
Master the Power of RegEx: A Step-by-Step Guide
Last Updated on July 17, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Tushar Aggarwal
Originally published on Towards AI.
{This article was written without the assistance or use of AI tools, providing an authentic and insightful exploration of RegEx}

Regular Expressions, or RegEx, is a powerful tool for text processing and manipulation. By mastering RegEx for Python, you can efficiently handle complex tasks such as data extraction, pattern matching, and string manipulation. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of RegEx for Python and illustrate its power through step-by-step examples. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of RegEx and its applications in Python.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to RegEx
- RegEx in Python: The
remodule - Basic RegEx Patterns
- Meta-characters and Special Sequences
- RegEx Functions in Python
- Grouping and Capturing
- Lookahead and Lookbehind Assertions
- Flags in RegEx
- Practical Applications of RegEx for Python
- Tips and Resources for Mastering RegEx
1. Introduction to RegEx
Regular Expressions, or RegEx, is a sequence of characters that define a search pattern. This search pattern can be used to match, locate, and manipulate strings. RegEx is widely used in various programming languages, including Python, for tasks such as data validation, data extraction, and text processing. By mastering RegEx, you can significantly enhance your text manipulation capabilities in Python.
2. RegEx in Python: The re module
Python provides the built-in re module to work with RegEx. This module contains various functions and methods to perform pattern matching and string manipulation using RegEx. To use the re module, you need to import it into your Python script:

With the re module imported, you can now use its functions to perform various RegEx operations in Python.
3. Basic RegEx Patterns
RegEx patterns are composed of ordinary characters (such as letters or digits) and special characters (called meta-characters), which have a special meaning. Here are some basic RegEx patterns:
a: Matches the character 'a'123: Matches the sequence of characters '123'
These basic patterns can be combined to form more complex patterns. For example, the pattern abc123 will match the string 'abc123'.
4. Meta-characters and Special Sequences
RegEx meta-characters are characters that have special meanings when used in a pattern. They allow you to create more complex search patterns. Here are some common meta-characters and their meanings:
.: Matches any character (except a newline)^: Matches the start of the string$: Matches the end of the string*: Matches zero or more repetitions of the preceding character+: Matches one or more repetitions of the preceding character?: Matches zero or one occurrence of the preceding character{m,n}: Matches at least 'm' and at most 'n' repetitions of the preceding characterU+007C: Acts as an OR operator, matching either the expression before or after it(): Defines a group, which can be used for capturing and applying quantifiers[]: Specifies a character set, allowing you to match any character within the brackets
Special sequences are character combinations that have special meanings in a RegEx pattern. Here are some common special sequences:
\d: Matches any decimal digit (0-9)\D: Matches any non-digit character\s: Matches any whitespace character (space, tab, newline, etc.)\S: Matches any non-whitespace character\w: Matches any alphanumeric character (letters and digits)\W: Matches any non-alphanumeric character
5. RegEx Functions in Python
Python’s re the module provides several functions for working with RegEx. Here are some commonly used functions:
re.search(pattern, string): Searches the string for a match to the pattern, returning a match object if a match is found, or None otherwise.re.match(pattern, string): Determines if the pattern matches at the beginning of the string, returning a match object if a match is found, or None otherwise.re.findall(pattern, string): Returns all non-overlapping matches of the pattern in the string, as a list of strings.re.finditer(pattern, string): Returns an iterator yielding match objects for all non-overlapping matches of the pattern in the string.re.sub(pattern, replacement, string): Replaces all occurrences of the pattern in the string with the given replacement, returning the modified string.re.split(pattern, string): Splits the string by the occurrences of the pattern, returning a list of strings.
6. Grouping and Capturing
Grouping allows you to apply quantifiers to a set of characters or to capture portions of the matched string. To create a group, use parentheses () around the pattern you want to group. For example, the pattern (ab)+ matches one or more repetitions of the string 'ab'.
Capturing refers to the process of extracting the matched portions of a string. In Python, you can use the group() method of the match object to access the captured groups. The group(0) method returns the entire match, while group(n) returning the nth captured group.

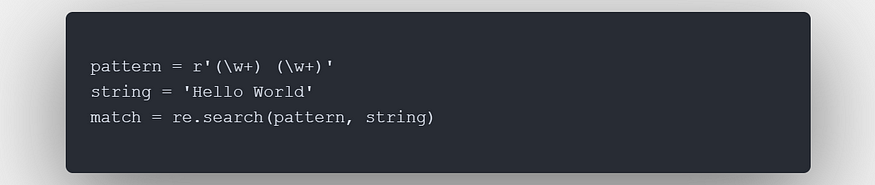

7. Lookahead and Lookbehind Assertions
Lookahead and lookbehind assertions are used to match a pattern only if it is followed (lookahead) or preceded (lookbehind) by another pattern, without consuming any characters from the string. These assertions are written as:
- Positive lookahead:
(?=pattern) - Negative lookahead:
(?!pattern) - Positive lookbehind:
(?<=pattern) - Negative lookbehind:
(?<!pattern)
For example, the pattern a(?=b) matches the character 'a' only if it is followed by the character 'b'.
8. Flags in RegEx
Flags are used to modify the behaviour of RegEx functions. Python’s re the module provides several flags, such as:
re.IGNORECASEorre.I: Makes the pattern case-insensitivere.MULTILINEorre.M: Allows start and end meta-characters (^and$) to match at the beginning and end of each line in the stringre.DOTALLorre.S: Makes the dot.meta-character matches any character, including a new line
Flags can be passed as an optional argument to the RegEx functions:



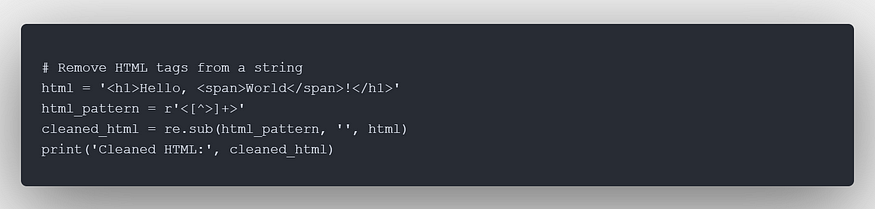
9. Practical Applications of RegEx for Python
RegEx can be used in various text processing tasks in Python, such as:
- Data validation (e.g., checking if a string is a valid email address)
- Data extraction (e.g., extracting dates or URLs from a text)
- String manipulation (e.g., removing unwanted characters or formatting text)
- Pattern matching (e.g., finding specific words or phrases in a text)
Here are some examples:


10. Tips and Resources for Mastering RegEx
Mastering RegEx takes time and practice. Here are some tips and resources to help you improve your RegEx skills:
- Practice writing RegEx patterns for various text-processing tasks.
- Use online RegEx tools, such as regex101, to test and debug your patterns.
- Read the Python
remodule documentation to learn more about its functions and features. - Consult RegEx tutorials and guides, such as Regular-Expressions.info, to deepen your understanding of RegEx concepts.
By following this step-by-step guide and utilizing the provided resources, you can now harness the power of RegEx for Python to solve complex text-processing tasks and enhance your programming skills.
U+1F916I write about the practical use of A.I. and life with it.
U+1F916My country isn’t supported by Medium Partner Program, so consider buying me a beer! https://www.buymeacoffee.com/TAggData
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














