Getting Started With Unix/Linux
Last Updated on July 20, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Pushkar Pushp
Originally published on Towards AI.
Computing
An introduction to Unix/Linux shell scripting
Introduction
Unix is a multi-user operating system built around 1969 at AT&T Bell Labs. The main purpose of UNIX was multi-tasking.
- Multi-user: Different users can share the same resources.
- Multi-tasking: Execution of more than one process at the same time.
Unix is a commercial, whereas Linux (technically a kernel)is open-source. The Linux operating system easily compiles the Unix software with POSIX standards and compliance.
Unix Architecture is composed of Kernel, Shell, Applications./Programs.

The kernel is the core component of the operating system. It interacts with the hardware and most of the tasks like memory management, task scheduling, and file management.
Shell is a command-line interface(CLI), in the initial days, there was no graphical user interface (GUI), so the command-line interface was needed to interact with the computer. For example, to create a directory/folder, we write the mkdir folder name. In a nutshell, Shell is a medium between user and computer. There are different types of the shell such as ;
- Korn shell
- Bourne shell
- GNU Bourne-Again Shell (BASH)
- C shell
- POSIX shell
- Zsh (macOS Catalina default shell)
Shell scripting is all the commands put together in a text file. The shell scripting is similar to a movie script that tells the actors what task they need to do. The shell executes the commands in the text file, just as if one had typed them. Zsh shell is the one we will be using throughout the blog.
Illustration of kernel-shell relationship suppose you want to move a file, so you type mv myfile in the shell and press enter. The shell searches the file ‘myfile’ in the file-store and request kernel via a system call to execute mv on myfile. The Linux file-store is a tree structure, an inverted tree with top known as the root, and is denoted by ‘/.’ The tilde (~) represents the home directory.
Applications are the utility programs that run on Shell, e.g., text editor.
Getting Started with shell scripting.
The shell scripting topic will be divided into six sections.
- Navigation
- File operations such as creation, deletion, migration.
- Search and Regular Expressions.
- File permissions
Let’s begin ;
Navigation
Open iterm2 with Zsh or terminal. I will be using iterm2, which is nothing but a terminal emulator for macOS.

How to check which shell is in the terminal?
echo is a command to display messages to the console.

So output says it is zsh shell.
The general structure of commands
[command] [options] [arguments]
- Options are mostly preceded by –
- Arguments are file_name, folder_name ,etc .
e.g., to display ‘Let us begin shell scripting’ to the console.

In the above example, echo is the command, and ‘Let us begin shell scripting’ is the argument.
Other useful commands
pwd: Print working directory, i.e., returns the absolute path of the working directory. The sequence of a directory from root to a working directory is called an absolute path. A similar interpretation is for a relative path, i.e., with reference to the current directory.

man command
for e.g.
man pwdgives entire description of pwd command.

ls: lists all the files and directories in the working directory.

ls -l: detail view of all the files and directories in the working directory. It shows read, write permission, file size, normal file or directory, and other information pertaining to each file.
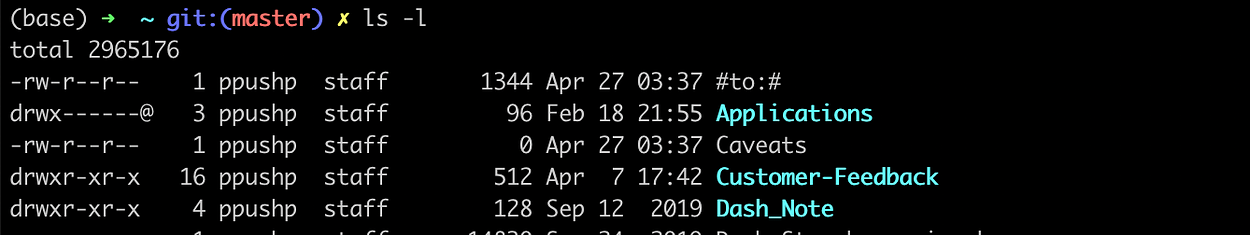
- The first columns specify whether it is a file or directory. If it starts with d, then it is directory else file.
- The second column represents the memory block.
- The third column represents the owner/creator.
- The fourth column represents a group of the owner.
- The fifth column specifies the size in bytes.
- The sixth column represents the creation/modification date.
- The last column represents the file name.
ls -l path: It shows a detailed view of all files present in a particular path.

cd: change directory to a given path.

So now /Users/ppushp/Desktop is our current working directory.
cd ..: moves one folder above the current working directory.
cd: without any argument points to the home directory.
cd .: points to the path of the current working directory.
cd ~: points to the home directory.

File operations such as creation, deletion, migration.
We have already seen that the Linux file-store is a tree structure, an inverted tree.
- Creation of a directory
mkdir [options] <Directory>
Let’s create a directory named script_tutorial. The command is mkdir directory_name.

We were at /Users/ppushp/Desktop/Shell_Training location and there was no file present there. Once we do mkdir , we can see script_tutorial there.
- Creation of file.
touch [options] <filename>
To create blank file ‘shell_scripting.txt’, use touch shell_scripting.txt

- Transfer from one location to another.
mv [options] <source> <destination>
Suppose we want to move shell_scripting.txt file from script_tutorial to Shell_Training.
mv script_tutorial/shell_scripting.txt /Users/ppushp/Desktop/Shell_Training

It even works for the directory. If we keep the source and destination path the same but pass the different names of the file in the destination, it will rename that file. Suppose you want to rename the file shell_scripting.txt to shell_script.txt.

- Copying files and folders.
cp [options] <source> <destination>
The task to copy shell_script.txt file to script_tutorial directory.
cp ../shell_script.txt ../script_tutorial

How about copying script_tutorial directory to Desktop?
The process is similar to copying a file but in a recursive manner, so pass the option -r.

- Deletion of files and folders.
Be careful before deleting any files or folders as no there is no reverse way to get back the files/directory.
rm [options] <file>
We want to delete the copy of the file ‘shell_script.txt’ kept in Desktop
rm ~/Desktop/script_tutorial/shell_script.txt

Now the directory script_tutorial is of no use, let’s delete it.
rm -r ~/Desktop/script_tutorial

Search and Regular Expressions.
Wildcards are a subset of metacharacters that are used to select files or folders based on some characters. In other words, it is a set of symbols for other characters.
The three widely used wildcards are :
- * wildcard: zero or more characters.
- ? wildcard: single character.
- [] wildcard: a range of characters.
Consider the following set of characters push, pull, puh, pushkar, ppush, ppushkar, prkh, pus, pth.
p*r stands for all characters which start with p and ends with r.
Output: pushkar, ppushkar
p??h: all characters which starts with p and ends with h, and have two characters between them.
Output: push, prkh
p[us]h: match characters which starts with p and end with h, has either u or s in between.
Output puh, psh
p[s-v]h: match characters which starts with p and end with h, has either character from s-v in between.
Output: psh, pth, puh.
Let me add some files to the shell_script folder and list it.

List all files with a JPEG extension.
ls *.jpeg

List all files with a four-letter extension.
ls *.????

List all files which contain any numeric.
ls *[0-9]*

- Regular expression.
I have a file player.txt which contains a list of top 200 test run makers.
Let’s see some detail report, say word count

It shows 200 rows/lines with 2615 words.

Grep is used to find lines containing a given expression.
grep <pattern> [path]
Find rows containing expression ‘Tend’
grep Tend player.txt

Combination of metacharacters and regular expression.
egrep [command line options] <pattern> [path]
examples:
grep r.a player.txt
It will fetch all rows containing the character “r”, followed by any character, followed by the character “a”.

If we want to see line number and count also use options -n and -c respectively.


The regular expression in itself is a broad topic that you read further in this blog.
find: It is used to find the location of files
find . -name path
To find the location of our file player.txt
find . -name player.txt

History and bash_history can be used to check previously used commands.
Pipe: It is used for chain operation, where the output of the first command is taken as the input of the second operation.

File permissions
- In Linux everything is a file, There are three types of files in Linux
- Ordinary Files are files on the system pertaining to data, text, or program.
- Special Files are files that provide access to hardware such as hard drives, CD-ROM drives, modems, etc.
- Directories store both special and ordinary files, similar to folders.
How to know whether it is an ordinary file or directory, just use the below command.
file path

The output points out that Desktop is a directory. Consider the below example where ‘file path’ command for ordinary files give output like,… with CLRF line terminators. CLRF is Carriage Return (ASCII 13, \r ) Line Feed (ASCII 10, \n ) in HTTP protocol, read more about it here.

File permissions.
Permissions mean operations that a user can perform such as read, write, and execute.
r: one can open the file.
w: one can make changes.
x: one can run or execute a file.
Users can be of three types:
owner: an individual who owns mostly the one who creates the file
group: each file belongs to a group
others: other than group members or an owner.
So every user has two option permission or no permission. In total there will be a 2*2*2 i.e 8 possibility.
0: no permission
1: has permission.

To interpret the above table, let us see an example.
user 0: representation is 0,0,0 means it doesn’t have any permission.
user 3: representation is 0,1,1 means it doesn’t have read permission, but has a write and execute permission.
How to change the permission?
chmod is the command to change the permission mode.
chmod [permissions] [path]

Break 751 into components, where 7 is for the owner, 5 for group and 1 for other
7: stands for 111, so the owner will have all the permissions
5: for 101, so the group will have read and executed permissions
1: for 001, so others have only executed permissions
Initial permission status of player.txt file was -rw-r- -r- which changed to-rwxr-x- -x-
Conclusion
This was all about getting started with Linux and bash, in my next article we will study process management, scripting, and scheduling.
Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














