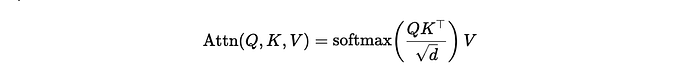
A comprehensive guide for handling outliers.
Last Updated on April 1, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Rohini Vaidya
Originally published on Towards AI.

Part: 2
In this second part of the statistics series, you will learn about the outliers in the dataset. What is an outlier in a dataset, different types of outliers, what is the effect of an outlier on the accuracy of our machine learning models, and how to deal with outliers?
If you haven’t read my first blog from the statistics series, please go through it first.
“Outliers can provide important information about the underlying process generating the data, but they can also distort the results of statistical analysis if not properly accounted for.”
— Andrew Gelman, statistician, and data scientist.
Outliers are those points that differ significantly from other observations present in a given dataset.
It can occur because of the variability of measurements and misinterpretations in filling data points.
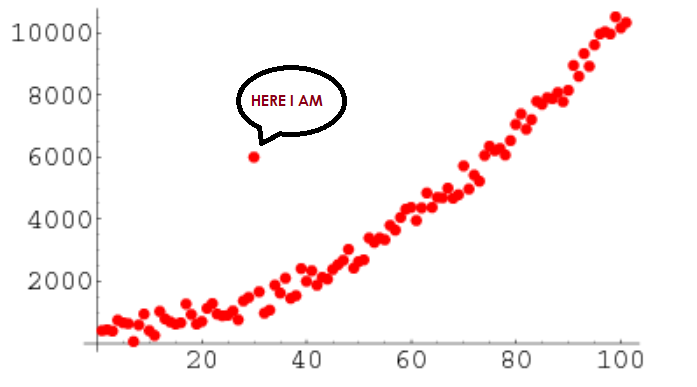
For Example, you can see the outlier in this list: [20,24,22,19,29,18,4300,30,18]
If the dataset contains less number of observations, then outliers from that dataset can be easily observable. But, if we consider larger datasets, we need to apply some methods to identify those outliers.
Outliers can be univariate outliers and multivariate outliers.
Univariate outliers are observations that have a very extreme value on a single variable compared to the rest of the data points. For example, if we have a dataset of students’ ages and one of the students is 60 years old, and the rest are between 10 to 15 years, then the student with 60 years old will be considered as a univariate outlier.
Multivariate outliers are observations that have extreme value on two or more variables. For example, if we have a dataset of a student’s age and their scores on a test, and one of the students is 60 years old and has a perfect score, while the rest of the students are between 10 to 15 years old and score is ranging from 50 to 90 then student with 60 years old will be considered as a multivariate outlier.
Different ways to identify outliers
- Box plot
- Interquartile range
- Standard deviation
- Z-score
- Mahalanobis distance
- Domain knowledge
1. Box plot: It is a graphical representation of a dataset that shows the data distribution along with information about the outliers. Box plots compare the distribution of multiple datasets and identify the differences between their central tendencies, variability, and skewness. Using a box plot, we will get an idea about the outliers in a dataset. The box is also called a box-and-whisker plot. Box plot will give the five-number summary of a dataset which is –
a) Minimum value: It is the minimum value in a given dataset, excluding outliers.
b) First quartile(Q1): 25% of the data points lie below the first or lower quartile value.
c) Median: It is the center value of a data point. 50% of the data lie above and below the median value.
d) Third quartile(Q3): 75% of the data lies below the third or upper quartile value.
e) Maximum value: This is the largest value in a given dataset, excluding outliers.

Implementation:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = pd.read_csv(r”Path of your data set location”)
dataset.head()
new_data = data[[“SepalLengthCm”, “SepalWidthCm”, “PetalLengthCm”, “PetalWidthCm”]]
print(new_data.head())

In the above plot, we can see there are some outliers in the sepal width. In this way, we can detect outliers in a dataset by visualizing data.
2. Interquartile range(IQR): IQR is another method to detect the outliers in a dataset. IQR can be calculated using the upper quartile(Q3)— lower quartile(Q1).
IQR = Q3 — Q1
Using the IQR, we can calculate the lower and upper bound.
lower bound = Q1–1.5(IQR)
upper bound = Q3 + 1.5(IQR)
The values below the lower bound value and above the upper band value are the outliers in a dataset.
Implementation:
data = [6, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 50]
sort_data = np.sort(data)
print("Sorted data:",sorted_data)
Q1 = np.percentile(data, 25, interpolation = ‘midpoint’)
Q3 = np.percentile(data, 75, interpolation = ‘midpoint’)
print(‘Q1 25 percentile of the given data is, ‘, Q1)
print(‘Q3 75 percentile of the given data is, ‘, Q3)
IQR = Q3 – Q1
print(‘Interquartile range is’, IQR)
low_lim = Q1 – 1.5 * IQR
up_lim = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
print(‘low_limit is’, low_lim)
print(‘up_limit is’, up_lim)
outlier =[]
for x in data:
if ((x> up_lim) or (x<low_lim)):
outlier.append(x)
print(‘ outlier in the dataset is’, outlier)

3. Standard deviation: Standard deviation is one of the methods to remove outliers. It is similar to the IQR in which we set a limit for an upper and lower bound. We can detect and remove the outliers depending on the set limit, either 2 times the standard deviation or 3 times the standard deviation.
lower limit = mean — 3*stdev
upper limit = mean + 3*stdev
The values below the lower limit and above the upper limit will be the data set’s outliers.
Implementation:
import numpy as np
data = [1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 1, 1, 15, 2, 2, 2, 3, 1, 1, 2]
mean = np.mean(data)
std = np.std(data)
print('mean of the dataset is, mean)
print('std. deviation is', std)
lower_limit = mean - (3 * std)
upper_limit = mean + (3 * std)
outlier = []
for I in data:
if ((i> upper_limit) or (i<lower_limit)):
outlier.append(i)
print(' outlier in the dataset is', outlier)

4. Z-score: The Z-score is just another form of standard deviation procedure. Z-score is used to convert the data into another dataset with a 0 mean value.

Here, the x bar is a mean value, and s is a standard deviation. Once the data has been converted, the center will be 0, and the z-score of each data point will be the distance from the center in terms of standard deviation. If the z-score of a particular data point is 1.5, then that data will be a 1.5 standard deviation away from the mean value. Generally, z-score =3 is considered a threshold point. The z-score values above +3 and below -3 will be considered an outlier of a given dataset.
Implementation:
import numpy as np
data = [1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 1, 1, 1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 1, 1, 2,5,60]
mean = np.mean(data)
std = np.std(data)
print('mean of the dataset is, mean)
print('std. deviation is', std)
threshold = 3
outlier = []
for I in data:
z = (i-mean)/std
if z > threshold:
outlier.append(i)
print('outlier in dataset is', outlier)

4. Mahalanobis distance: Mahalanobis Distance (MD) is an effective distance metric that finds the distance between the point and distribution. It works quite effectively for multivariate data points as it uses a covariance matrix of the variables to find a distance between the data points and the center.

Here, x is the vector of the data, m is the vector of the mean values of independent variables, and C inverse is the Inverse Covariance matrix of independent variables.
The Mahalanobis distance measures the number of standard deviations from a data point’s center of data distribution. Data points with a Mahalanobis distance greater than a certain threshold value of 3 or 4 are often used to identify outliers. The main advantage of using Mahalanobis distance is that it uses a covariance distance between the variables in a dataset. This can be particularly useful when working with high-dimensionality datasets, where traditional methods like z-score and IQR will not be more effective.
Implementation:
import numpy as np from scipy.spatial.distance import mahalanobis
# generate some sample data
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.random.randn(100, 3) # 100 samples with 3 features
# calculate the mean and covariance matrix
mean = np.mean(X, axis=0)
cov = np.cov(X.T)
# calculate the inverse of the covariance matrix
inv_cov = np.linalg.inv(cov)
# calculate the Mahalanobis distance for each sample
dist = np.zeros(X.shape[0])
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
dist[i] = mahalanobis(X[i], mean, inv_cov)
# identify outliers using a threshold
threshold = np.mean(dist) + 3*np.std(dist)
outliers = np.where(dist > threshold)[0]
print(f”Number of outliers: {len(outliers)}”)
print(“Outlier indices:”, outliers)
Number of outliers: 1 Outlier indices: [90]
5. Domain knowledge: Domain knowledge refers to knowledge specific to a particular field or domain. Using the domain knowledge, identify the outliers that are potential outliers based on the complete data set. Using domain knowledge for outlier detection can be a powerful technique, as it allows you to leverage your expertise in a particular field to identify potential outliers. However, it’s important to validate any potential outliers using statistical methods or other techniques before taking any action.
Conclusion:
These are some commonly used outlier detection methods. According to your dataset, you can try out different methods of handling outliers.
If you found this article insightful, follow me on Linkedin and medium. you can also subscribe to get notified when I publish articles.
Stay tuned !!!
Thank you !!!
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.