, he argues advancements could compress the next 50–100 years of biological progress into just 5–10 years. This future could see breakthroughs in biology, mental health, economic development, and peace, drastically improving human life. Although risks and challenges are real, the essay focuses on the potential for AI to catalyze widespread positive outcomes, from curing diseases to supporting global governance and human well-being.
Why should you care?
Could this year be just the beginning of AI starting to sweep the Nobel prizes and playing a core role in the majority of scientific advancements? While there are still many limitations on what AI can do on its own, AI tools and capabilities are becoming an increasingly valuable complement to many areas of scientific research. AI’s capacity to analyze massive datasets, identify complex patterns, and generate predictive models is accelerating advancements across various fields. From uncovering new materials with unique properties to better models of proteins and modeling climate change scenarios with unprecedented accuracy, AI is pushing the boundaries of what scientists can achieve.
The potential for AI to contribute to scientific breakthroughs raises important questions about the future of research and innovation. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they might assist in faster and more comprehensive research, data analysis, and experiments, as well as autonomously generate hypotheses and design studies. For the broader public, this evolution means that scientific progress could accelerate, leading to faster development of solutions to pressing global challenges like diseases, environmental degradation, and energy shortages. However, new solutions often also create new problems; hence, time should always be spent trying to ensure the new problems you create are smaller than the ones you are solving! Anticipating the consequences of these new AI capabilities and ensuring these powerful new tools are accessible, transparent, and used responsibly will be crucial.
— Louie Peters — Towards AI Co-founder and CEO
Some key updates from the latest version of Building LLMs for Production:
🔹A new chapter on Indexes, Retrievers, and Data Preparation, focusing on efficiently managing large datasets and retrieving information.
🔹 More examples and real-world applications throughout the chapters to offer a deeper understanding.
🔹 Detailed insights into model distillation techniques, with a case study on Google’s Gemma 2 that explores reducing inference costs and improving latency.
🔹 Expanded coverage of deploying LLMs on cloud platforms like Together AI, Groq, Fireworks AI, and Replicate, offering a wider perspective on scalable solutions.
🔹 A step-by-step guide to building a RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipeline, helping readers implement modern frameworks such as LlamaIndex and LangChain more effectively.
These updates aim to provide a more comprehensive resource for those working with LLMs, particularly around deployment and optimization in real-world contexts.
Get a copy of the updated version from your local Amazon!
Hottest News
1. Scientists Who Built ‘Foundation’ for AI Awarded Nobel Prize
Geoffrey Hinton and John Hopfield were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their foundational work on artificial neural networks, including the Boltzmann machine and Hopfield network. These networks have been pivotal in advancing machine learning applications such as image recognition and pattern generation.
2. Chemistry Nobel Goes to Developers of AlphaFold AI That Predicts Protein Structures
Google DeepMind’s Demis Hassabis and John Jumper, alongside David Baker, received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their pioneering work on protein structures. Hassabis and Jumper developed AlphaFold2, an AI model that predicts protein structures, while Baker designed novel proteins. Their work accelerates research in pharmaceuticals and environmental science.
3. Anthropic Hires OpenAI Co-Founder Durk Kingma
Durk Kingma, one of the lesser-known co-founders of OpenAI, today announced that he’ll be joining Anthropic.
4. OpenAI Introduces MLE-Bench
OpenAI researchers have developed MLE-bench, a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates AI agents on various ML engineering challenges inspired by real-world scenarios. MLE-bench is a novel benchmark to evaluate how well AI agents can perform end-to-end ML engineering. It is constructed using a collection of 75 ML engineering competitions sourced from Kaggle.
5. Anthropic Introduces the Message Batches API News
Anthropic has introduced a new Message Batches API in public beta, enabling asynchronous processing of up to 10,000 queries per batch with a 50% cost reduction. It supports various Claude models, integrates with Amazon Bedrock, and will soon support Google Cloud’s Vertex AI.
6. AMD Launches AI Chip To Rival Nvidia’s Blackwell
AMD launched a new artificial intelligence chip directly targeting Nvidia’s data center GPUs. The Instinct MI325X’s rollout will pit it against Nvidia’s upcoming Blackwell chips, which will start shipping in significant quantities early next year.
7. Apple Releases Depth Pro, an AI Model That Rewrites the Rules of 3D Vision
Apple’s AI research team has developed a new model that could significantly advance how machines perceive depth. The system, called Depth Pro, can generate detailed 3D depth maps from single 2D images in a fraction of a second without relying on the camera data traditionally needed to make such predictions.
Five 5-minute reads/videos to keep you learning
The article studies the evolution of Generative AI towards “System 2” thinking, emphasizing the transition from rapid, pre-trained responses to advanced reasoning capabilities. It highlights the consolidation of foundational AI layers, the emergence of reasoning layers, and new cognitive architectures, with OpenAI’s Strawberry model exemplifying these inference-time reasoning advancements.
2. LLM-Powered Metadata Extraction Algorithm
The volume of unstructured data is constantly growing — social media posts, customer reviews, articles, etc. Processing this data and extracting meaningful insights is crucial for businesses to understand customer feedback. This article focuses on LLM capabilities to extract meaningful metadata from product reviews, specifically using OpenAI API.
3. Inference Time Scaling Laws
The blog highlights the growing significance of inference time scaling laws in AI, as demonstrated by OpenAI’s o1 model. This approach shifts compute resources from pre-training to inference, improving AI’s long-term processing and reasoning abilities. This advancement could enhance AI capabilities in complex reasoning and strategic planning.
4. Three Subtle Examples of Data Leakage
The article examines data leakage in data science projects through anonymized cases, highlighting its potential to distort model performance. It stresses the importance of vigilant data handling to prevent biased outcomes and notes the variability of data leakage’s impact across different contexts, as well as its frequent oversight in the industry despite standard methodologies.
5. TGI Multi-LoRA: Deploy Once, Serve 30 models
The Multi-LoRA serving approach provides a solution to the cost and complexity barriers associated with managing multiple specialized models. This article introduces the approach, how to use it, what are some practical considerations, and more.
Repositories & Tools
- The OpenAI Swarm repository is an experimental framework for exploring multi-agent orchestration.
- LightRAG is a simple and fast retrieval-augmented generation.
- Manim is a community-maintained Python framework for creating mathematical animations.
- Unkey is an open-source API authentication and authorization platform.
- Agent S is an open agentic framework that uses computers like a human.
Top Papers of The Week
The Diff Transformer introduces differential attention by subtracting one softmax attention map from another, enhancing sparse attention patterns and reducing noise. This approach outperforms traditional Transformers in long-context modeling, key information retrieval, hallucination mitigation, in-context learning, and robustness to order permutation, making it a promising architecture for advancing large language models.
2. LLMs Know More Than They Show: On the Intrinsic Representation of LLM Hallucinations
The study shows that LLMs encode detailed truthfulness information, which can enhance error detection, though this encoding varies across datasets, challenging a universal truthfulness metric. LLMs can also predict error types, aiding in countermeasure development. LLMs sometimes internally recognize correct answers but output incorrect ones, indicating a gap between internal knowledge and external expression.
3. MLE-bench: Evaluating Machine Learning Agents on Machine Learning Engineering
MLE-bench is a benchmark for measuring how well AI agents perform in machine learning engineering. It curates 75 ML engineering-related competitions from Kaggle, creating a diverse set of challenging tasks that test real-world ML engineering skills, such as training models, preparing datasets, and running experiments. It also establishes human baselines for each competition using Kaggle’s publicly available leaderboards.
4. OmniGenBench: Automating Large-scale in-silico Benchmarking for Genomic Foundation Models
OmniGenBench is a framework designed to automate benchmarking for genomic foundation models (GFMs). It addresses the scarcity of tools in genomic studies by integrating millions of genomic sequences for various tasks, thus standardizing and democratizing GFM applications. GFMBench includes user-friendly interfaces, tutorials, and a public leaderboard to advance genome modeling.
5. When a Language Model Is Optimized for Reasoning, Does It Still Show Embers of Autoregression?
The study evaluates OpenAI’s new language model, o1, which is optimized for reasoning. While o1 demonstrates notable performance improvements, particularly in uncommon tasks, it retains autoregressive traits and sensitivity to example probability, similar to its predecessors, indicating persistent limitations despite enhanced reasoning capabilities.
6. One Initialization to Rule them All: Fine-tuning via Explained Variance Adaptation
This paper proposes an Explained Variance Adaptation (EVA). It enhances LoRA by initializing the new weights in a data-driven manner by computing singular value decomposition on mini-batches of activation vectors. It also initializes the LoRA matrices with the obtained right-singular vectors and re-distributes ranks among all weight matrices to explain the maximum variance and continue the standard LoRA fine-tuning procedure.
Mistral published a paper sharing the details behind Pixtral, its multimodal LLM unveiled last month. Pixtral uses a vision encoder trained from scratch as well as a very innovative text model, which allows it to process both images and documents with a high level of performance
Quick Links
1. OpenAI has introduced its meta-prompt, a tool designed to simplify and optimize the creation of prompts for language models. Integrated into the Playground’s prompt optimization feature, the meta-prompt helps users generate and refine effective prompts using structured guidelines.
2. Inflection AI introduces Inflection for Enterprise. The company says its unique approach to RLHF sets it apart. Instead of relying on anonymous data labeling, it sought feedback from 26,000 school teachers and university professors through a proprietary feedback platform to aid in the fine-tuning process.
Who’s Hiring in AI
Senior/Specialist Python Engineer — Remoto @Capco (Sao Paulo, Brazil)
AI/ML Architect @CGI Technologies and Solutions, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA)
Machine Learning Engineer @Manulife (Toronto, Canada)
Data Partnerships Manager (9-month contract) @Cohere (Remote)
ML Ops Engineer @Insight Global (Irving, TX, USA)
Summer 2025 — AI Software Engineer Intern @Salesforce (Palo Alto, California, USA)
Interested in sharing a job opportunity here? Contact sponsors@towardsai.net.
Think a friend would enjoy this too? Share the newsletter and let them join the conversation.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.