Using NLP (Doc2Vec) and Neural Networks (with Keras): Removing Hate Speech and Offensive Tweets
Author(s): Greg Postalian-Yrausquin
Originally published on Towards AI.

This is a great example of how more than one ML step can be used to achieve a goal.
In this exercise, I will combine NLP (Doc2Vec) with binary classification to extract offensive and hate language from a set of tweets.
Doc2Vec is chosen in this case because it is not pretrained, so it does not rely on a previously provided vocabulary (who knows what we might find… and the tweets are filled with typos, etc). Doc2Vec is a good tool because: 1) as I say does not rely on pre-defined vocabulary and 2) it is a “complete” model, it considers the word in the context of its sentence, gives more accurate results than simpler vectorization tools like TF-IDF.
First, let’s import the libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import json
pd.options.mode.chained_assignment = None
from io import StringIO
from html.parser import HTMLParser
import re
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
nltk.download('stopwords')
nltkstop = stopwords.words('english')
from gensim.models.doc2vec import Doc2Vec, TaggedDocument
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem.snowball import SnowballStemmer
nltk.download('punkt')
snow = SnowballStemmer(language='english')
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import seaborn as sns
import warnings
import tensorflow as tf
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.utils import resample
I have uploaded two datasets, one with a list of possibly offensive tweets and another with a list of generic tweets, with them, I build the dataset to study.
Also, I am uploading several datasets that I use to clean the data from words that bring no or generic meaning like place names, personal names, etc. There are many versions of these available on the internet, they can be found with a simple search. Before uploading them I made sure they made sense and cleaned them.
maindataset = pd.read_csv("labeled_data.csv")
maindataset2 = pd.read_csv("twitter_dataset.csv", encoding = "ISO-8859-1")
countries = pd.read_json("countries.json")
countries["country"] = countries["country"].str.lower()
countries = pd.DataFrame(countries["country"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
countries.columns = ['word']
countries["replacement"] = "xcountryx"
provincies = pd.read_csv("countries_provincies.csv")
provincies1 = provincies[["name"]]
provincies1["name"] = provincies1["name"].str.lower()
provincies1 = pd.DataFrame(provincies1["name"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
provincies1.columns = ['word']
provincies1["replacement"] = "xprovincex"
provincies2 = provincies[["name_alt"]]
provincies2["name_alt"] = provincies2["name_alt"].str.lower()
provincies2 = pd.DataFrame(provincies2["name_alt"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
provincies2.columns = ['word']
provincies2["replacement"] = "xprovincex"
provincies3 = provincies[["type_en"]]
provincies3["type_en"] = provincies3["type_en"].str.lower()
provincies3 = pd.DataFrame(provincies3["type_en"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
provincies3.columns = ['word']
provincies3["replacement"] = "xsubdivisionx"
provincies4 = provincies[["admin"]]
provincies4["admin"] = provincies4["admin"].str.lower()
provincies4 = pd.DataFrame(provincies4["admin"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
provincies4.columns = ['word']
provincies4["replacement"] = "xcountryx"
provincies5 = provincies[["geonunit"]]
provincies5["geonunit"] = provincies5["geonunit"].str.lower()
provincies5 = pd.DataFrame(provincies5["geonunit"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
provincies5.columns = ['word']
provincies5["replacement"] = "xcountryx"
provincies6 = provincies[["gn_name"]]
provincies6["gn_name"] = provincies6["gn_name"].str.lower()
provincies6 = pd.DataFrame(provincies6["gn_name"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
provincies6.columns = ['word']
provincies6["replacement"] = "xcountryx"
provincies = pd.concat([provincies1,provincies2,provincies3,provincies4,provincies5,provincies6], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
currencies = pd.read_json("country-by-currency-name.json")
currencies1 = currencies[["country"]]
currencies1["country"] = currencies1["country"].str.lower()
currencies1 = pd.DataFrame(currencies1["country"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
currencies1.columns = ['word']
currencies1["replacement"] = "xcountryx"
currencies2 = currencies[["currency_name"]]
currencies2["currency_name"] = currencies2["currency_name"].str.lower()
currencies2 = pd.DataFrame(currencies2["currency_name"].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
currencies2.columns = ['word']
currencies2["replacement"] = "xcurrencyx"
currencies = pd.concat([currencies1,currencies2], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
firstnames = pd.read_csv("interall.csv", header=None)
firstnames = firstnames[firstnames[1]>=10000]
firstnames = firstnames[[0]]
firstnames[0] = firstnames[0].str.lower()
firstnames = pd.DataFrame(firstnames[0].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
firstnames.columns = ['word']
firstnames["replacement"] = "xfirstnamex"
lastnames = pd.read_csv("intersurnames.csv", header=None)
lastnames = lastnames[lastnames[1]>=10000]
lastnames = lastnames[[0]]
lastnames[0] = lastnames[0].str.lower()
lastnames = pd.DataFrame(lastnames[0].apply(lambda x: str(x).replace('-',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('_',' ').replace(',',' ').replace(':',' ').split(" ")).explode())
lastnames.columns = ['word']
lastnames["replacement"] = "xlastnamex"
temporaldata = pd.read_csv("temporal.csv")
dictionary = pd.concat([lastnames,temporaldata,firstnames,currencies,provincies,countries], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
dictionary = dictionary.groupby(["word"]).first().reset_index(drop=False)
dictionary = dictionary.dropna()
maindataset

It might be necessary to understand the data a little. From Kaggle:
“count number of CrowdFlower users who coded each tweet (min is 3, sometimes more users coded a tweet when judgments were determined to be unreliable by CF)
hate_speech number of CF users who judged the tweet to be hate speech
offensive_language number of CF users who judged the tweet to be offensive
neither number of CF users who judged the tweet to be neither offensive nor non-offensive
class class label for majority of CF users. 0 — hate speech 1 — offensive language 2 — neither”
With that, I will filter out the column for class and keep only two, if at least one user flag the tweet as offensive or hate speech then it is.
maindataset['hate_speech'] = np.where(maindataset['hate_speech']>0,1,0)
maindataset['offensive_language'] = np.where(maindataset['offensive_language']>0,1,0)
maindataset = maindataset[['hate_speech', 'offensive_language', 'tweet']]
maindataset

Now, I’ll prepare the other dataset (with the clean tweets), and join it to the original one
maindataset2 = maindataset2[['text']]
maindataset2.columns = ['tweet']
maindataset2['hate_speech'] = 0
maindataset2['offensive_language'] = 0
maindataset2 = maindataset2[['hate_speech','offensive_language','tweet']]
maindataset = pd.concat([maindataset,maindataset2], ignore_index=True)
Here I use several functions to clean the text that I like to keep in my belt:
- Strip HTML tags
- Replace words using the dictionary crafted above
- Remove punctuation, double spaces, etc.
class MLStripper(HTMLParser):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.reset()
self.strict = False
self.convert_charrefs= True
self.text = StringIO()
def handle_data(self, d):
self.text.write(d)
def get_data(self):
return self.text.getvalue()
def strip_tags(html):
s = MLStripper()
s.feed(html)
return s.get_data()
def replace_words(tt, lookp_dict):
temp = tt.split()
res = []
for wrd in temp:
res.append(lookp_dict.get(wrd, wrd))
res = ' '.join(res)
return res
def preprepare(eingang):
ausgang = strip_tags(eingang)
ausgang = eingang.lower()
ausgang = ausgang.replace(u'\xa0', u' ')
ausgang = re.sub(r'^\s*$',' ',str(ausgang))
ausgang = ausgang.replace('|', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('ï', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('»', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('¿', '. ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('"', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace("'", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace('?', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('!', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace(',', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace(';', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('.', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace("(", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace(")", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("{", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("}", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("[", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("]", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("~", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("@", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("#", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("$", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("%", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("^", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("&", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("*", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("<", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace(">", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("/", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("\\", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("`", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("+", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("=", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("_", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace("-", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace(':', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace('\n', ' ').replace('\r', ' ')
ausgang = ausgang.replace(" +", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace(" +", " ")
ausgang = ausgang.replace('?', ' ')
ausgang = re.sub('[^a-zA-Z]', ' ', ausgang)
ausgang = re.sub(' +', ' ', ausgang)
ausgang = re.sub('\ +', ' ', ausgang)
ausgang = re.sub(r'\s([?.!"](?:\s|$))', r'\1', ausgang)
return ausgang
Clean up the dictionary data
dictionary["word"] = dictionary["word"].apply(lambda x: preprepare(x))
dictionary = dictionary[dictionary["word"] != " "]
dictionary = dictionary[dictionary["word"] != ""]
dictionary = {row['word']: row['replacement'] for index, row in dictionary.iterrows()}
Preparation of the text data to convert: created a new column with the cleaned version of the text. This is what will be converted to vectors. Then I replace the stopwords and words in the dictionary
maindataset["NLPtext"] = maindataset["tweet"]
maindataset["NLPtext"] = maindataset["NLPtext"].str.lower()
maindataset["NLPtext"] = maindataset["NLPtext"].apply(lambda x: preprepare(str(x)))
maindataset["NLPtext"] = maindataset["NLPtext"].apply(lambda x: ' '.join([word for word in x.split() if word not in (nltkstop)]))
maindataset["NLPtext"] = maindataset["NLPtext"].apply(lambda x: replace_words(str(x), dictionary))
The last part of preparing the text is stemming (make “studies”=”study”). This is done in this case, since anyways I am training the model from scratch. I do this because it is likely that some of the offensive language is not even in pre-trained models
def steming(sentence):
words = word_tokenize(sentence)
singles = [snow.stem(plural) for plural in words]
oup = ' '.join(singles)
return oup
maindataset["NLPtext"] = maindataset["NLPtext"].apply(lambda x: steming(x))
maindataset['lentweet'] = maindataset["tweet"].apply(lambda x: len(str(x).split(' ')))
maindataset = maindataset[maindataset['NLPtext'].notna()]
maindataset = maindataset[maindataset['lentweet']>=3]
maindataset = maindataset.reset_index(drop=False)
maindataset
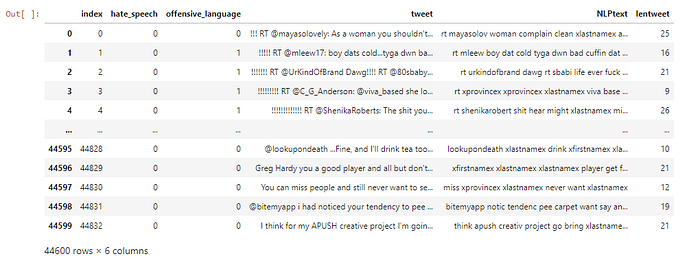
See the difference between the original text and the clean, ready-to-feed to the model one.
Now, we are finally ready to train the Doc2Vec model
trainset = maindataset.sample(frac=1).reset_index(drop=True)
trainset = trainset[(trainset['NLPtext'].str.len() >= 3)]
trainset = trainset.sample(frac=1).reset_index(drop=True)
trainset = trainset[["NLPtext"]]
tagged_data = []
for index, row in trainset.iterrows():
part = TaggedDocument(words=word_tokenize(row[0]), tags=[str(index)])
tagged_data.append(part)
model = Doc2Vec(vector_size=350, min_count=3, epochs=50, window=10, dm=1)
model.build_vocab(tagged_data)
model.train(tagged_data, total_examples=model.corpus_count, epochs=model.epochs)
model.save("d2v.model")
print("Model Saved")
Apply the model and vectorize the tweets (convert text to numbers)
a = []
for index, row in maindataset.iterrows():
nlptext = row['NLPtext']
ids = row['index']
vector = model.infer_vector(word_tokenize(nlptext))
vector = pd.DataFrame(vector).T
vector.index = [ids]
a.append(vector)
textvectors = pd.concat(a)
textvectors

I use this small function for standardization
def properscaler(simio):
scaler = StandardScaler()
resultsWordstrans = scaler.fit_transform(simio)
resultsWordstrans = pd.DataFrame(resultsWordstrans)
resultsWordstrans.index = simio.index
resultsWordstrans.columns = simio.columns
return resultsWordstrans
datasetR = properscaler(textvectors)
I split the sets in training and testing, and visualize the distribution of the response
datasetR['target'] = maindataset['offensive_language'].values
outp = train_test_split(datasetR, train_size=0.7)
finaleval=outp[1]
subset=outp[0]
x_subset = subset.drop(columns=["target"]).to_numpy()
y_subset = subset['target'].to_numpy()
x_finaleval = finaleval.drop(columns=["target"]).to_numpy()
y_finaleval = finaleval[['target']].to_numpy()
sns.displot(y_subset)

The distribution of the response is important to select the proper activation function in NN and to determine if it is necessary to apply any steps to rebalance the classes. In this case a sigmoid is selected as the final function since it is the selected outcome of a binary classification (the function tends to 0 or 1). No rebalance is needed
This is the definition of the neural networks using Keras
#initialize
neur = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
#layers
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=100, activation='linear'))
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=200, activation='relu'))
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=500, activation='tanh'))
#last layer
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=1, activation='sigmoid'))
#for binary classification: cross entropy as loss function, sigmoid for optimizer, recall and precision as metrics
neur.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='sgd', metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.Precision(),tf.keras.metrics.Recall()])
Train the model
neur.fit(x_subset, y_subset, batch_size=20000, epochs=700)

We see on the last steps that the precision and recall are not improving anymore, so we are sure the model has done everything it can do at this point. Now I evaluate the test set.
test_out = neur.predict(x_finaleval)
output = outp[1][[0]]
scal = MinMaxScaler()
output['predicted'] = scal.fit_transform(test_out)
output['actual'] = y_finaleval
output = output.drop(columns=[0])
output = pd.merge(output, maindataset[['index','tweet']], left_index=True, right_on=['index'])
output = output.sort_values(['predicted'], ascending=False)
pd.options.display.max_colwidth = 150
output

Confusion Matrix (cut point at 0.5)
output["predictedVal"] = np.where(output['predicted']>=0.5,1,0)
print(classification_report(output['actual'],output["predictedVal"] ))
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_predictions(y_true=output['actual'] ,y_pred=output['predictedVal'] , cmap='PuBu')

Using the same approach now for the hate speech dataset
datasetR['target'] = maindataset['hate_speech'].values
outp = train_test_split(datasetR, train_size=0.7)
finaleval=outp[1]
subset=outp[0]
x_subset = subset.drop(columns=["target"]).to_numpy()
y_subset = subset['target'].to_numpy()
x_finaleval = finaleval.drop(columns=["target"]).to_numpy()
y_finaleval = finaleval[['target']].to_numpy()
#size of the training set
print(len(y_subset))
sns.displot(y_subset)

In this example the classes are unbalanced. I used this small function to rebalance the classes using resample.
def rebalance(sset, min, max):
classes = list(set(sset["target"]))
a = []
for clas in classes:
positives = sset[sset['target']==clas]
if len(positives) < min:
positives = resample(positives, n_samples=min, replace=True)
if len(positives) > max:
positives = resample(positives, n_samples=max, replace=False)
a.append(positives)
rebalanced = pd.concat(a, axis=0, ignore_index=True)
return rebalanced
subsetR = rebalance(sset=subset, min=round(5000), max=round(7000))
x_subset = subsetR.drop(columns=["target"]).to_numpy()
y_subset = subsetR['target'].to_numpy()
print(len(y_subset))
sns.displot(y_subset)
The new updated dataset looks better now

Now, let’s train the neural network
#initialize
neur = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
#layers
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=100, activation='linear'))
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=200, activation='relu'))
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=500, activation='tanh'))
#output layer
neur.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=1, activation='sigmoid'))
#using mse for regression. Simple and clear
neur.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='sgd', metrics=[tf.keras.metrics.Precision(),tf.keras.metrics.Recall()])
neur.fit(x_subset, y_subset, batch_size=10000, epochs=700)

Doing the inference on the test set, these are the results for the offensive dataset
test_out = neur.predict(x_finaleval)
output2 = outp[1][[0]]
scal = MinMaxScaler()
output2['predicted'] = scal.fit_transform(test_out)
output2['actual'] = y_finaleval
output2 = output2.drop(columns=[0])
output2 = pd.merge(output2, maindataset[['index','tweet']], left_index=True, right_on=['index'])
output2 = output2.sort_values(['predicted'], ascending=False)
pd.options.display.max_colwidth = 150
output2

Let’s now review the confusion matrix
output2["predictedVal"] = np.where(output2['predicted']>=0.5,1,0)
print(classification_report(output2['actual'],output2["predictedVal"] ))
ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_predictions(y_true=output2['actual'] ,y_pred=output2['predictedVal'] , cmap='PuBu')

The results are far from perfect but some steps can be done at this point to improve the results:
- Use different parameters to rebalance the classes.
- Use a different cut point to determine when a tweet is offensive (play with the balance between false positives and false negatives)
- Try a more elaborated neural network, until the point of overfitting and then reduce the overfitting with regularization and/or dropout
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI














