
Agent-Based Modeling in NetLogo
Last Updated on May 13, 2020 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Prabod Dunuwila

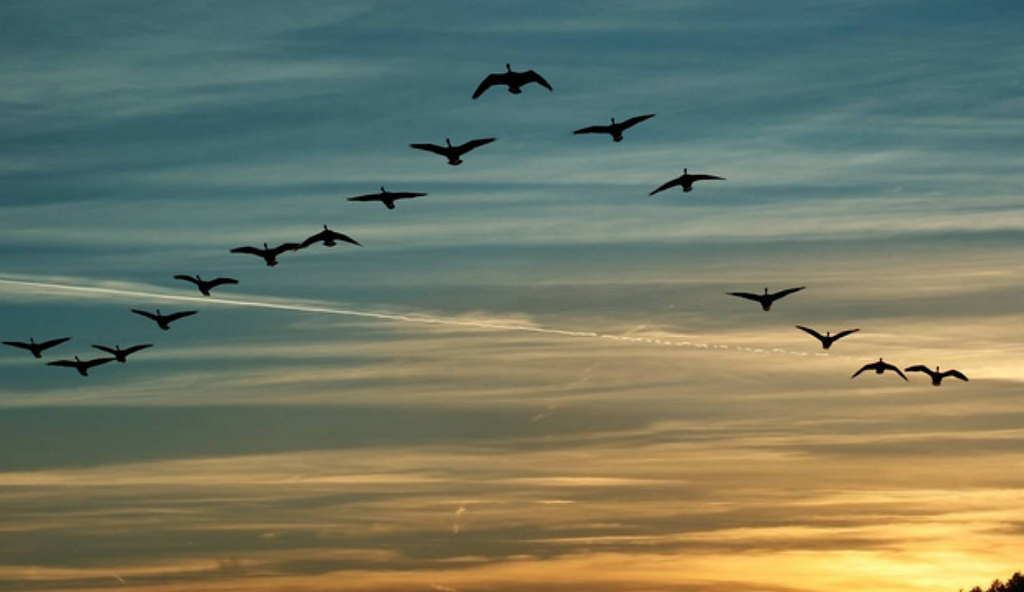
Agent-based modeling is a simulation technique that focuses on building a model of a system with a collection of autonomous decision-making entities called agents. Each individual agent can make decisions based on a set of rules provided with regard to their situation or properties. Using ABM techniques, people have identified that more complex patterns emerge as a result of simple interactions between individuals. Some of the examples are traffic jams, a flock of birds flying in V shape, housing patterns, and so on.
You have probably seen a flock of birds flying in ‘V formed shape.’ Most of you have probably thought that the leader bird is in the front, and other birds follow it. This is not the case. What happens is, rather than the same bird staying at their position, different birds occupy different spots while flying based on the independent movement based on the flying direction of the flock, avoiding other birds and not getting far away from the neighbor birds.
Likewise, ABM computational methodology enables us to model complex systems. ABM models are composed of agents, and agents have properties. In NetLogo, each agent has a graphical representation on the computer screen. Let’s try to build a simple scenario of a virus spread in society using NetLogo. In society, there are people(agents) who could be identified as infected and non-infected. So when agents interact with each other, infected agents may spread the virus to other agents. So let’s build a simple model to see how a virus is spread through a society based on a simple set of rules.
Properties of agents :
- ‘status’ to store whether infected or non-infected
Rules :
- each individual move randomly
- a virus is infected if the non-infected individual is within the radius of the infected individual based on a spread rate
First, let’s build the interface of the model by using the ‘interface’ in NetLogo. Here I have used two buttons named ‘setup’ procedure to set up the environment and ‘go’ procedure to run the model forever.
Then let’s create inputs named ‘infected-count’ and ‘people-count.’
A slider is used to change the global variable value’ spread-rate.’
Move to the ‘code’ tab in NetLogo. Since we are using a global variable ‘counter’ and creating a new breed type, we have to define it at the top of the code. Here the breed type is ‘people,’ and we can use it to call all ‘person’ agent set. And also, we have to define its properties.
globals[counter]
breed[people person]
people-own[infected?]
Let’s look at what we have to do in the ‘setup’ procedure. We have to clear the environment first, then set up the environment with agents and reset the ticks. So the code will look like this.
to setup
clear-all
initialize-people
reset-ticks
end
You will get an error if you ‘check’ the code using the ‘Check’ button because you have not yet written ‘initialize people’ procedure. We have to write that separately below setup. Write the ‘initialize-people’ procedure to create the agents of people type based on the people-count provided. Agents will be of shape “person” and random x, y coordinates. And people will have ‘infected?’ property true or false based on the initial ‘infected-count.’
to initialize-people
set counter infected-count
create-people people-count[
set shape "person"
setxy random-xcor random-ycor
(ifelse (counter > 0)
[set color red
set infected? true]
[set color white
set infected? false])
set counter counter - 1
]
end
Then in the ‘go’ procedure, we have to write what we expect to do when the model is running. So I will simply make people move randomly and spread the disease. I will not focus on the recovery of the infected people agents, and the model will stop when all the people get infected with the disease.
to go
(ifelse any? people with [color = white] [
move-people
spread-disease
]
[stop])
tick
end
We have to write two separate procedures named ‘move-people’ and ‘spread-disease’ to run the model. First, let’s look at the move-people method. It will ask people to pick a random whole number between 0 and 50. Then the agent turns right this number of degrees. And then ask to choose a random number between 0 and 50 and turns left that number of degrees. Then move forward with the specified step value.
to move-people
ask people [
rt random 50
lt random 50
forward 0.1
]
end
In the ‘spread-disease’ procedure, when a non-infected person meets an infected person, he/she will get infected with the disease based on the ‘spread-rate’ provided.
to spread-disease
ask people [
if any? people with [infected? = true] in-radius 0.5 [
if random 100 < spread-rate * 100 [
set color red
set infected? true
]
]
]
end
Move back to the ‘interface’ tab, and let’s create a plot to show the count of infected and non-infected people at each tick when the model is running.
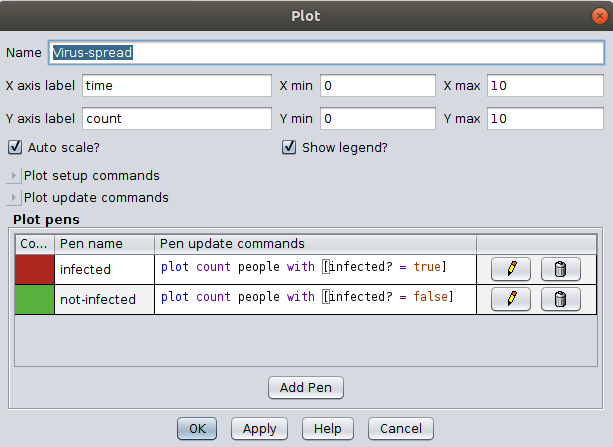
So the final interface will look like below after making all the changes.
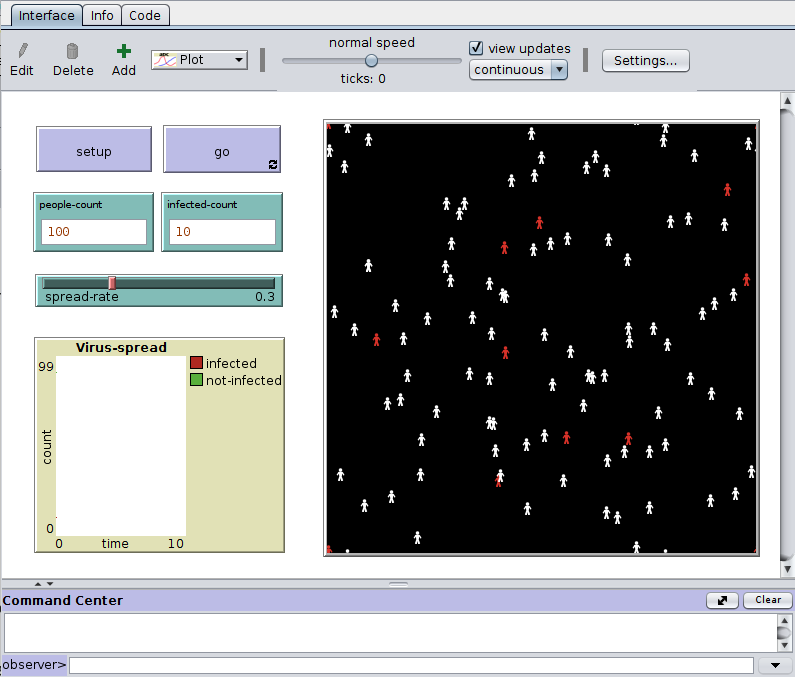
Before you run the model, don’t forget to fill input values for the input boxes.
I hope all of you have got an understanding of Agent-Based Modelling using NetLogo. If you want to read and learn more about ABM simulation using NetLogo, check out the references provided below.
References
[1] NetLogo Home Page
[2] An Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling Modeling Natural, Social, and Engineered Complex Systems with NetLogo by Uri Wilensky, William Rand
Agent-Based Modeling in NetLogo was originally published in Towards AI — Multidisciplinary Science Journal on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.












