
Some Technical Notes About Llama 3
Last Updated on April 25, 2024 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Jesus Rodriguez
Originally published on Towards AI.

I recently started an AI-focused educational newsletter, that already has over 165,000 subscribers. TheSequence is a no-BS (meaning no hype, no news, etc) ML-oriented newsletter that takes 5 minutes to read. The goal is to keep you up to date with machine learning projects, research papers, and concepts. Please give it a try by subscribing below:
TheSequence | Jesus Rodriguez | Substack
The best source to stay up-to-date with the developments in the machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data…
thesequence.substack.com
Since the debut of the original version, Llama has become one of the foundational blocks of the open source generative AI space. I prefer to use the term “open models,” given that these releases are not completely open source, but that’s just my preference. Last week, the trend in open models became even hotter with the release Llama 3.
The release of Llama 3 builds on incredible momentum within the open model ecosystem and brings its own innovations. The 8B and 70B versions of Llama 3 are available, with a 400B version currently being trained.
The Llama 3 architecture is based on a decoder-only model and includes a new, highly optimized 128k tokenizer. This is quite notable, given that, with few exceptions, most large language models simply reuse the same tokenizers. The new tokenizer leads to major performance gains. Another area of improvement in the architecture is the grouped query attention, which was already used in Llama 2 but has been enhanced for the larger models. Grouped query attention helps improve inference performance by caching key parameters. Additionally, the context window has also increased.
Training is one area in which Llama 3 drastically improves over its predecessors. The model was trained on 15 trillion tokens, making the corpus quite large for an 8B parameter model, which speaks to the level of optimization Meta achieved in this release. It’s interesting to note that only 5% of the training corpus consisted of non-English tokens. The training infrastructure utilized 16,000 GPUs, achieving a throughput of 400 TFLOPs, which is nothing short of monumental.
Architecture
Meta AI’s Llama 3 features a standard, decoder-only transformer structure. Llama 3 introduces a tokenizer equipped with a 128K token vocabulary, which enhances language encoding efficiency, significantly boosting model performance. To enhance the inference capabilities, Llama 3 integrates grouped query attention (GQA) across models sized at 8B and 70B. These models are trained with sequences up to 8,192 tokens long, using a masking technique to prevent self-attention across document boundaries.

1)Tokenizer
The latest iteration of Llama 3 showcases an innovative tokenizer. This tokenizer operates with a vocabulary comprising 128K tokens, optimized beyond its predecessors to yield superior inference performance. Notably, the Llama 3–8B model was trained using an impressive 15 trillion tokens, a feat made possible through effective parameter utilization.
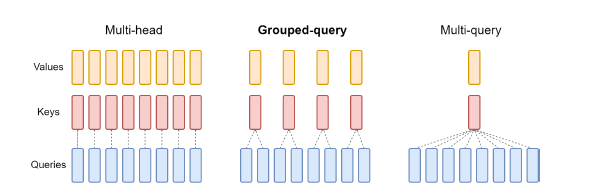
2) GQA
Grouped-query attention (GQA) ingeniously combines aspects of multi-head attention (MHA) and multi-query attention (MQA) to form an efficient attention mechanism. By caching keys and values from prior tokens, GQA lessens memory demands as batch sizes or context windows expand, thereby streamlining the decoding process in Transformer models.
3) RoPE
Llama 3 employs Rotary Positional Encoding (RoPE), a sophisticated encoding mechanism that strikes a balance between absolute positional encodings and relative positional encodings. This method not only retains a fixed embedding for each token but also applies a rotational computation to the vectors, enhancing the model’s attention calculations.
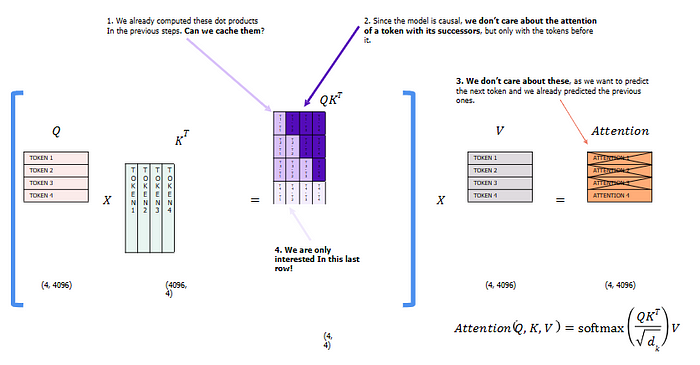
4) KV Cache
Key-Value (KV) caching is a technique deployed to speed up the inference in autoregressive models like GPT and Llama. By storing previously computed keys and values, the model reduces repetitive calculations, thus expediting matrix multiplications and enhancing overall efficiency.
Training
Meta AI has pre-trained Llama 3 on over 15 trillion tokens gathered from public sources. The training set is seven times larger than that used for Llama 2 and includes a significantly higher volume of code. With more than 5% of the training data consisting of high-quality, non-English content covering over 30 languages, Llama 3 prepares for multilingual applications, although performance in these languages may not equal that in English.
In pursuit of the highest data quality, Meta AI developed sophisticated filtering systems, including heuristic and NSFW filters, semantic deduplication, and text classifiers. These systems were refined using insights from previous model generations, particularly Llama 2, which was instrumental in generating training data for Llama 3’s quality-assurance classifiers.
For its largest models, Llama 3 utilizes a trio of parallelization strategies: data, model, and pipeline parallelization. Its most effective setup reaches over 400 TFLOPS per GPU, facilitated by training on 16,000 GPUs simultaneously within two custom-built 24,000 GPU clusters. Meta AI has also innovated a new training stack that automates error detection, handling, and maintenance to optimize GPU utilization.
Llama 3 Instruct
In refining its pretrained models for chat applications, Meta AI has employed a hybrid of supervised fine-tuning (SFT), rejection sampling, proximal policy optimization (PPO), and direct preference optimization (DPO). The selection and quality assurance of prompts and preference rankings significantly influence model performance. Moreover, to ensure model safety, these instruction-fine-tuned models undergo rigorous testing, including red-teaming by experts using adversarial prompts to identify and mitigate potential misuse risks.
The Results
Llama 3 achieves top-tier performance across leading industry benchmarks like MMLU and CommonSense QA.
Additionally, Meta AI has curated a new, high-quality human evaluation set comprising 1,800 prompts spanning 12 critical use cases. Access to this set is restricted even within Meta AI to prevent potential overfitting by the modeling teams.
An Impressive Model
Llama 3 is a very welcome addition to the open model generative AI stack. The initial benchmark results are quite impressive, and the 400B version could rival GPT-4. Distribution is one area where Meta excelled in this release, making Llama 3 available on all major machine learning platforms. It’s been just a few hours, and we are already seeing open source innovations using Llama 3.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.















