Genetic Algorithm Optimization
Last Updated on July 25, 2023 by Editorial Team
Author(s): Chinmay Bhalerao
Originally published on Towards AI.
A detailed explanation of the evolutionary and nature-inspired optimization algorithm
“The environment selects those few mutations that enhance survival, resulting in a series of slow transformations of one lifeform into another, the origin of a new species.”- CARL SAGAN, 1934–1996
Edit: This article has been selected as Best Article of the week and has been featured in TowardsAI weekly newsletter.”
Evolution
The concept of natural selection and biological evolution changed the perspective of thinking about evolution theory. Evolution is always a slow and gradual process that takes many centuries to work. Millions of species present on earth today arose from a single original life form through a branching process called speciation. complex creatures evolve from more simplistic ancestors naturally over time. In a nutshell, as random genetic mutations occur within an organism’s genetic code, the beneficial mutations are preserved because they aid survival — a process known as “natural selection.”
DNA changes with time with different mutations and a combination of random inheritance, which is a recombination of parental DNA and mutational behaviors. This is conveniently described using tools from probability theory and stochastic processes.
“Evolution is the aggregation of thousands of semi-random events and the natural pressure to reproduce or die”-Darwinian evolution
To understand evolution, there is a great example of the prey and predator system. Fox eats rabbits, and faster rabbits tend to save their lives, whereas slower one has more probability of getting caught. Given a population, Smarter and quicker individuals are less likely to be consumed by foxes. As a result, they can continue to reproduce, which is what rabbits do best. Some of the less intelligent and slower rabbits also make it by chance. As the remaining population begins to reproduce, a good combination of rabbit genetic material is produced.

some slow rabbits breed with fast rabbits, some fast rabbits breed with fast rabbits, And on top of that, nature throws in a wild hare every once in a while by mutating some of the rabbit's genetic material. Because more parents who were quicker and smarter survived the foxes, the resulting rabbits (on average) are faster and smarter than those in the original group. The good thing is that the foxes are also undergoing a similar procedure. Otherwise, the rabbits would develop into creatures that are too quick and intelligent for the foxes to capture.
Genetic Algorithm optimization
GAs was first proposed by John Holland in the 1960s. GA incorporates methods proposed by and inspired by the natural selection process. As I mentioned in the above example, the fittest individual has more chance or probability to survive. The same in GA. From the pool of solutions, the one who has more fitness has more chance to survive. Let's start the actual understanding of the Genetic Algorithm. Let's understand basic terminologies.
Genetic Algorithm terminologies
Parent: The one from which offspring is produced. member of the current generation.
Offspring: Also known as a child. offspring is a member of the next generation
Population: Population is a set of all possible solutions or chromosomes exhibiting similar gene structure
Fitness: Fitness is a number assigned to an individual representing a measure of goodness. More fitter, the more chance of survival and reproduction.
Chromosome: Chromosome is a coded form of a possible set of solutions consisting of genes made of one of two or more versions of DNA sequence (alleles).
Crossover: Crossover is the phenomenon where generally two parents produce two offspring by gene exchange.
Mutation: Mutation is a random change of the value of a gene we flip a bit and change 0 to 1 and 1 to zero.
Generation: Generation is a successively created population. In Genetic Algorithms, it is also termed as “iterations”.
Outline of genetic algorithm
- The genetic algorithm starts with defining a proper problem statement and creating a set of initial possible populations of solutions.
- The population is randomly generated chromosomes. like the evolution procedure, the procedure of natural selection starts.
- During successive generations, chromosomes in the population are rated for their fitness or rated for their chance to become the solution.
- Now, based on the evaluation of their fitness value, the new set of Chromosomes forms using a selection operation followed by crossover and mutation.
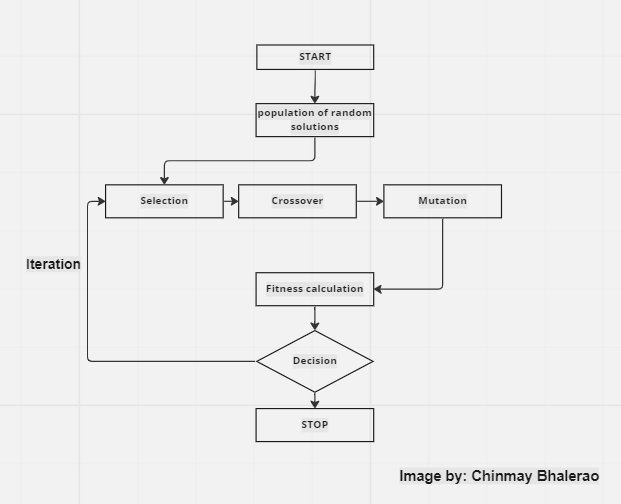
Selection
The first important step in Genetic algorithm operations is selection. You might have a question here! what are we selecting? I will answer this question. The fittest solution or fittest offspring/Child is our aim. for that, obviously, we have to select a parent depending on its fitness. If we have population “X”, then selection creates an intermediate population of “ X’ ” [X_hash] with the copies of chromosomes of X. More fitter chromosomes will have more copies of it !!! After this, the selection mechanism starts.
The selection operation is carried out in two ways :
- Roulette wheel selection
You know the word Roulette wheel from casino or gambling, right? It's a much similar concept. In gambling, we have wheels, and we predict numbers. That is, the dice will land on that predicted number or not! In the GA roulette wheel selection, the wheel is the same. just a stop point is introduced at a fixed point. The chromosome takes the value on the pie or roulette wheel exactly equal to the fitness it has.

It is obvious that a more physically fit individual has a larger pie on the wheel and a higher chance of landing in front of the fixed point when the wheel is revolved. As a result, an individual likelihood of selection is directly correlated with their fitness.

- Calculate the total sum [S]of fitnesses.
- Generate a random number between 0 and the total sum[S].
- Calculate the partial sum of P.
- The Chromosome for which P exceeds S is the chosen individual.
Sum = F1 + F2 +F3+F4 + F5
Selection = (F1+F2+F3+F4+ F5)/Sum <P < (F 1 +F 2 +F 3 +F 4 + F 5 )/Sum
2. Tournament selection
In the N-Way tournament, we randomly choose N people from the population, and we choose the best of these to become parents. The following parent is chosen using the same procedure as before. Due to its ability to function even when fitness values are negative, tournament selection is a very common literary device.

Crossover
Crossover is the operation where we combine the properties of both parents. features of two parent chromosomes are mixed in such a way that there can be the possibility of good chromosomes offsprings.
Crossover operators have a role in the balance between exploitation and exploration, which will allow the extraction of characteristics from both parents, and hope that the resulting offspring possess good characteristics from the parents (Gallard & Esquivel, 2001).
Crossover is usually applied in a GA with a high probability [pc]. According to the position of a crossover, crossovers are divided into various types:
and for other types of crossovers, refer THIS.
If you have a question about how to select type and crossover probability, then you can refer to this link's comprehensive paper on Crossover Probability.
Mutation
According to National Geographic, A mutation is a change in the structure of a gene, the unit of heredity. Genes are made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), a long molecule composed of building blocks called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is built around one of four different subunits called bases. These bases are known as guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine. A gene carries information in the sequence of its nucleotides, just as a sentence carries information in the sequence of its letters.
In GA, the mutation is the step where we assure that the search space will never be zero. We know that in traditional optimization algorithms like gradient descent, there is always a probability that it will stuck at local maxima/minima and assume it as a final solution. To overcome this kind of scenario, this extra effort of mutation is taken, and it helps to avoid sticking on local bulges.


In essence, mutation probability measures the likelihood that unrelated random chromosomal fragments may flip over and become something different. If your chromosome is encoded as a binary string of length 100, for instance, and your mutation risk is 1%, this indicates that, on average, 1 out of every 100 bits chosen at random will be flipped. Crossover is typically performed in GAs in a variety of ways, essentially simulating sexual genetic recombination similarly to in human reproduction.
Termination
GA’s iteration process is repeated until a termination condition has been reached, like,
- A user-defined threshold criterion is reached
- The fixed number of iterations reached
- exhausted with a maximum number of possible solutions
- Maximum fitness reached
- Computational power termination criteria
This was just a theoretical overview of GA, but I am planning to take a case study to implement GA on it still if you want to work on a simple mathematical solution of the problem by GA with code, then refer to THIS informative blog on GA by Niranjan Pramanik, Ph.D.
You can simulate the evolution process over HERE.
Anylogic simulated the supply chain distribution routing problem [ vehicle routing problem] and solved it using a Genetic algorithm.

You can get this simulation HERE.
Anylogic cloud has a lot of different and interesting simulations based on real-life scenarios you can check it HERE.
If you have found this article insightful
If you found this article insightful, follow me on Linkedin and medium. you can also subscribe to get notified when I publish articles. Let’s create a community! Thanks for your support!
If you want to support me :
As Your following and clapping is the most important thing, but you can also support me by buying coffee. COFFEE.
You can also read my blogs related to
A Chatbot With the Least Number of Lines Of Code
Chatbot and NLP in the simplest form
pub.towardsai.net
An Introduction to Federated Learning
Data privacy and security with Federated learning
pub.towardsai.net
“To understand humans better”: Cognitive science and AI
“To understand humans better” ….
medium.com
OCR : The Incredible reading capability of Machine
What if you have thousands of paper documents and forms and you want to store it digitally! typing each word can help…
medium.com
References :
1] Real-Coded Genetic Algorithms
2] On Enhancing Genetic Algorithms Using New Crossovers
3] Optimised crossover genetic algorithm for capacitated vehicle routing problem

Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor.
Published via Towards AI
Take our 90+ lesson From Beginner to Advanced LLM Developer Certification: From choosing a project to deploying a working product this is the most comprehensive and practical LLM course out there!
Towards AI has published Building LLMs for Production—our 470+ page guide to mastering LLMs with practical projects and expert insights!

Discover Your Dream AI Career at Towards AI Jobs
Towards AI has built a jobs board tailored specifically to Machine Learning and Data Science Jobs and Skills. Our software searches for live AI jobs each hour, labels and categorises them and makes them easily searchable. Explore over 40,000 live jobs today with Towards AI Jobs!
Note: Content contains the views of the contributing authors and not Towards AI.














