What is a Canny Edge Detection Algorithm?
Last Updated on September 18, 2020 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Charanraj Shetty
Computer Vision
A Canny edge detector is a multi-step algorithm to detect the edges for any input image. It involves the below-mentioned steps to be followed while detecting edges of an image.
1. Removal of noise in input image using a Gaussian filter.
2. Computing the derivative of Gaussian filter to calculate the gradient of image pixels to obtain magnitude along x and y dimension.
3. Considering a group of neighbors for any curve in a direction perpendicular to the given edge, suppress the non-max edge contributor pixel points.
4. Lastly, use the Hysteresis Thresholding method to preserve the pixels higher than the gradient magnitude and neglect the ones lower than the low threshold value.
Before deep-diving into the steps below are the three conclusions that J.K Canny who derived the algorithm :
– Good Detection: The optimal detector must eliminate the possibility of getting false positives and false negatives.
– Good Localisation: The detected edges must be as close to true edges.
– Single Response Constraint: The detector must return one point only for each edge point.
Steps to followed during Canny Algorithm:
Noise Removal or Image Smoothing:
During the noise present, the pixel may not be close to being similar to its neighboring pixels. This might result in obtaining improper or inappropriate detection of edges. To avoid the same, we use the Gausian filter, which is convolved with the image and removes the noise, preventing the desired edges in output images.
In the below example, we are convolving gausian filter or kernel g(x,y) with an image I. Here we wish to make sure that any given pixel must be similar to its neighboring pixels in output and so we use the matrix [1 1 1] to maintain the similarity between pixels and remove the noise.
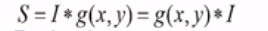
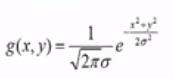
g(x,y)= Gausian Distribution
I = input image
Derivative :
Calculate the derivative of filter w.r.t X and Y dimensions and convolve it with I to give the gradient magnitude along the dimensions. Also, the direction of the image can be calculated using the tangent of the angle between the two dimensions.

The above convolution results in a gradient vector that has magnitude and direction.

Below is an example of Gausian Derivatives, which finally contribute to edges in output images.

Non-Max Suppression
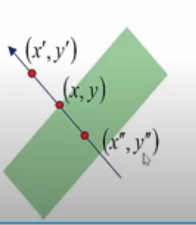
Along an edge, it is generally observed that few points make the visibility of the edge clearer. So we can neglect those edge points which don’t contribute more towards feature visibility. To achieve the same, we use the Non Maximum Suppression method. Here we mark the points on the curve of the edge where the magnitude is largest. This can be obtained by looking for a maximum along with a slice normal to the curve.
Consider the edge in the below figure, which has three edge points. Assume point (x,y) as the point having the largest gradient of edge. Check for the edge points in the direction perpendicular to the edge and verify if their gradient is less than (x,y). If the values are less than (x,y) gradient, then we can suppress those non-maxima points along the curve.
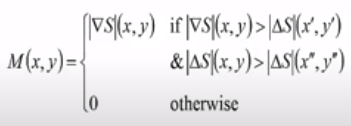
Hysteresis Thresholding :

If the gradient at a pixel is :
– Above “High” declare it as an ‘edge pixel.’
– Below, “Low” declares it as a ‘non-edge pixel.’
– Between “low” and “high.”
- Consider its neighbors iteratively then declare it an “edge pixel” if it’s connected to an “edge pixel” or via pixels between “low” and “high.”
Thanks for reading !!
Source Reference of Dr. Mubarak Shah youtube videos.
What is a Canny Edge Detection Algorithm? was originally published in Towards AI — Multidisciplinary Science Journal on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.















